Intro
Discover 5 crucial Drug DNA test facts, revealing genetic predispositions to addiction, pharmacogenomics, and personalized medicine, helping individuals understand substance sensitivity and response.
The concept of drug DNA testing has gained significant attention in recent years, particularly in the context of personalized medicine and targeted therapies. This approach involves analyzing an individual's genetic makeup to predict their response to certain drugs, thereby optimizing treatment outcomes and minimizing adverse reactions. As the field of pharmacogenomics continues to evolve, it is essential to understand the underlying principles and applications of drug DNA testing.
The integration of genetic testing into clinical practice has the potential to revolutionize the way we approach drug treatment. By identifying specific genetic variants associated with drug metabolism, healthcare providers can tailor treatment plans to individual patients, enhancing efficacy and reducing the risk of adverse events. Moreover, drug DNA testing can help identify individuals who are more likely to experience severe side effects, allowing for alternative treatment options to be explored.
The importance of drug DNA testing extends beyond the realm of personalized medicine, with implications for public health and pharmaceutical research. As our understanding of the genetic factors influencing drug response grows, so too does the potential for developing more effective and targeted therapies. Furthermore, drug DNA testing can inform the development of new drugs, enabling researchers to design clinical trials that account for genetic variability and optimize treatment outcomes.
Introduction to Drug DNA Testing

Key Principles of Drug DNA Testing
The key principles of drug DNA testing involve the analysis of specific genetic variants associated with drug metabolism. This includes the identification of genetic variants that influence the activity of enzymes involved in drug metabolism, as well as those that affect the function of drug transporters. By understanding how these genetic variants impact drug response, healthcare providers can develop personalized treatment plans that optimize efficacy and minimize adverse reactions.Benefits of Drug DNA Testing

Applications of Drug DNA Testing
The applications of drug DNA testing are diverse, with implications for various fields of medicine. Some of the key areas where this approach is being explored include: * Oncology: Drug DNA testing is being used to develop personalized treatment plans for cancer patients, optimizing efficacy and minimizing adverse reactions. * Psychiatry: This approach is being explored in the context of psychiatric disorders, enabling healthcare providers to develop targeted treatment plans that account for genetic variability. * Cardiology: Drug DNA testing is being used to optimize treatment outcomes for patients with cardiovascular disease, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions and enhancing efficacy.How Drug DNA Testing Works

Interpreting Drug DNA Test Results
Interpreting drug DNA test results requires a comprehensive understanding of the genetic factors influencing drug response. This involves analyzing the specific variants identified and determining how they impact drug metabolism. Healthcare providers can then use this information to develop personalized treatment plans, optimizing efficacy and minimizing adverse reactions.Common Drugs Affected by Genetics
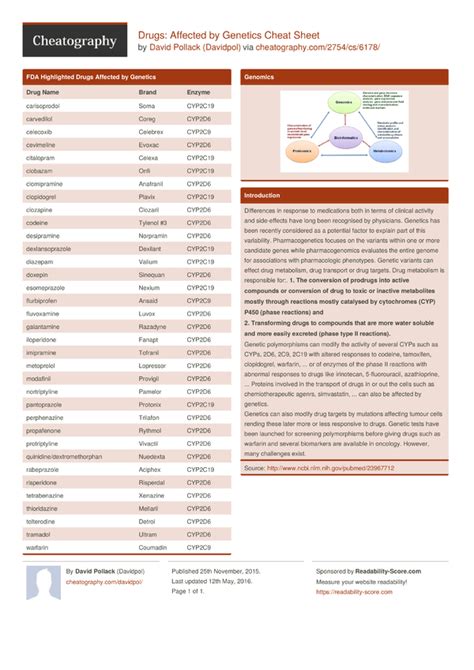
Genetic Variants and Drug Response
Genetic variants can significantly impact drug response, with some individuals experiencing enhanced efficacy and others experiencing adverse reactions. For example, individuals with a specific variant of the CYP2C9 enzyme may require lower doses of warfarin to achieve optimal anticoagulation, while those with a variant of the CYP2D6 enzyme may experience reduced efficacy with codeine.Limitations and Challenges of Drug DNA Testing
Future Directions for Drug DNA Testing
The future of drug DNA testing is promising, with ongoing research aimed at developing more effective and targeted therapies. As our understanding of the genetic factors influencing drug response grows, so too does the potential for personalized medicine.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with drug DNA testing, either by commenting below or sharing this article with others. By working together, we can advance our understanding of this promising approach and explore its potential applications in clinical practice.
What is drug DNA testing?
+Drug DNA testing involves analyzing an individual's genetic code to predict their response to certain drugs, thereby optimizing treatment outcomes and minimizing adverse reactions.
How does drug DNA testing work?
+Drug DNA testing involves the analysis of an individual's genetic code, specifically focusing on variants associated with drug metabolism. This typically involves a simple blood test or cheek swab, which provides a sample of DNA for analysis.
What are the benefits of drug DNA testing?
+The benefits of drug DNA testing include enhanced efficacy, improved safety, and targeted therapies. By understanding the genetic factors influencing drug response, healthcare providers can develop personalized treatment plans that optimize efficacy and minimize adverse reactions.
What are the limitations of drug DNA testing?
+The limitations of drug DNA testing include cost, complexity, and limited evidence. While there is growing evidence supporting the use of drug DNA testing, more research is needed to fully understand its applications and limitations.
What is the future of drug DNA testing?
+The future of drug DNA testing is promising, with ongoing research aimed at developing more effective and targeted therapies. As our understanding of the genetic factors influencing drug response grows, so too does the potential for personalized medicine.
