Intro
Burns are a type of injury that can be caused by various factors, including heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, and radiation. The severity of a burn is typically classified based on its depth and the percentage of body surface area affected. Understanding the degree of burns is crucial for providing appropriate treatment and care. In this article, we will delve into the different degrees of burns, their characteristics, and the necessary steps for treatment and prevention.
Burns can be minor or severe, and it is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of each degree to ensure prompt medical attention. The degree of a burn is determined by the depth of the injury, with first-degree burns being the least severe and fourth-degree burns being the most severe. Each degree of burn has distinct characteristics, and understanding these differences is vital for effective treatment and care.
The importance of recognizing the degree of burns cannot be overstated. Proper diagnosis and treatment can significantly impact the outcome of a burn injury, reducing the risk of complications and promoting optimal healing. Furthermore, understanding the degree of burns can help individuals take preventive measures to avoid such injuries in the first place. By being aware of the causes and risks associated with burns, people can take steps to minimize their exposure to hazardous situations and substances.
Degree Of Burns Classification
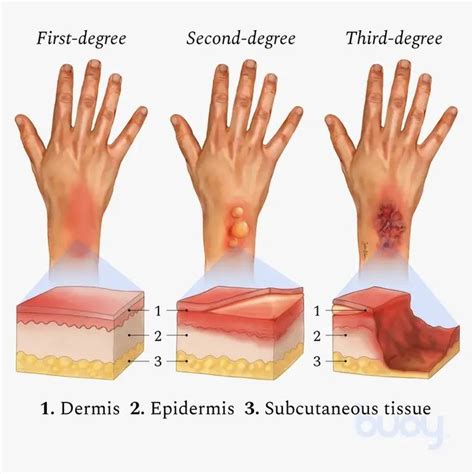
The classification of burns is based on the depth and severity of the injury. The most commonly used classification system is the first-degree to fourth-degree burn classification. This system provides a clear and concise way to describe the severity of a burn, allowing healthcare professionals to develop effective treatment plans. The classification of burns is as follows:
- First-degree burns: These burns affect only the outermost layer of skin, causing redness, swelling, and pain.
- Second-degree burns: These burns extend into the middle layer of skin, causing blisters, redness, and swelling.
- Third-degree burns: These burns destroy both layers of skin and may also damage underlying tissues, causing charred skin, white or leathery skin, and little or no pain.
- Fourth-degree burns: These burns extend through all layers of skin and into underlying tissues, such as muscle and bone, causing charred skin, white or leathery skin, and little or no pain.
First Degree Burns
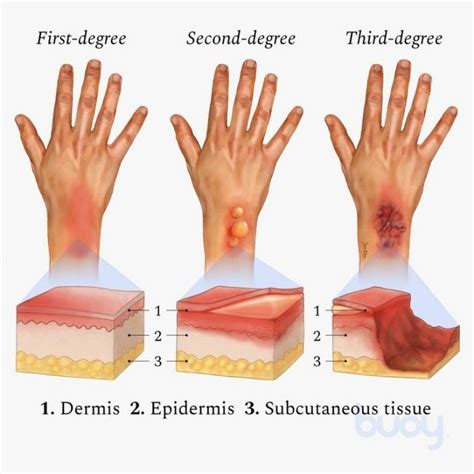
First-degree burns are the least severe type of burn and typically affect only the outermost layer of skin. These burns are often caused by minor accidents, such as touching a hot stove or spilling hot coffee. The symptoms of first-degree burns include redness, swelling, and pain. First-degree burns can be treated with basic first aid, including cooling the burn with cool water, applying a topical antibiotic ointment, and covering the burn with a non-stick bandage.
Treatment For First Degree Burns
The treatment for first-degree burns is relatively simple and can be done at home. However, it is essential to monitor the burn for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus. If the burn becomes infected, it is crucial to seek medical attention. In addition to basic first aid, there are several home remedies that can help soothe and heal first-degree burns, including aloe vera gel, honey, and tea tree oil.Second Degree Burns
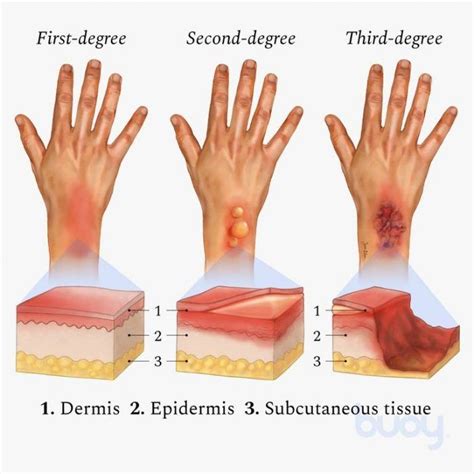
Second-degree burns are more severe than first-degree burns and extend into the middle layer of skin. These burns are often caused by more significant accidents, such as scalds from hot water or contact with an open flame. The symptoms of second-degree burns include blisters, redness, and swelling. Second-degree burns can be treated with basic first aid, including cooling the burn with cool water, applying a topical antibiotic ointment, and covering the burn with a non-stick bandage. However, second-degree burns may require medical attention if they are large or deep.
