Intro
Explore ECT medical treatment options, including electroconvulsive therapy benefits, side effects, and alternatives, to understand its role in managing mental health conditions like depression and anxiety disorders.
Electroconvulsive therapy, commonly referred to as ECT, has been a topic of interest and debate in the medical community for several decades. Despite its controversial nature, ECT remains a widely used and effective treatment option for various mental health conditions, including severe depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. The importance of understanding ECT and its applications cannot be overstated, as it has the potential to significantly improve the quality of life for individuals struggling with these conditions.
The history of ECT dates back to the 1930s, when it was first introduced as a treatment for mental illness. Over the years, the procedure has undergone significant modifications and improvements, making it a safer and more effective treatment option. Today, ECT is recognized as a valuable tool in the treatment of mental health conditions, particularly in cases where other treatments have proven ineffective. Despite its benefits, ECT remains shrouded in mystery, and many people are unaware of its potential benefits and risks.
As we delve into the world of ECT, it is essential to understand the underlying principles and mechanisms that make it an effective treatment option. ECT involves the use of electrical impulses to induce seizures in the brain, which can help to alleviate symptoms of mental health conditions. The exact mechanisms behind ECT are not fully understood, but research suggests that it can help to regulate brain chemistry, improve mood, and enhance cognitive function. With its rich history and proven effectiveness, ECT has become an essential component of modern psychiatry, offering new hope to individuals struggling with mental health conditions.
What is ECT?
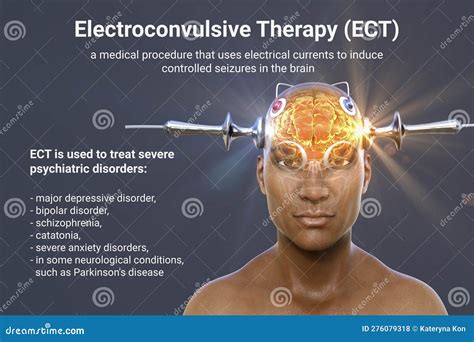
Types of ECT
There are several types of ECT, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Unilateral ECT, for example, involves the placement of electrodes on one side of the brain, typically the right side. This type of ECT is often preferred for its reduced cognitive side effects and is commonly used in patients with depression. Bilateral ECT, on the other hand, involves the placement of electrodes on both sides of the brain and is often used in patients with more severe symptoms, such as psychosis or catatonia.Benefits of ECT

ECT for Depression
ECT is commonly used to treat severe depression, particularly in cases where other treatments have proven ineffective. The procedure has been shown to be highly effective in reducing symptoms of depression, including improved mood, reduced anxiety, and enhanced cognitive function. ECT can also help to reduce the risk of suicide, which is a significant concern in individuals with severe depression.How ECT Works
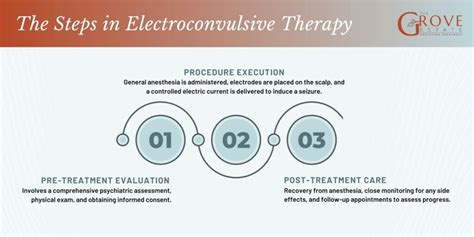
ECT Procedure
The ECT procedure typically involves the following steps: * The patient is given general anesthesia to ensure comfort and relaxation during the procedure. * The patient is closely monitored throughout the treatment, with electrodes placed on the brain to measure brain activity. * The ECT machine is used to deliver a controlled electrical impulse to the brain, inducing a seizure. * The patient is closely monitored after the procedure to ensure their safety and comfort.Risks and Side Effects of ECT

Minimizing Risks and Side Effects
To minimize the risks and side effects associated with ECT, it is essential to: * Carefully evaluate the patient's medical history and current health status. * Use the lowest effective dose of electricity. * Monitor the patient closely during and after the procedure. * Provide adequate follow-up care and support.ECT and Other Treatments
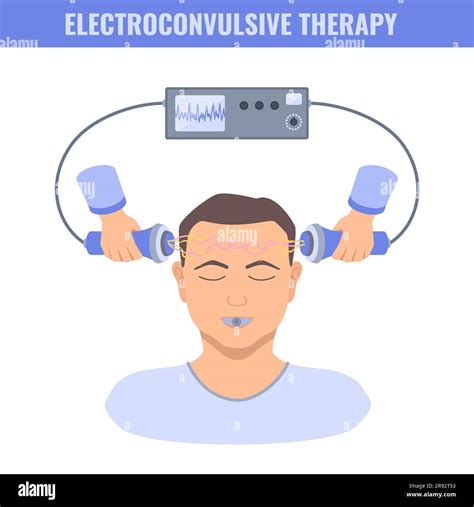
ECT and Medication
ECT can be used in conjunction with medication to treat mental health conditions. The combination of ECT and medication can help to enhance treatment outcomes, reduce symptoms, and improve quality of life. Medications commonly used in conjunction with ECT include antidepressants, mood stabilizers, and antipsychotics.Conclusion and Future Directions

Future Research Directions
Future research directions for ECT include: * Investigating the mechanisms behind ECT and its effects on brain chemistry and function. * Developing new ECT technologies and techniques to enhance treatment outcomes and reduce side effects. * Exploring the use of ECT in conjunction with other treatments, such as medication and therapy.What is ECT used to treat?
+ECT is commonly used to treat severe depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia, as well as other mental health conditions.
Is ECT safe?
+While ECT is generally considered safe, there are potential risks and side effects associated with the procedure, including memory loss, confusion, and headache.
How does ECT work?
+ECT involves the use of electrical impulses to induce seizures in the brain, which can help to regulate brain chemistry, improve mood, and enhance cognitive function.
Can ECT be used in conjunction with other treatments?
+Yes, ECT can be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as medication and therapy, to provide comprehensive care for individuals with mental health conditions.
What are the benefits of ECT?
+The benefits of ECT include rapid relief from symptoms, improved mood, reduced anxiety, and enhanced cognitive function, making it an essential component of modern psychiatry.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of ECT and its applications. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with ECT, please don't hesitate to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can work to reduce the stigma surrounding mental health conditions and promote greater understanding and acceptance of ECT as a valuable treatment option.
