Diltiazem is a medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various cardiovascular conditions. Its importance in the management of certain heart-related diseases cannot be overstated, making it a crucial topic for discussion. Understanding the mechanisms, benefits, and potential side effects of diltiazem is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients who are prescribed this medication. As we delve into the world of diltiazem, it becomes clear that this medication plays a significant role in improving the quality of life for many individuals. With its ability to effectively manage symptoms and prevent complications, diltiazem has become a cornerstone in the treatment of certain cardiovascular diseases.
The significance of diltiazem lies in its unique pharmacological properties, which set it apart from other medications in its class. By selectively blocking calcium channels, diltiazem is able to reduce the heart's workload and improve blood flow to the body's tissues. This mechanism of action has made diltiazem an invaluable tool in the management of conditions such as hypertension, angina pectoris, and certain types of arrhythmias. Furthermore, the medication's relatively long history of use has provided a wealth of information regarding its efficacy and safety profile, making it a trusted choice among healthcare providers.
As we explore the topic of diltiazem in greater depth, it becomes evident that there is much to learn about this complex medication. From its chemical structure to its clinical applications, diltiazem is a fascinating subject that warrants thorough examination. Whether you are a healthcare professional seeking to expand your knowledge or a patient looking to understand your treatment, this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of diltiazem, covering its key aspects, benefits, and considerations.
Introduction to Diltiazem
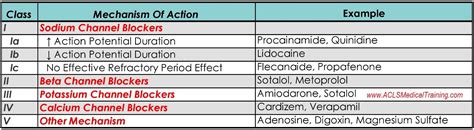
Diltiazem belongs to a class of medications known as calcium channel blockers. These drugs work by inhibiting the influx of calcium ions into cardiac and smooth muscle cells, thereby reducing muscle contraction and promoting vasodilation. This action leads to decreased blood pressure, reduced heart rate, and increased oxygen supply to the heart muscle. Diltiazem is specifically classified as a non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker, which distinguishes it from other calcium channel blockers in terms of its pharmacological effects.
Pharmacological Properties of Diltiazem
The pharmacological properties of diltiazem are characterized by its selective blockade of L-type calcium channels. This selectivity allows diltiazem to exert its effects primarily on the heart and vascular smooth muscle, with minimal impact on other tissues. The medication's ability to reduce cardiac afterload and increase coronary blood flow makes it particularly useful in the treatment of conditions such as angina pectoris and hypertension. Additionally, diltiazem's negative inotropic effect (reduction in heart muscle contraction force) and negative chronotropic effect (reduction in heart rate) contribute to its therapeutic benefits in certain cardiovascular diseases.
Clinical Applications of Diltiazem
Diltiazem has several clinical applications, including the treatment of hypertension, angina pectoris, and certain types of arrhythmias. In hypertension, diltiazem helps to lower blood pressure by reducing peripheral resistance and promoting vasodilation. For angina pectoris, the medication increases oxygen supply to the heart muscle, reducing the frequency and severity of angina attacks. Diltiazem is also used to control ventricular rate in patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter, showcasing its versatility in managing various cardiovascular conditions.
Benefits of Diltiazem
The benefits of diltiazem are multifaceted, reflecting its efficacy in managing symptoms and preventing complications associated with cardiovascular diseases. Some of the key benefits include:
- Reduced blood pressure: Diltiazem helps to lower blood pressure, reducing the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes.
- Increased oxygen supply to the heart: By promoting vasodilation and reducing cardiac afterload, diltiazem increases oxygen supply to the heart muscle, alleviating symptoms of angina pectoris.
- Improved exercise tolerance: Patients with angina pectoris may experience improved exercise tolerance due to the increased oxygen supply to the heart muscle.
- Reduced risk of cardiovascular events: The medication's ability to lower blood pressure and reduce cardiac workload contributes to a decreased risk of cardiovascular events.
Potential Side Effects of Diltiazem
While diltiazem is generally well-tolerated, it can cause potential side effects in some patients. Common side effects include:
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue
- Edema (swelling of the legs, ankles, or feet)
- Constipation
It is essential for patients to discuss any concerns or side effects with their healthcare provider, as adjustments to the treatment plan may be necessary.
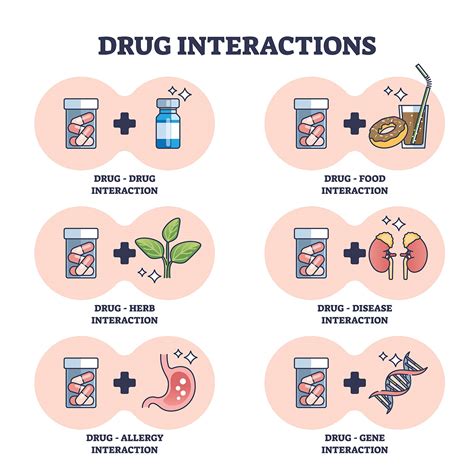
Interactions with Other Medications
Diltiazem can interact with other medications, either enhancing or reducing their effects. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter drugs, as well as herbal supplements. Some medications that may interact with diltiazem include:
- Beta blockers: Concomitant use with beta blockers may lead to additive effects on heart rate and blood pressure.
- Digoxin: Diltiazem may increase digoxin levels, potentially leading to toxicity.
- Cyclosporine: Diltiazem may increase cyclosporine levels, potentially leading to toxicity.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of diltiazem vary depending on the specific condition being treated and the patient's response to the medication. Diltiazem is available in various formulations, including tablets, capsules, and injectable solutions. Patients should follow their healthcare provider's instructions regarding dosage and administration, as well as any adjustments to the treatment plan.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, diltiazem is a valuable medication in the management of various cardiovascular conditions. Its unique pharmacological properties, clinical applications, and benefits make it an essential tool for healthcare providers. As research continues to uncover new aspects of diltiazem's effects and interactions, its role in cardiovascular therapy is likely to evolve. Patients and healthcare professionals alike should remain informed about the latest developments and guidelines regarding diltiazem, ensuring optimal use and maximizing its therapeutic potential.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with diltiazem in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns about this medication, please do not hesitate to ask. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with anyone who may benefit from this information, helping to promote awareness and understanding of diltiazem's importance in cardiovascular health.
What is the primary mechanism of action of diltiazem?
+
Diltiazem works by selectively blocking L-type calcium channels, reducing the influx of calcium ions into cardiac and smooth muscle cells.
What are the common side effects of diltiazem?
+
Common side effects of diltiazem include dizziness, headache, nausea, fatigue, edema, and constipation.
Can diltiazem be used in patients with atrial fibrillation?
+
Yes, diltiazem can be used to control ventricular rate in patients with atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter.