Intro
Dehydration can cause diarrhea, triggering a vicious cycle. Learn how dehydration leads to diarrhea, its symptoms, and related issues like electrolyte imbalance and water deficiency, to manage and prevent it effectively.
Dehydration and diarrhea are two closely related health issues that can have a significant impact on an individual's overall well-being. Diarrhea, which is characterized by loose, watery stools, can lead to dehydration if not properly managed. In fact, dehydration is one of the most common complications of diarrhea, particularly in children, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems. In this article, we will delve into the relationship between dehydration and diarrhea, exploring the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for these two interconnected health issues.
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, causing an imbalance in the body's water and electrolyte levels. This can happen for a variety of reasons, including diarrhea, vomiting, excessive sweating, and inadequate fluid intake. When the body becomes dehydrated, it can lead to a range of symptoms, including dry mouth, dark urine, fatigue, and dizziness. If left untreated, dehydration can lead to more severe complications, such as heat stroke, kidney damage, and even death.
Diarrhea, on the other hand, is a common health issue that affects people of all ages. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including viral or bacterial infections, food poisoning, and certain medications. When the body is infected with a virus or bacteria, it can cause the intestines to become inflamed, leading to an increase in the production of stool and the loss of fluids and electrolytes. This can lead to dehydration if the body is not able to replenish the lost fluids and electrolytes quickly enough.
Understanding Dehydration
Dehydration is a serious health issue that can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status. It occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, causing an imbalance in the body's water and electrolyte levels. This can happen for a variety of reasons, including diarrhea, vomiting, excessive sweating, and inadequate fluid intake. When the body becomes dehydrated, it can lead to a range of symptoms, including dry mouth, dark urine, fatigue, and dizziness. If left untreated, dehydration can lead to more severe complications, such as heat stroke, kidney damage, and even death.
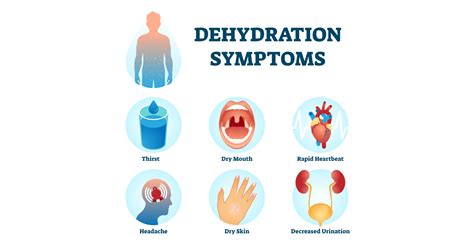
Symptoms of Dehydration
The symptoms of dehydration can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mild dehydration may cause symptoms such as: * Dry mouth and throat * Dark urine * Fatigue * Headaches * Dizziness Severe dehydration, on the other hand, can cause more serious symptoms, including: * Rapid heartbeat * Low blood pressure * Sunken eyes * Decreased urine output * Confusion and disorientationThe Relationship Between Dehydration and Diarrhea

Diarrhea and dehydration are two closely related health issues. Diarrhea can lead to dehydration if not properly managed, and dehydration can exacerbate the symptoms of diarrhea. When the body is infected with a virus or bacteria, it can cause the intestines to become inflamed, leading to an increase in the production of stool and the loss of fluids and electrolytes. This can lead to dehydration if the body is not able to replenish the lost fluids and electrolytes quickly enough.
Treatment Options for Dehydration and Diarrhea
The treatment for dehydration and diarrhea depends on the severity of the condition. Mild dehydration can be treated with oral rehydration solutions, such as sports drinks or Pedialyte. These solutions help to replenish the lost fluids and electrolytes, and can be found at most pharmacies and grocery stores. Severe dehydration, on the other hand, may require intravenous fluids and electrolytes, and should be treated by a medical professional.For diarrhea, the treatment options include:
- Oral rehydration solutions
- Anti-diarrheal medications
- Probiotics
- Dietary changes, such as avoiding spicy or fatty foods It's also important to practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently, to prevent the spread of infection.
Preventing Dehydration and Diarrhea
Preventing dehydration and diarrhea requires a combination of good hygiene practices, a healthy diet, and adequate fluid intake. Here are some tips to help prevent dehydration and diarrhea:
- Practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently
- Avoid close contact with people who have diarrhea or other illnesses
- Avoid eating undercooked or raw foods, such as meat, poultry, and eggs
- Avoid drinking untreated water, such as from a well or stream
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids, such as water, clear broth, and electrolyte-rich beverages like sports drinks
- Eat a healthy diet, including plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
Complications of Dehydration and Diarrhea
If left untreated, dehydration and diarrhea can lead to a range of complications, including: * Heat stroke * Kidney damage * Electrolyte imbalances * Malnutrition * Weakened immune system It's essential to seek medical attention if you or someone you know is experiencing severe symptoms of dehydration or diarrhea.Treatment for Specific Populations
Certain populations, such as children, older adults, and people with weakened immune systems, may require special consideration when it comes to treating dehydration and diarrhea. For example:
- Children under the age of 5 are at higher risk of dehydration and diarrhea, and may require more frequent and smaller amounts of oral rehydration solutions.
- Older adults may be more susceptible to dehydration and diarrhea due to age-related changes, such as decreased thirst sensation and impaired kidney function.
- People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, may be more prone to dehydration and diarrhea, and may require more aggressive treatment.
Home Remedies for Dehydration and Diarrhea
There are several home remedies that can help to alleviate the symptoms of dehydration and diarrhea, including: * Drinking plenty of fluids, such as water, clear broth, and electrolyte-rich beverages like sports drinks * Eating small, frequent meals, such as bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast (BRAT diet) * Avoiding spicy or fatty foods * Taking anti-diarrheal medications, such as loperamide (Imodium) * Practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequentlyConclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, dehydration and diarrhea are two closely related health issues that can have a significant impact on an individual's overall well-being. It's essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for these two conditions, as well as how to prevent them. By practicing good hygiene, staying hydrated, and eating a healthy diet, you can reduce your risk of dehydration and diarrhea. If you or someone you know is experiencing severe symptoms of dehydration or diarrhea, it's essential to seek medical attention immediately.
We encourage you to share this article with friends and family, and to leave a comment below if you have any questions or concerns about dehydration and diarrhea. Remember, staying informed and taking proactive steps to protect your health is the best way to prevent dehydration and diarrhea, and to ensure overall wellness.
What are the symptoms of dehydration?
+The symptoms of dehydration can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but may include dry mouth, dark urine, fatigue, headaches, and dizziness.
How can I prevent dehydration and diarrhea?
+Preventing dehydration and diarrhea requires a combination of good hygiene practices, a healthy diet, and adequate fluid intake. Practice good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently, and avoid close contact with people who have diarrhea or other illnesses.
What are the complications of dehydration and diarrhea?
+If left untreated, dehydration and diarrhea can lead to a range of complications, including heat stroke, kidney damage, electrolyte imbalances, malnutrition, and weakened immune system.
