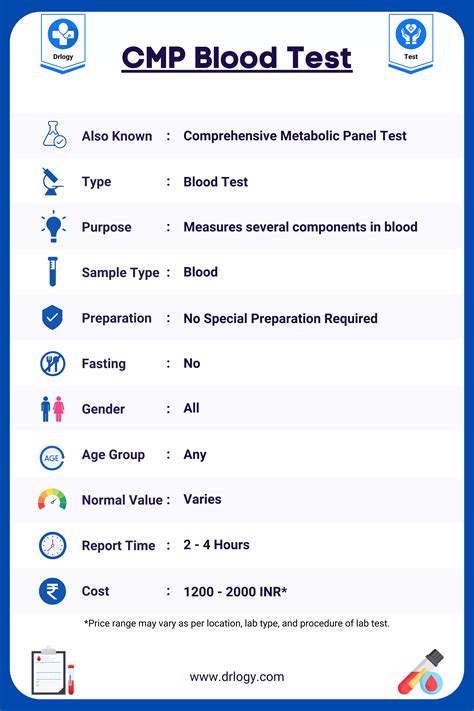
Intro
Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP) blood work is a crucial diagnostic tool used by healthcare professionals to assess a patient's overall health and detect potential metabolic disorders. This type of blood test measures various components of the blood to provide insights into the body's metabolic functions, including glucose and electrolyte levels, kidney and liver function, and acid-base balance. The importance of CMP blood work lies in its ability to help diagnose and monitor a wide range of conditions, from diabetes and kidney disease to liver dysfunction and electrolyte imbalances.
CMP blood work is often performed as part of a routine health examination or when a patient presents with symptoms that may indicate a metabolic disorder. The test is typically conducted in the morning, after an overnight fast, to ensure accurate results. A healthcare professional will collect a blood sample from the patient's vein, usually in the arm, and send it to a laboratory for analysis. The results of the CMP blood work are then used to guide further testing, diagnosis, and treatment.
The CMP blood test is a comprehensive panel that includes a range of measurements, making it an essential tool for healthcare professionals. By analyzing the results of the CMP blood work, healthcare providers can identify potential health issues early on, allowing for timely intervention and treatment. This can help prevent complications and improve patient outcomes. Furthermore, CMP blood work can be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments and make adjustments as needed.
What is Included in CMP Blood Work
CMP blood work typically includes a range of measurements, such as glucose, electrolytes, kidney function tests, liver function tests, and acid-base balance tests. The specific components of the CMP blood test may vary depending on the laboratory and the healthcare provider's requests. However, most CMP panels include measurements of:
- Glucose: to assess blood sugar levels and detect diabetes or pre-diabetes
- Electrolytes: such as sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate, to evaluate the body's acid-base balance and detect electrolyte imbalances
- Kidney function tests: including creatinine and urea, to assess kidney function and detect potential kidney disease
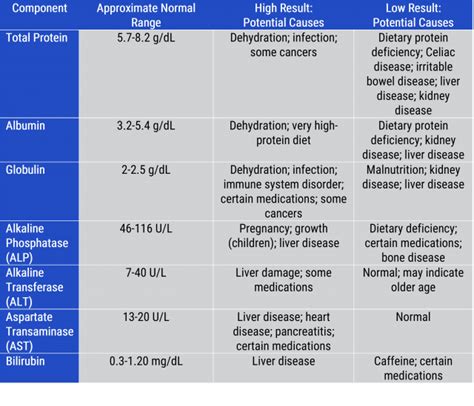
- Liver function tests: such as alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST), to evaluate liver function and detect potential liver disease
- Acid-base balance tests: including anion gap and arterial blood gas analysis, to assess the body's acid-base balance and detect potential respiratory or metabolic disorders
Benefits of CMP Blood Work
The benefits of CMP blood work are numerous, making it a valuable diagnostic tool for healthcare professionals. Some of the key benefits include:- Early detection of metabolic disorders: such as diabetes, kidney disease, and liver dysfunction
- Monitoring of treatment effectiveness: allowing healthcare providers to adjust treatments and improve patient outcomes
- Identification of potential health risks: such as electrolyte imbalances and acid-base disorders
- Comprehensive assessment of overall health: providing a complete picture of a patient's metabolic functions
How to Prepare for CMP Blood Work
Preparing for CMP blood work is relatively straightforward. Patients are typically required to fast for 8-12 hours before the test, which means avoiding food and drink, except for water. It is essential to follow the healthcare provider's instructions carefully to ensure accurate results. Additionally, patients should:
- Avoid strenuous exercise and physical activity before the test
- Refrain from smoking and consuming caffeine for at least 2 hours before the test
- Inform their healthcare provider about any medications or supplements they are taking
- Arrive at the testing facility with a list of their medications and any relevant medical history
Understanding CMP Blood Work Results
Understanding the results of CMP blood work requires a comprehensive approach. Healthcare providers will review the results and look for any abnormalities or trends that may indicate a metabolic disorder. The results are typically reported in a range of values, with normal ranges varying depending on the laboratory and the specific test. Some common abnormal results include:- Elevated glucose levels: indicating diabetes or pre-diabetes
- Electrolyte imbalances: such as low sodium or high potassium levels
- Abnormal kidney function tests: indicating potential kidney disease
- Elevated liver enzymes: indicating potential liver disease
- Acid-base balance disorders: such as respiratory acidosis or metabolic alkalosis
Common Uses of CMP Blood Work
CMP blood work has a range of common uses, including:
- Diagnosing and monitoring metabolic disorders: such as diabetes, kidney disease, and liver dysfunction
- Evaluating the effectiveness of treatments: such as medications and lifestyle interventions
- Assessing overall health: providing a comprehensive picture of a patient's metabolic functions
- Screening for potential health risks: such as electrolyte imbalances and acid-base disorders
- Monitoring patients with chronic conditions: such as kidney disease, liver disease, and diabetes
Limitations of CMP Blood Work
While CMP blood work is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has some limitations. These include:- Limited sensitivity and specificity: some metabolic disorders may not be detected by CMP blood work
- Variability in laboratory results: different laboratories may have different normal ranges and testing methods
- Limited ability to diagnose certain conditions: such as some types of kidney disease or liver dysfunction
- Requires careful interpretation: healthcare providers must carefully review the results and consider the patient's medical history and symptoms
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, CMP blood work is a powerful diagnostic tool that provides valuable insights into a patient's metabolic functions. By understanding the benefits, limitations, and common uses of CMP blood work, healthcare providers can make informed decisions and develop effective treatment plans. Patients who have undergone CMP blood work should discuss their results with their healthcare provider and ask questions about any abnormal findings. Additionally, patients can take steps to maintain their overall health, such as:
- Eating a balanced diet
- Staying hydrated
- Exercising regularly
- Managing stress
- Getting enough sleep
By working together, healthcare providers and patients can use CMP blood work to improve health outcomes and prevent complications.
What is the purpose of CMP blood work?
+CMP blood work is used to assess a patient's overall health and detect potential metabolic disorders, such as diabetes, kidney disease, and liver dysfunction.
How do I prepare for CMP blood work?
+Patients should fast for 8-12 hours before the test, avoid strenuous exercise and physical activity, and refrain from smoking and consuming caffeine for at least 2 hours before the test.
What do abnormal CMP blood work results indicate?
+Abnormal results may indicate a range of conditions, including diabetes, kidney disease, liver dysfunction, electrolyte imbalances, and acid-base balance disorders.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of CMP blood work and its importance in diagnosing and monitoring metabolic disorders. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment or share this article with others. By working together, we can improve health outcomes and prevent complications.
