Intro
Discover the uses and benefits of Dexamethasone, a potent steroid medication, for treating inflammation, autoimmune diseases, and cancer, with its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant properties.
The world of medicine is vast and complex, with numerous treatments and medications available for various conditions. One such medication that has gained significant attention in recent years is dexamethasone. This corticosteroid has been widely used for its potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties, making it a valuable tool in the management of several diseases. In this article, we will delve into the uses and benefits of dexamethasone, exploring its mechanisms of action, therapeutic applications, and potential side effects.
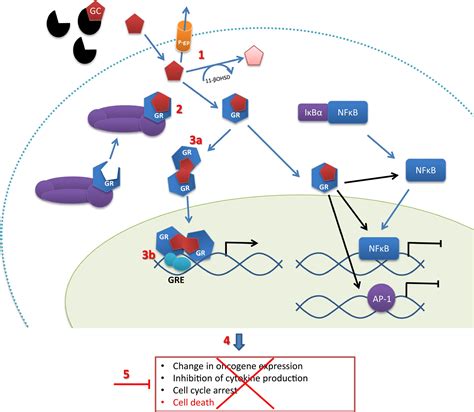
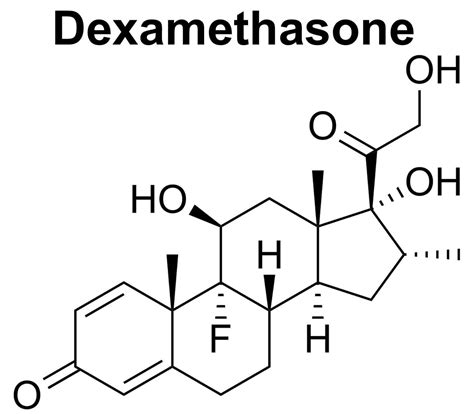
Dexamethasone is a synthetic member of the glucocorticoid class of steroid drugs, which are known for their ability to mimic the effects of the hormone cortisol in the body. Cortisol is a naturally occurring steroid hormone produced by the adrenal gland that plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, including the immune response, metabolism, and stress response. By mimicking the effects of cortisol, dexamethasone can help to reduce inflammation, suppress the immune system, and regulate various bodily functions.
The importance of dexamethasone lies in its versatility and efficacy in treating a wide range of conditions. From inflammatory disorders and autoimmune diseases to cancer and respiratory conditions, dexamethasone has been shown to be a valuable therapeutic agent. Its ability to reduce inflammation and modulate the immune response makes it an attractive option for managing conditions characterized by excessive inflammation or immune system dysregulation.
Dexamethasone Mechanism of Action
Dexamethasone Uses
Dexamethasone Benefits
The benefits of dexamethasone are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages of using dexamethasone include: * Rapid reduction of inflammation and immune system suppression * Effective management of symptoms and disease progression * Improved quality of life and functional capacity * Reduced need for other medications and therapies * Cost-effective treatment option compared to other therapiesDexamethasone Side Effects

Dexamethasone Dosage and Administration
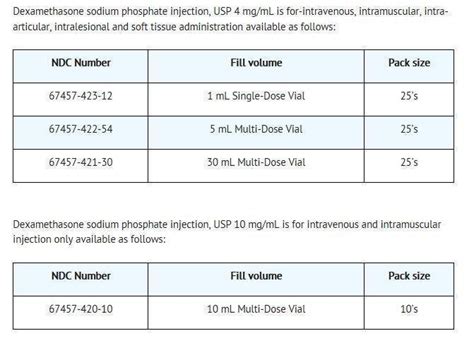
Dexamethasone Interactions
Dexamethasone Contraindications

Dexamethasone Overdose

Dexamethasone Withdrawal

What is dexamethasone used for?
+Dexamethasone is used to treat a range of conditions, including inflammatory disorders, autoimmune diseases, cancer, and respiratory conditions.
What are the side effects of dexamethasone?
+The side effects of dexamethasone include weight gain, mood changes, sleep disturbances, increased risk of infections, and osteoporosis.
Can dexamethasone be used in pregnancy and breastfeeding?
+Dexamethasone is contraindicated in pregnancy and breastfeeding due to the potential risk of harm to the fetus or baby.
How long does it take for dexamethasone to work?
+The onset of action of dexamethasone can vary depending on the condition being treated, but it can start to work within a few hours to a few days.
Can dexamethasone be used in combination with other medications?
+Dexamethasone can be used in combination with other medications, but it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to minimize the risk of interactions and side effects.
In conclusion, dexamethasone is a versatile and effective medication that has been widely used for its potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. While it can cause side effects and interact with other medications, the benefits of dexamethasone make it a valuable therapeutic agent in the management of various diseases. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with dexamethasone in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns about dexamethasone or its uses, please do not hesitate to ask.
