Intro
Understand 5 diabetic glucose ranges, including normal, prediabetes, and diabetes levels, to manage blood sugar and prevent complications like hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by high levels of glucose in the blood, which can lead to a range of serious health complications if left unmanaged. One of the key aspects of managing diabetes is monitoring blood glucose levels, which involves tracking the amount of glucose in the blood to ensure it remains within a healthy range. In this article, we will explore the different diabetic glucose ranges, their significance, and how they can be managed.
The importance of monitoring blood glucose levels cannot be overstated. It helps individuals with diabetes to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication, which are crucial for maintaining good health. By keeping track of blood glucose levels, individuals can identify patterns and trends, which can help them to adjust their treatment plan accordingly. Moreover, monitoring blood glucose levels can help to prevent serious health complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage, which are common among people with unmanaged diabetes.
Effective management of diabetes requires a comprehensive approach that involves lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels. By understanding the different diabetic glucose ranges, individuals can take control of their condition and make informed decisions about their health. In the following sections, we will delve into the different aspects of diabetic glucose ranges, including their significance, how they are measured, and how they can be managed.
Understanding Diabetic Glucose Ranges
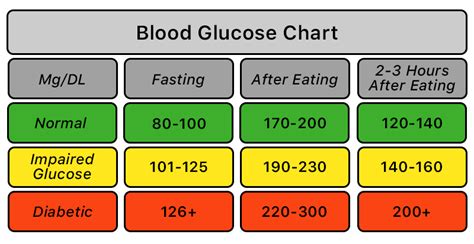
Normal Glucose Range
A normal glucose range is typically defined as a fasting blood glucose level of less than 100 mg/dL. This range is considered normal because it indicates that the body is able to regulate blood glucose levels effectively. Individuals with a normal glucose range are not at risk of developing diabetes, and they do not require any special treatment or management.Prediabetes Glucose Range
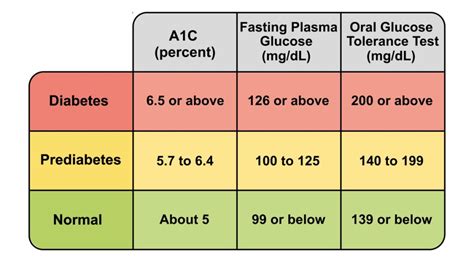
Different Types of Diabetes
There are several types of diabetes, including type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Each type of diabetes has a different cause and requires a different treatment approach. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body's immune system attacks the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder that occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin. Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy, typically in the second or third trimester.Diabetes Glucose Range

Importance of Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Monitoring blood glucose levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes. It helps them to track their glucose levels, identify patterns and trends, and make informed decisions about their treatment plan. By monitoring blood glucose levels, individuals can adjust their diet, exercise, and medication to maintain good health. Moreover, monitoring blood glucose levels can help to prevent serious health complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.Managing Diabetic Glucose Ranges
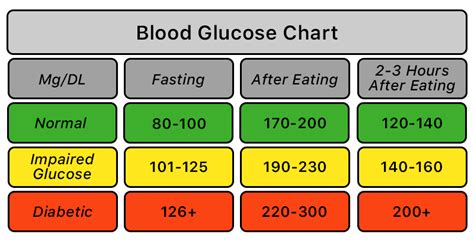
- Eat a healthy diet that is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates
- Engage in regular physical activity, such as walking or cycling
- Take medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider
- Monitor blood glucose levels regularly
- Get enough sleep and manage stress
Benefits of Managing Diabetic Glucose Ranges
Managing diabetic glucose ranges has several benefits, including:- Reducing the risk of serious health complications, such as heart disease and kidney damage
- Improving overall health and well-being
- Increasing energy levels and reducing fatigue
- Enhancing cognitive function and reducing the risk of dementia
- Improving sleep quality and reducing the risk of sleep disorders
Common Mistakes to Avoid

- Not monitoring blood glucose levels regularly
- Not taking medication as prescribed
- Eating a diet that is high in sugar and refined carbohydrates
- Not engaging in regular physical activity
- Not getting enough sleep and managing stress
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, managing diabetic glucose ranges is crucial for individuals with diabetes. By understanding the different diabetic glucose ranges, monitoring blood glucose levels, and making informed decisions about treatment, individuals can take control of their condition and maintain good health. If you have diabetes, it is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that includes lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels.To learn more about diabetic glucose ranges and how to manage them, consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian. They can provide personalized guidance and support to help you achieve your health goals. Additionally, there are many online resources and support groups available that can provide education, guidance, and support for individuals with diabetes.
What is the normal glucose range for adults?
+A normal glucose range for adults is typically defined as a fasting blood glucose level of less than 100 mg/dL.
What are the symptoms of high blood glucose levels?
+The symptoms of high blood glucose levels include increased thirst and urination, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How can I manage my diabetic glucose ranges?
+You can manage your diabetic glucose ranges by eating a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, taking medication as prescribed, and monitoring your blood glucose levels regularly.
What are the benefits of managing diabetic glucose ranges?
+The benefits of managing diabetic glucose ranges include reducing the risk of serious health complications, improving overall health and well-being, and increasing energy levels and reducing fatigue.
How often should I monitor my blood glucose levels?
+You should monitor your blood glucose levels regularly, ideally before meals and before bedtime, to track your glucose levels and make informed decisions about your treatment plan.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of diabetic glucose ranges and how to manage them. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian. Remember, managing diabetic glucose ranges is crucial for maintaining good health and preventing serious health complications. By working together with healthcare professionals and making informed decisions about treatment, individuals with diabetes can take control of their condition and live a long and healthy life.
