Intro
Discover accurate Cephalexin dosing guidelines, including dosage calculations, administration schedules, and pharmacokinetics to ensure effective antibiotic treatment and minimize side effects, with expert advice on pediatric and adult dosing, renal impairment, and potential interactions.
The importance of understanding cephalexin dosing guidelines cannot be overstated, as this antibiotic is widely used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. Cephalexin, also known as Keflex, is a cephalosporin antibiotic that works by interfering with the formation of the bacterial cell wall, ultimately leading to the death of the bacteria. It is effective against a range of Gram-positive and some Gram-negative bacteria, making it a versatile treatment option for infections such as pneumonia, skin infections, and urinary tract infections. However, to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment and minimize the risk of side effects, it is crucial to follow the recommended dosing guidelines.
Cephalexin dosing guidelines are typically provided by a healthcare professional and are based on the type and severity of the infection being treated, as well as the patient's age, weight, and kidney function. The dosage may vary from one patient to another, and it is essential to adhere to the prescribed dosage to achieve the best possible outcomes. Deviating from the recommended dosage can lead to reduced efficacy, increased risk of side effects, or the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Furthermore, cephalexin is available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, and oral suspensions, which can affect how the medication is administered and absorbed by the body.
The proper use of cephalexin and adherence to dosing guidelines are critical for several reasons. Firstly, taking the correct dose ensures that the infection is adequately treated, reducing the risk of complications and the spread of infection to other parts of the body. Secondly, following the recommended dosage helps to minimize the risk of side effects, such as gastrointestinal upset, allergic reactions, and interactions with other medications. Lastly, responsible use of antibiotics like cephalexin is essential for combating the growing problem of antibiotic resistance, which occurs when bacteria evolve to become resistant to the effects of antibiotics, making infections harder to treat.
Cephalexin Dosing Guidelines for Adults
Cephalexin dosing guidelines for adults vary depending on the type of infection being treated. For uncomplicated urinary tract infections, the typical dose is 250 mg every 6 hours or 500 mg every 12 hours. For skin and soft tissue infections, the dose is usually 250 mg to 500 mg every 6 hours. In the case of streptococcal pharyngitis, the recommended dose is 500 mg every 12 hours. It is essential to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed by the healthcare provider, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication, to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.
Factors Influencing Cephalexin Dosage in Adults
The dosage of cephalexin in adults may need to be adjusted based on certain factors, including renal function. Patients with impaired kidney function may require lower doses to prevent the accumulation of the drug in the body, which can increase the risk of side effects. Additionally, the dosage may need to be adjusted in elderly patients, as they may be more susceptible to the effects of the medication due to age-related changes in drug metabolism and excretion.Cephalexin Dosing Guidelines for Children
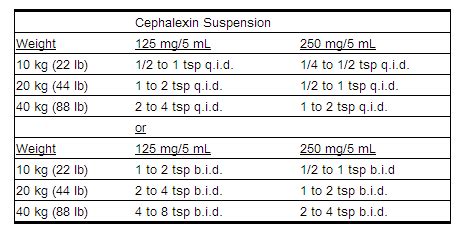
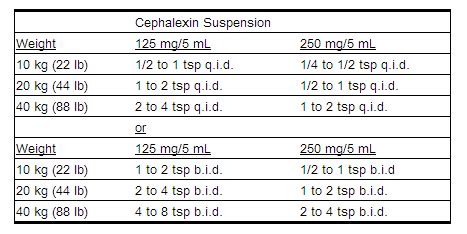
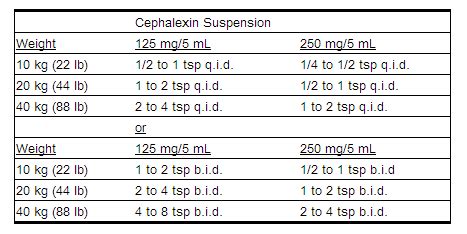
For children, cephalexin dosing guidelines are based on the child's weight, typically ranging from 25 mg to 50 mg per kilogram of body weight per day, divided into 2 to 4 doses. The specific dose and frequency depend on the type of infection being treated. For example, for streptococcal pharyngitis, the dose is usually 25 mg per kilogram per day, given in 2 divided doses. It is crucial for parents or caregivers to measure the dose accurately and administer the medication as directed to ensure the child receives the correct amount of medication.
Administration Considerations for Children
When administering cephalexin to children, it is essential to use the oral suspension form if the child has difficulty swallowing capsules or tablets. The suspension should be shaken well before each use, and the dose should be measured carefully using a calibrated measuring device to ensure accuracy. Additionally, cephalexin can be taken with or without food, but taking it with food may help reduce gastrointestinal side effects.Cephalexin Dosage Adjustments for Renal Impairment
Patients with renal impairment require careful consideration when prescribing cephalexin, as the drug is primarily excreted by the kidneys. Dosage adjustments are necessary to prevent drug accumulation and potential toxicity. For patients with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 50-80 mL/min), the dose may not need to be adjusted. However, for those with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 10-49 mL/min), the dose should be reduced by 50%. In severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance of less than 10 mL/min), the dose should be reduced by 75%.
Monitoring Renal Function
It is crucial to monitor renal function in patients with pre-existing kidney disease or those at risk of developing renal impairment during cephalexin treatment. Regular assessment of creatinine clearance and monitoring for signs of renal toxicity, such as increased serum creatinine levels, are essential for early detection and management of potential renal issues.Common Side Effects and Interactions

Cephalexin, like all medications, can cause side effects and interact with other drugs. Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. More severe side effects, such as allergic reactions, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea, can occur but are rare. Cephalexin can also interact with other medications, including blood thinners, metformin, and probenecid, which may require dosage adjustments or close monitoring.
Minimizing Side Effects and Interactions
To minimize the risk of side effects and interactions, patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and herbal products they are taking. Additionally, maintaining good hydration, taking the medication with food if necessary, and completing the full course of treatment as directed can help reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects and ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, understanding and following cephalexin dosing guidelines are critical for the effective treatment of bacterial infections and minimizing the risk of side effects. As antibiotic resistance continues to pose a significant threat to public health, responsible use of antibiotics like cephalexin is more important than ever. Future research should focus on developing new antibiotics and improving our understanding of how to optimize dosing regimens to combat resistance and ensure the continued efficacy of these lifesaving medications.
What is the typical dose of cephalexin for an adult with a urinary tract infection?
+The typical dose of cephalexin for an adult with an uncomplicated urinary tract infection is 250 mg every 6 hours or 500 mg every 12 hours.
How should cephalexin be administered to children?
+Cephalexin for children is typically administered based on the child's weight, ranging from 25 mg to 50 mg per kilogram of body weight per day, divided into 2 to 4 doses. The oral suspension form should be used for children who have difficulty swallowing capsules or tablets.
What adjustments are needed for patients with renal impairment?
+Patient with renal impairment may require dosage adjustments to prevent drug accumulation. For moderate renal impairment, the dose should be reduced by 50%, and for severe renal impairment, the dose should be reduced by 75%.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with cephalexin dosing guidelines in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us provide the most accurate and helpful content possible.
