Intro
Discover how high WBC count affects health, including infection risks, inflammation, and immune system responses, impacting overall wellbeing and disease prevention, with 5 key ways to manage elevated white blood cell levels.
A high white blood cell (WBC) count, also known as leukocytosis, can be a sign of an underlying infection, inflammation, or disease. White blood cells are an essential part of the immune system, helping to fight off infections and diseases. However, when the WBC count becomes elevated, it can have various effects on overall health. In this article, we will explore the importance of understanding high WBC counts and their potential impact on health.
Elevated WBC counts can be caused by a range of factors, including bacterial or viral infections, autoimmune disorders, and certain types of cancer. When the body detects an infection or inflammation, it produces more white blood cells to help combat the invading organisms. While an elevated WBC count can be a normal response to an infection, persistently high levels can indicate a more serious underlying condition. It is essential to understand the potential effects of high WBC counts on health to seek medical attention if necessary.
The impact of high WBC counts on health can be significant, ranging from mild to severe effects. In some cases, elevated WBC counts can be a sign of an underlying condition that requires medical attention. In other cases, high WBC counts can be a temporary response to an infection or inflammation, resolving on their own once the underlying condition is treated. Understanding the potential effects of high WBC counts on health can help individuals take proactive steps to manage their condition and prevent complications.
Introduction to High WBC Counts
Causes of High WBC Counts
High WBC counts can be caused by a range of factors, including: * Bacterial or viral infections * Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus * Certain types of cancer, such as leukemia or lymphoma * Inflammatory conditions, such as appendicitis or diverticulitis * Allergic reactions or asthma * Stress or anxietyEffects of High WBC Counts on Health
Types of High WBC Counts
There are several types of high WBC counts, including: * Neutrophilia: An increase in neutrophils, a type of white blood cell that helps to fight off bacterial infections. * Lymphocytosis: An increase in lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell that helps to fight off viral infections. * Monocytosis: An increase in monocytes, a type of white blood cell that helps to fight off infections and inflammation. * Eosinophilia: An increase in eosinophils, a type of white blood cell that helps to fight off parasitic infections and allergic reactions.Diagnosis and Treatment of High WBC Counts
Managing High WBC Counts
Managing high WBC counts involves treating the underlying cause and reducing inflammation. Some ways to manage high WBC counts include: * Getting plenty of rest: To help the body recover from an infection or inflammation * Staying hydrated: To help the body function properly and reduce inflammation * Eating a healthy diet: To provide the body with essential nutrients and vitamins * Reducing stress: To help reduce inflammation and promote overall health * Avoiding irritants: To reduce inflammation and prevent further irritationComplications of High WBC Counts

Prevention of High WBC Counts
Preventing high WBC counts involves reducing the risk of infection and inflammation. Some ways to prevent high WBC counts include: * Practicing good hygiene: To reduce the risk of infection * Getting vaccinated: To reduce the risk of infection * Avoiding irritants: To reduce inflammation and prevent further irritation * Managing stress: To reduce inflammation and promote overall health * Eating a healthy diet: To provide the body with essential nutrients and vitaminsConclusion and Next Steps

We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with high WBC counts in the comments section below. Your input can help others better understand the effects of high WBC counts on health and promote awareness about this important health topic. Additionally, if you have any questions or concerns about high WBC counts, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional for guidance and support.
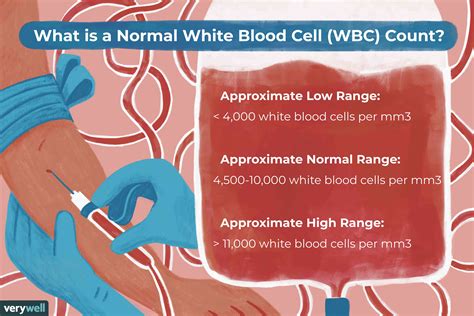
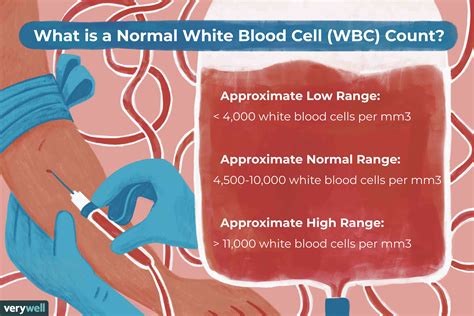
What is a normal white blood cell count?
+A normal white blood cell count is typically between 4,000 and 11,000 cells per microliter of blood.
What are the symptoms of high WBC counts?
+Symptoms of high WBC counts can include fatigue, weakness, weight loss, and a general feeling of being unwell.
How are high WBC counts diagnosed?
+High WBC counts are typically diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as a complete blood count (CBC) test.
What is the treatment for high WBC counts?
+Treatment for high WBC counts depends on the underlying cause and may include antibiotics, antiviral medications, anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroids, or chemotherapy.
Can high WBC counts be prevented?
+While high WBC counts cannot be completely prevented, reducing the risk of infection and inflammation can help to minimize the risk of developing high WBC counts.
