Intro
Discover the CRP medical abbreviation meaning, related to C-Reactive Protein, inflammation, and medical diagnosis, understanding its role in healthcare and lab tests.
The medical field is filled with abbreviations and acronyms that can be confusing for those not familiar with them. One such abbreviation is CRP, which stands for C-Reactive Protein. Understanding what CRP is and its significance in medical diagnosis and treatment is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients alike. In this article, we will delve into the world of CRP, exploring its meaning, functions, and the role it plays in various medical conditions.
CRP is a protein that the liver produces in response to inflammation. It is part of the body's defense mechanisms and is used as a marker to detect inflammation in the body. The level of CRP in the blood increases when there is inflammation, which can be caused by a variety of conditions, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and chronic diseases. The CRP test is a blood test that measures the level of CRP in the blood, providing valuable information for diagnosing and monitoring diseases.
The importance of CRP lies in its ability to indicate the presence and severity of inflammation. High levels of CRP are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, which makes it a useful tool for assessing cardiovascular risk. Additionally, CRP levels can help in monitoring the effectiveness of treatments for conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. Understanding CRP is essential for managing and treating various medical conditions effectively.
What is CRP Medical Abbreviation
CRP, or C-Reactive Protein, is a protein found in the blood that increases in response to inflammation and infection. It is an acute-phase protein that rises in response to inflammation throughout the body. The CRP test is a commonly used laboratory test to measure the level of CRP in the blood. It is used to detect inflammation, infection, and to monitor diseases. The test can also help determine if an infection is present, if an inflammatory disease is causing symptoms, and if a treatment is effective.
The CRP test is particularly useful because it can provide results quickly, often within a few hours. This rapid turnaround time allows healthcare providers to make timely decisions about patient care. Furthermore, the CRP test is relatively inexpensive compared to other diagnostic tests, making it a valuable tool in both clinical and research settings.
CRP Test and Its Significance

The CRP test is significant because it helps healthcare providers diagnose and monitor various conditions. For instance, high CRP levels can indicate the presence of an inflammatory disease such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or rheumatic fever. It can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments for these conditions. In addition, CRP levels can help diagnose and monitor infections, such as sepsis, and can be used to assess the risk of cardiovascular disease.
The test is usually performed on a blood sample, which is sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results are typically reported as milligrams per liter (mg/L) or milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). The interpretation of CRP levels can vary depending on the context and the individual's overall health. Generally, low levels of CRP are considered normal, while high levels may indicate inflammation or infection.
How CRP Test is Performed
The CRP test is performed by drawing a blood sample from a vein in the arm. This is typically done in a healthcare provider's office or in a laboratory. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory where it is analyzed for CRP levels. The test is relatively quick and easy, and results are usually available within a few hours.
Before the test, patients are usually asked to fast for a certain period, typically 8-12 hours, to ensure accurate results. However, this may vary depending on the specific instructions provided by the healthcare provider. It is also important to inform the healthcare provider about any medications or supplements being taken, as these can affect CRP levels.
CRP Levels and Their Interpretation
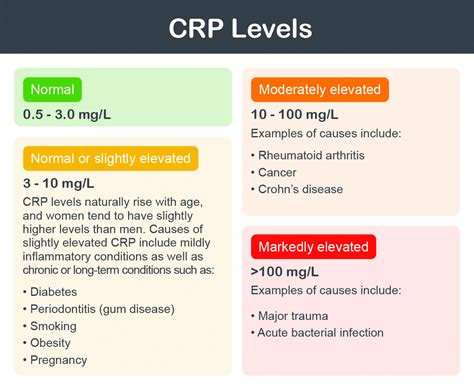
Interpreting CRP levels requires careful consideration of the individual's overall health and medical history. Generally, CRP levels are categorized as follows:
- Low risk: Less than 1 mg/L
- Average risk: 1-3 mg/L
- High risk: More than 3 mg/L
High CRP levels can indicate inflammation or infection, while low levels suggest minimal or no inflammation. However, it is essential to consider these results in the context of other diagnostic tests and clinical evaluations.
