Intro
Discover what anxiety is, its symptoms, and effects. Learn about anxiety disorders, stress, and mental health, to understand this common condition.
Anxiety is a common and complex emotional state that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by feelings of worry, nervousness, and fear that are persistent and overwhelming, interfering with an individual's daily life. Anxiety can manifest in various forms, including generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and phobias, among others. The importance of understanding anxiety cannot be overstated, as it has a significant impact on mental and physical health, relationships, and overall well-being.
Anxiety is a natural human response to stress, and it serves as a warning system to alert us to potential dangers. However, when anxiety becomes excessive and irrational, it can be debilitating and disrupt daily life. The consequences of untreated anxiety can be severe, including decreased productivity, strained relationships, and a weakened immune system. Furthermore, anxiety can also increase the risk of developing other mental health conditions, such as depression and substance abuse. Therefore, it is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of anxiety and seek help when needed.
The prevalence of anxiety is staggering, with approximately 30% of the global population experiencing an anxiety disorder at some point in their lives. Anxiety can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background, and it is not a sign of weakness or a personal failing. In fact, many successful and accomplished individuals have spoken publicly about their struggles with anxiety, highlighting the need to reduce stigma and promote awareness. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for anxiety, we can work towards creating a more supportive and compassionate environment for those affected.
Understanding Anxiety Disorders
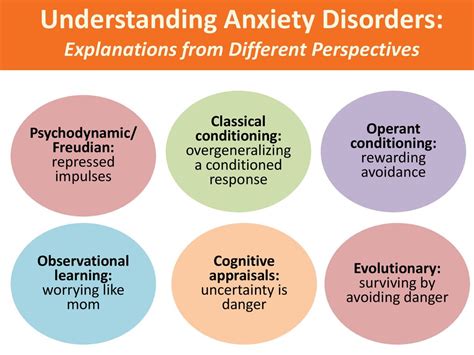
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions that share similar characteristics, including excessive and persistent fear or anxiety. The most common types of anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias. Each type of anxiety disorder has distinct symptoms and treatment approaches, and a comprehensive diagnosis by a mental health professional is essential for effective management.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders can be categorized into several subtypes, including: * Generalized anxiety disorder: characterized by excessive and persistent worry about everyday things, such as work, finances, or relationships. * Panic disorder: marked by recurring panic attacks, which are intense episodes of fear or discomfort that peak within minutes. * Social anxiety disorder: involves excessive and persistent fear or anxiety in social situations, such as public speaking or meeting new people. * Specific phobias: involve an intense and irrational fear of a specific object, situation, or activity, such as spiders or heights.Causes and Risk Factors

The causes of anxiety are complex and multifaceted, involving a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Some of the key risk factors for developing an anxiety disorder include:
- Family history: individuals with a family history of anxiety disorders are more likely to develop an anxiety disorder.
- Trauma: experiencing a traumatic event, such as physical or emotional abuse, can increase the risk of developing an anxiety disorder.
- Brain chemistry: imbalances in neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, can contribute to anxiety.
- Personality traits: certain personality traits, such as perfectionism and low self-esteem, can increase the risk of developing an anxiety disorder.
Biological and Psychological Factors
Biological and psychological factors, such as brain structure and function, also play a crucial role in the development of anxiety disorders. For example: * Abnormalities in brain regions, such as the amygdala and prefrontal cortex, have been linked to anxiety disorders. * Psychological factors, such as cognitive distortions and negative thinking patterns, can contribute to the development and maintenance of anxiety disorders.Treatment Options
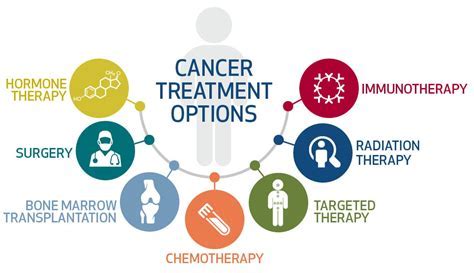
Fortunately, anxiety disorders are treatable, and a range of effective treatment options are available. The most common treatment approaches include:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): a type of psychotherapy that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Medications: such as antidepressants and benzodiazepines, which can help reduce symptoms of anxiety.
- Lifestyle changes: such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and stress management techniques, which can help reduce stress and anxiety.
Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies, such as mindfulness-based stress reduction and yoga, have also been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety. These therapies can be used in conjunction with traditional treatments or as a standalone approach.Coping Strategies

In addition to seeking professional help, there are several coping strategies that can help individuals manage anxiety. Some effective coping strategies include:
- Deep breathing exercises: can help reduce stress and anxiety by slowing down breathing and promoting relaxation.
- Progressive muscle relaxation: involves tensing and relaxing different muscle groups to reduce physical tension.
- Journaling: can help individuals process their thoughts and emotions, reducing feelings of overwhelm and anxiety.
Building Resilience
Building resilience is also essential for managing anxiety. This can involve: * Developing a support network: surrounding oneself with positive and supportive people. * Engaging in regular self-care: such as exercise, meditation, and hobbies. * Practicing gratitude: focusing on the positive aspects of life and expressing gratitude.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, anxiety is a complex and multifaceted condition that affects millions of people worldwide. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for anxiety, we can work towards creating a more supportive and compassionate environment for those affected. If you or someone you know is struggling with anxiety, it is essential to seek help from a mental health professional. With the right treatment and support, it is possible to manage anxiety and improve overall well-being.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with anxiety in the comments below. Your input can help raise awareness and promote understanding of this important topic. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from the information.
What is the difference between anxiety and fear?
+Anxiety and fear are related but distinct emotions. Fear is a response to a specific threat or danger, whereas anxiety is a more general feeling of worry or apprehension that is not necessarily tied to a specific threat.
Can anxiety be cured?
+While anxiety cannot be "cured" in the classical sense, it can be effectively managed with treatment and lifestyle changes. With the right approach, individuals can learn to manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
How can I help someone with anxiety?
+Helping someone with anxiety involves being supportive, understanding, and non-judgmental. Encourage them to seek professional help, offer to help them with daily tasks, and provide a listening ear when they need to talk.
