The use of dexamethasone, a synthetic member of the glucocorticoid class of steroid drugs, has been a cornerstone in the treatment of various medical conditions, including inflammatory disorders, immune system diseases, and certain types of cancer. Its potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties make it a valuable therapeutic agent. However, like all medications, dexamethasone is not without its side effects, which can range from mild to severe and, in some cases, may be life-threatening. Understanding the potential side effects of dexamethasone is crucial for patients and healthcare providers to weigh the benefits and risks of treatment and to monitor for any adverse reactions.
Dexamethasone's widespread use across different medical specialties underscores its versatility and efficacy. From reducing inflammation in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis to managing symptoms of cancer, its applications are diverse. Nonetheless, the drug's impact on the body's hormonal balance and immune response can lead to a variety of side effects. Some patients may experience mild side effects that are temporary and manageable, while others may encounter more severe reactions that necessitate medical intervention. The variability in individual responses to dexamethasone highlights the importance of personalized medical care and close monitoring during treatment.
The administration of dexamethasone, whether orally, intravenously, or via other routes, introduces the drug into the body's systemic circulation, where it can affect multiple organ systems. This systemic effect is responsible for both the therapeutic benefits and the potential side effects. Patients starting dexamethasone should be aware of the possible side effects and report any concerns to their healthcare provider promptly. Early recognition and management of side effects can significantly improve the safety and tolerability of dexamethasone treatment. As research continues to uncover the complexities of glucocorticoid therapy, the balance between efficacy and safety remains a key focus in the clinical use of dexamethasone.
Dexamethasone Mechanism of Action
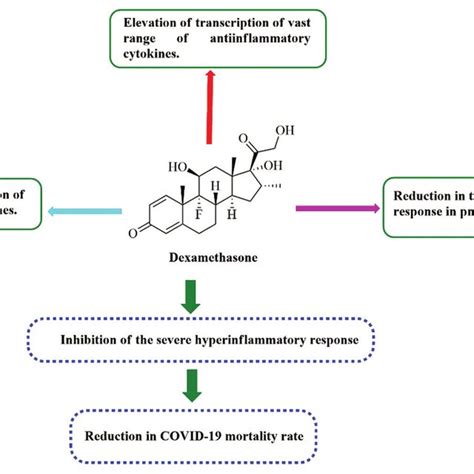
Dexamethasone exerts its effects by binding to glucocorticoid receptors in cells, which then translocate to the nucleus and influence gene expression. This process leads to the suppression of inflammatory genes and the promotion of genes involved in metabolic and immune responses. The drug's high potency and long biological half-life contribute to its efficacy but also to its potential for side effects. Understanding the mechanism of action of dexamethasone provides insights into how it can modulate the body's response to inflammation and immune challenges, as well as how it might interfere with normal physiological processes.
Common Side Effects of Dexamethasone
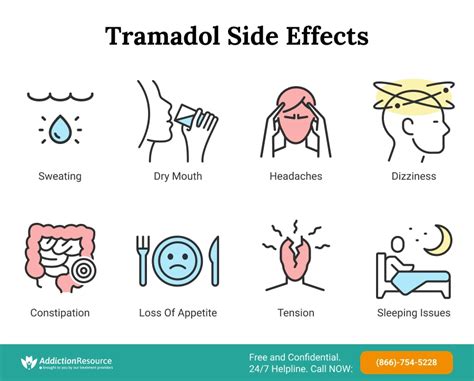
Common side effects of dexamethasone include weight gain, mood changes (such as mood swings, anxiety, or insomnia), increased appetite, and changes in skin appearance (like thinning of the skin or easy bruising). Gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, or stomach upset, can also occur. These side effects are often dose-dependent and may resolve on their own or with adjustments to the treatment regimen. However, it's crucial for patients to discuss any concerns with their healthcare provider, as some side effects may signal a more serious issue or the need for a different therapeutic approach.
Severe Side Effects of Dexamethasone
Severe side effects of dexamethasone can include osteoporosis, glaucoma, cataracts, and an increased risk of infections due to immunosuppression. Long-term use can lead to adrenal insufficiency, where the body's natural production of cortisol is suppressed, requiring careful tapering of the drug when treatment is discontinued. Psychological effects, such as depression or psychotic episodes, can also occur, especially in vulnerable individuals. The risk of these severe side effects underscores the need for careful patient selection, monitoring, and dose adjustment to minimize risks while maximizing therapeutic benefits.
Special Considerations and Precautions
Certain patient populations, such as pregnant or breastfeeding women, children, and individuals with diabetes or hypertension, require special consideration when dexamethasone is prescribed. The drug can affect blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and fetal development, among other factors. Patients with a history of tuberculosis or other chronic infections should be closely monitored due to the immunosuppressive effects of dexamethasone. Additionally, the potential for drug interactions with other medications, such as anticoagulants or certain antibiotics, necessitates a thorough review of a patient's medication list before initiating dexamethasone therapy.
Dexamethasone Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of dexamethasone vary widely depending on the condition being treated, the patient's age and weight, and the route of administration. Oral and parenteral forms are available, allowing for flexibility in treatment plans. The initial dose and duration of treatment are critical factors in minimizing side effects while achieving therapeutic goals. Patients should follow the prescribed regimen closely and attend scheduled follow-up appointments to monitor their response to the medication and address any emerging side effects.
Monitoring and Management of Side Effects
Effective monitoring and management of dexamethasone side effects involve regular clinical assessments, laboratory tests (such as blood glucose and blood pressure checks), and patient education. Patients should be informed about the potential side effects, how to recognize them, and when to seek medical help. For certain side effects, such as osteoporosis or glaucoma, specific preventive measures or treatments may be recommended. The goal is to balance the therapeutic benefits of dexamethasone with the minimization of its adverse effects, ensuring the best possible outcomes for patients.
Alternatives and Future Directions
Research into new glucocorticoids and alternative therapeutic strategies aims to develop treatments with improved safety profiles and reduced side effects. For some conditions, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), biologic agents, or other classes of drugs may offer viable alternatives to dexamethasone. The ongoing quest for safer and more effective treatments underscores the dynamic nature of medical science and the commitment to enhancing patient care.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, while dexamethasone is a valuable therapeutic agent, its use must be carefully considered due to its potential side effects. By understanding the drug's mechanism of action, common and severe side effects, and the importance of monitoring and management, healthcare providers and patients can work together to optimize treatment outcomes. As medical research continues to evolve, it is likely that new and improved treatments will become available, offering better options for managing inflammatory and immune-related conditions.
We invite readers to share their experiences or questions regarding dexamethasone and its side effects in the comments below. Your insights can help others better understand the complexities of this medication and its role in modern medicine. Furthermore, we encourage the sharing of this article with anyone who might benefit from this information, contributing to a more informed and supportive community.
What are the most common side effects of dexamethasone?
+
The most common side effects include weight gain, mood changes, increased appetite, and changes in skin appearance. These side effects are often dose-dependent and may resolve on their own or with adjustments to the treatment regimen.
Can dexamethasone cause severe side effects?
+
Yes, severe side effects can include osteoporosis, glaucoma, cataracts, and an increased risk of infections due to immunosuppression. Long-term use can also lead to adrenal insufficiency.
How can I minimize the risk of side effects while taking dexamethasone?
+
Minimizing the risk of side effects involves careful patient selection, monitoring, and dose adjustment. Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are crucial to address any emerging side effects and adjust the treatment plan as needed.