CRP and Cardiovascular Disease
The relationship between CRP and cardiovascular disease has been extensively studied. High CRP levels are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease. This is because CRP is a marker of inflammation, and chronic inflammation is a known risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
The use of CRP as a marker for cardiovascular risk has led to the development of strategies to reduce CRP levels and subsequently the risk of cardiovascular disease. These strategies include lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, and medications that reduce inflammation.
CRP in Pregnancy and Infection
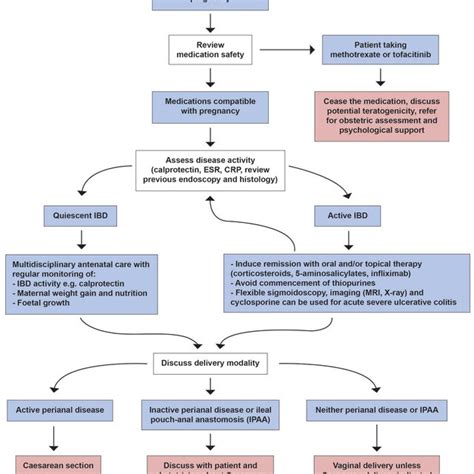
CRP levels can also be useful in monitoring pregnancy and detecting infections. During pregnancy, CRP levels can increase, which is a normal response to the inflammatory changes that occur during this period. However, significantly elevated CRP levels can indicate the presence of an infection or other complications.
In the context of infection, CRP levels can help diagnose and monitor the severity of the infection. For example, in cases of sepsis, a life-threatening condition caused by an overwhelming infection, CRP levels can be extremely high. Monitoring CRP levels can help healthcare providers assess the effectiveness of treatment and adjust it as necessary.
Limitations and Controversies of CRP Testing

While CRP testing is a valuable tool in medical diagnosis and monitoring, it also has its limitations and controversies. One of the main limitations is that CRP is a non-specific marker of inflammation, meaning that elevated levels can be caused by a variety of conditions, not just the one being tested for. This can lead to false positives and unnecessary further testing or treatment.
Additionally, there is controversy surrounding the use of CRP testing for cardiovascular risk assessment. Some argue that the test is not specific enough and can lead to overtreatment of individuals who are not at high risk. Others argue that it is a useful tool when used in conjunction with other risk factors and diagnostic tests.
Steps to Reduce CRP Levels
To reduce CRP levels and subsequently the risk of chronic diseases, several steps can be taken: - Maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise - Do not smoke - Limit alcohol consumption - Manage stress through relaxation techniques - Get regular check-ups to monitor CRP levels and overall healthConclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, CRP is a valuable marker of inflammation that plays a significant role in medical diagnosis and treatment. Understanding CRP levels and their interpretation is essential for healthcare providers to make informed decisions about patient care. As research continues to uncover the complexities of CRP and its role in various diseases, its utility in clinical practice is likely to expand.
Future directions in CRP research include exploring its potential as a therapeutic target for reducing inflammation and improving outcomes in chronic diseases. Additionally, the development of more sensitive and specific CRP tests could enhance its diagnostic and monitoring capabilities.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about CRP and its role in medical diagnosis and treatment. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us provide the most accurate and helpful information possible.
What does CRP stand for in medical terms?
+CRP stands for C-Reactive Protein, a protein that the liver produces in response to inflammation.
What is the purpose of the CRP test?
+The CRP test measures the level of CRP in the blood to detect inflammation, infection, and to monitor diseases.
How is the CRP test performed?
+The CRP test is performed by drawing a blood sample from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
What do high CRP levels indicate?
+High CRP levels can indicate inflammation, infection, or an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
How can CRP levels be reduced?
+CRP levels can be reduced through lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight, not smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, managing stress, and getting regular check-ups.