Treatment For Second Degree Burns
The treatment for second-degree burns is more complex than for first-degree burns. In addition to basic first aid, second-degree burns may require debridement, which is the removal of dead skin and tissue. This can be done by a healthcare professional and may require pain management. Second-degree burns may also require dressing changes and wound care to promote healing and prevent infection.Third Degree Burns
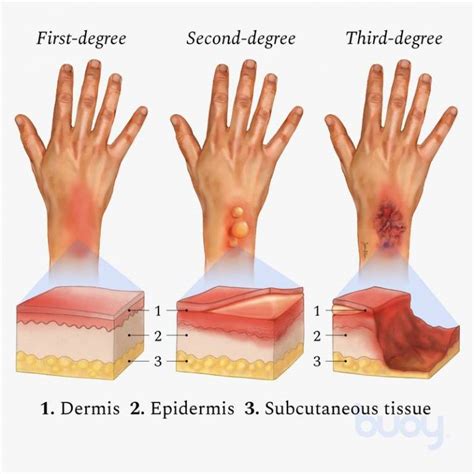
Third-degree burns are the most severe type of burn and destroy both layers of skin and may also damage underlying tissues. These burns are often caused by severe accidents, such as explosions or electrical fires. The symptoms of third-degree burns include charred skin, white or leathery skin, and little or no pain. Third-degree burns require immediate medical attention and may require surgical intervention, including skin grafts and debridement.
Treatment For Third Degree Burns
The treatment for third-degree burns is complex and requires immediate medical attention. Third-degree burns may require surgical intervention, including skin grafts and debridement. In addition, third-degree burns may require pain management, wound care, and dressing changes to promote healing and prevent infection. Third-degree burns may also require rehabilitation, including physical therapy and occupational therapy, to restore function and mobility.Fourth Degree Burns
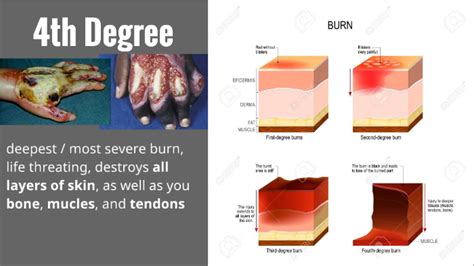
Fourth-degree burns are the most severe type of burn and extend through all layers of skin and into underlying tissues, such as muscle and bone. These burns are often caused by severe accidents, such as explosions or electrical fires. The symptoms of fourth-degree burns include charred skin, white or leathery skin, and little or no pain. Fourth-degree burns require immediate medical attention and may require surgical intervention, including amputation and skin grafts.
Treatment For Fourth Degree Burns
The treatment for fourth-degree burns is complex and requires immediate medical attention. Fourth-degree burns may require surgical intervention, including amputation and skin grafts. In addition, fourth-degree burns may require pain management, wound care, and dressing changes to promote healing and prevent infection. Fourth-degree burns may also require rehabilitation, including physical therapy and occupational therapy, to restore function and mobility.What are the different degrees of burns?
+The different degrees of burns are first-degree, second-degree, third-degree, and fourth-degree burns. Each degree of burn has distinct characteristics and requires different treatment approaches.
How are burns classified?
+Burns are classified based on the depth and severity of the injury. The classification system includes first-degree to fourth-degree burns, with first-degree burns being the least severe and fourth-degree burns being the most severe.
What are the symptoms of first-degree burns?
+The symptoms of first-degree burns include redness, swelling, and pain. First-degree burns typically affect only the outermost layer of skin and can be treated with basic first aid.
How are second-degree burns treated?
+Second-degree burns are treated with basic first aid, including cooling the burn with cool water, applying a topical antibiotic ointment, and covering the burn with a non-stick bandage. Second-degree burns may also require debridement and dressing changes to promote healing and prevent infection.
What are the symptoms of third-degree burns?
+The symptoms of third-degree burns include charred skin, white or leathery skin, and little or no pain. Third-degree burns require immediate medical attention and may require surgical intervention, including skin grafts and debridement.
In conclusion, understanding the degree of burns is crucial for providing appropriate treatment and care. The classification of burns is based on the depth and severity of the injury, with first-degree burns being the least severe and fourth-degree burns being the most severe. Each degree of burn has distinct characteristics and requires different treatment approaches. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of each degree of burn, individuals can take prompt action to ensure proper treatment and care. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with burns in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to ask. Remember to always prioritize burn prevention and take necessary precautions to avoid such injuries.
