Intro
Distinguish between cold and flu symptoms, treatments, and prevention methods, understanding key differences to manage respiratory infections, fever, and congestion effectively.
When it comes to common illnesses, two of the most frequently confused conditions are the cold and the flu. While both are respiratory infections, they are caused by different viruses and have distinct symptoms. Understanding the differences between the cold and the flu is crucial for proper diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. In this article, we will delve into the world of cold and flu, exploring their causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
The common cold is a viral infection that affects the upper respiratory system, including the nose, throat, and lungs. It is estimated that adults can expect to contract a cold two to four times a year, while children may experience even more frequent episodes. The cold is usually caused by rhinoviruses, coronaviruses, or adenoviruses, and its symptoms can range from mild to severe. On the other hand, the flu, also known as influenza, is a more serious and contagious respiratory illness caused by the influenza virus. The flu can lead to severe complications, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinus and ear infections, especially in high-risk groups like the elderly, young children, and people with certain chronic health conditions.
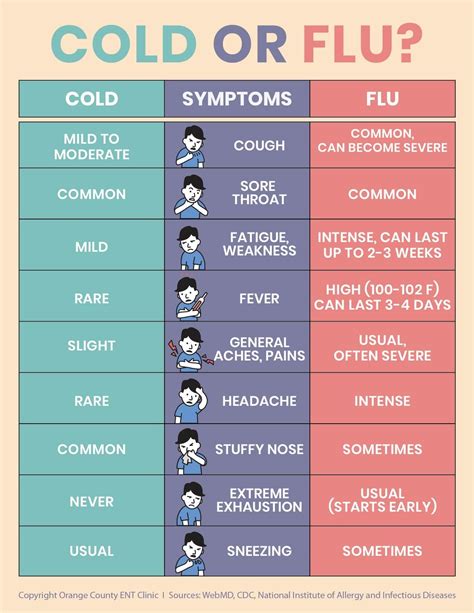
The distinction between the cold and the flu is not always clear-cut, as both conditions can present with similar symptoms, such as coughing, sneezing, and a runny nose. However, there are some key differences that can help you determine which condition you are dealing with. For instance, the flu is often accompanied by a high fever, chills, and body aches, whereas the cold tends to be milder and more focused on the upper respiratory system. Additionally, the flu can lead to more severe complications, such as pneumonia and bronchitis, especially in vulnerable populations.
Cold Symptoms and Treatment
Over-the-Counter Medications for Cold
Some of the most commonly used over-the-counter medications for the cold include: * Pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to reduce fever and alleviate headaches and body aches * Decongestants, such as pseudoephedrine or phenylephrine, to relieve nasal congestion * Antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine or loratadine, to reduce sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes * Cough suppressants, such as dextromethorphan, to relieve coughingFlu Symptoms and Treatment

Antiviral Medications for Flu
Some of the most commonly used antiviral medications for the flu include: * Oseltamivir, which can reduce the severity and duration of the flu by inhibiting the replication of the influenza virus * Zanamivir, which can relieve symptoms and prevent complications by blocking the release of the influenza virus from infected cells * Peramivir, which can reduce the severity and duration of the flu by inhibiting the replication of the influenza virusPrevention Strategies

Importance of Vaccination
Vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent the flu and reduce the risk of serious complications. The flu vaccine is typically administered annually, and it is recommended for everyone six months and older, especially high-risk groups like the elderly, young children, and people with certain chronic health conditions.Complications and Risks
Risk Factors for Complications
Certain groups are at higher risk for developing complications from the cold and flu, including: * Older adults, who may have weakened immune systems and underlying health conditions * Young children, who may have underdeveloped immune systems and be more susceptible to infection * People with certain chronic health conditions, such as heart disease, lung disease, and diabetes * Pregnant women, who may be more susceptible to infection and complications due to changes in their immune systemDiagnosis and Testing

Types of Diagnostic Tests
Some common diagnostic tests used to diagnose the cold and flu include: * Rapid influenza diagnostic test (RIDT), which can detect the presence of the influenza virus in respiratory secretions * Viral culture, which can identify the specific type of virus causing the infection * Polymerase chain reaction (PCR), which can detect the genetic material of the virus in respiratory secretionsManagement and Recovery

Importance of Rest and Hydration
Rest and hydration are crucial for managing the cold and flu, as they can help: * Reduce the severity and duration of symptoms * Prevent dehydration and electrolyte imbalances * Boost the immune system and promote recovery * Reduce the risk of complications, such as pneumonia and bronchitisWhat is the main difference between the cold and the flu?
+The main difference between the cold and the flu is the severity of symptoms and the risk of complications. The flu is a more severe and contagious respiratory illness that can lead to serious complications, especially in high-risk groups, whereas the cold is a milder and more self-limiting condition.
How can I prevent the spread of the cold and flu?
+Preventing the spread of the cold and flu requires practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and getting vaccinated against the flu. Additionally, avoiding sharing personal items and staying home from work or school when sick can help reduce the risk of infection.
What are the most effective treatment options for the cold and flu?
+The most effective treatment options for the cold and flu include over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers, decongestants, and antihistamines, as well as antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir or zanamivir, which can reduce the severity and duration of the flu. Additionally, rest, hydration, and good hygiene can help alleviate symptoms and promote recovery.
As we conclude our discussion on the cold and flu, it is essential to remember that both conditions can have a significant impact on our daily lives and overall health. By understanding the differences between the cold and the flu, we can take proactive steps to prevent infection, manage symptoms, and reduce the risk of complications. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with the cold and flu in the comments section below and to explore our website for more information on maintaining a healthy and balanced lifestyle.
