Intro
Discover 5 effective ways to manage diabetes, including diet control, exercise routines, and stress management, to regulate blood sugar levels and prevent complications, promoting a healthy lifestyle with diabetes management tips and strategies.
Living with diabetes requires a significant amount of dedication and self-care. Managing the condition effectively is crucial to preventing complications and improving the quality of life. Diabetes management involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring of blood sugar levels. Effective management can help individuals with diabetes lead active and healthy lives. It is essential to understand the importance of managing diabetes and the various strategies that can be employed to achieve this goal. By taking control of their condition, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing complications and improve their overall well-being.
The prevalence of diabetes is increasing globally, and it is essential to address this issue through education, awareness, and effective management strategies. Diabetes management is a multifaceted approach that involves healthcare providers, individuals with diabetes, and their families. It requires a comprehensive understanding of the condition, its causes, and its effects on the body. By working together, individuals with diabetes can develop personalized management plans that cater to their unique needs and circumstances. This collaborative approach can help individuals with diabetes achieve their health goals and improve their quality of life.
Effective diabetes management can have a significant impact on an individual's overall health and well-being. By maintaining good blood sugar control, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Good blood sugar control can also improve energy levels, reduce the risk of infections, and promote wound healing. Furthermore, effective diabetes management can help individuals with diabetes maintain a healthy weight, improve their mental health, and enhance their overall quality of life. With the right strategies and support, individuals with diabetes can manage their condition effectively and lead active, healthy, and fulfilling lives.
Understanding Diabetes

Types of Diabetes
There are several types of diabetes, each with its unique causes and characteristics. Type 1 diabetes is typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, while type 2 diabetes is often diagnosed in adulthood. Gestational diabetes is diagnosed during pregnancy, usually between 24 and 28 weeks. Other forms of diabetes include latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA), maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY), and secondary diabetes, which is caused by certain medications or medical conditions.Diabetes Management Strategies

- Eating a healthy and balanced diet that is low in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats
- Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or cycling
- Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly to ensure that they are within the target range
- Taking medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider
- Getting enough sleep and managing stress levels
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications are an essential part of diabetes management. Eating a healthy and balanced diet can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve overall health. A diabetes-friendly diet should include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources. Regular physical activity can also help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of complications. It is essential to choose activities that are enjoyable and sustainable in the long term.Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
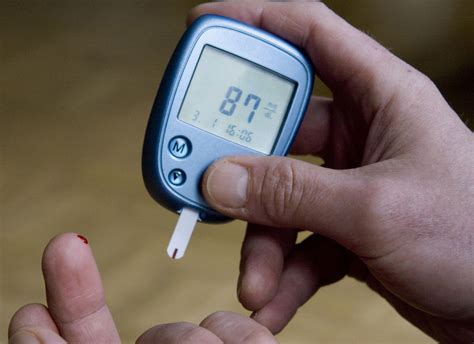
Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is a relatively new technology that allows individuals with diabetes to track their blood sugar levels continuously throughout the day. CGM systems use a small sensor that is inserted under the skin to measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. This information is then transmitted to a receiver or smartphone app, providing real-time data on blood sugar levels. CGM can be particularly useful for individuals with type 1 diabetes or those who experience frequent hypoglycemia.Treatment Options

- Medication: There are several types of medication that can be used to manage diabetes, including metformin, sulfonylureas, and meglitinides.
- Insulin therapy: Insulin therapy is often used to manage type 1 diabetes and may also be used to manage type 2 diabetes in some cases.
- Lifestyle modifications: Lifestyle modifications, such as eating a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity, are an essential part of diabetes management.
Emerging Therapies
There are several emerging therapies for diabetes, including stem cell therapy, gene therapy, and immunotherapy. These therapies aim to address the underlying causes of diabetes, such as insulin deficiency or insulin resistance. While these therapies are still in the experimental stages, they offer promising new approaches to diabetes management.Complications of Diabetes
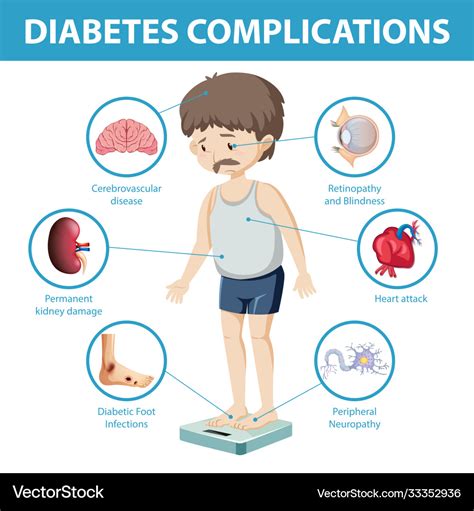
- Heart disease: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease, including heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure.
- Kidney disease: Diabetes is a leading cause of kidney disease, which can lead to kidney failure and the need for dialysis or a kidney transplant.
- Nerve damage: Diabetes can cause nerve damage, which can lead to numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet.
Preventing Complications
Preventing complications is an essential part of diabetes management. This can be achieved by maintaining good blood sugar control, managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Regular health check-ups and screenings can also help identify potential complications early, enabling prompt treatment and prevention.Conclusion and Next Steps

If you have diabetes, it is essential to take an active role in managing your condition. This can involve setting health goals, developing a management plan, and tracking your progress. By taking control of your diabetes, you can reduce your risk of complications, improve your quality of life, and lead a long and healthy life.
We invite you to share your experiences and tips for managing diabetes in the comments section below. Your insights and advice can help others who are living with the condition, and we appreciate your contributions to the conversation. Additionally, if you have any questions or concerns about diabetes management, please do not hesitate to ask. We are here to provide you with the information and support you need to manage your condition effectively.
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
+The symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How can I manage my blood sugar levels?
+You can manage your blood sugar levels by eating a healthy and balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly, and taking medication as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
What are the complications of diabetes?
+The complications of diabetes include heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and blindness. These complications can be prevented or delayed by maintaining good blood sugar control and managing other risk factors.
