Intro
Discover 5 ways to manage knee effusion, including treatment options and home remedies, to reduce swelling and alleviate knee pain, promoting joint health and mobility with effective effusion reduction techniques.
Knee effusion, also known as water on the knee, is a condition where excess fluid accumulates in the knee joint. This can cause swelling, pain, and stiffness, making it difficult to move the knee. Knee effusion can be caused by various factors, including injury, infection, or underlying medical conditions such as arthritis. Understanding the causes and treatment options for knee effusion is essential for managing the condition and preventing further complications.
Knee effusion can significantly impact a person's quality of life, making everyday activities challenging. It is crucial to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time. A healthcare professional can diagnose knee effusion through physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans. Treatment for knee effusion depends on the underlying cause and may involve drainage of the excess fluid, medication, physical therapy, or surgery in severe cases.
The knee joint is a complex structure consisting of bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. Any damage or inflammation to these components can lead to knee effusion. In some cases, knee effusion can be a recurring problem, requiring ongoing management and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for knee effusion, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and prevent further complications.
Knee Effusion Causes and Risk Factors
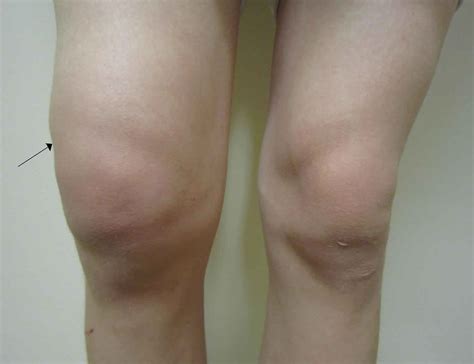
Common Causes of Knee Effusion
Some common causes of knee effusion include: * Ligament sprains * Meniscal tears * Fractures * Infection (septic arthritis) * Osteoarthritis * Rheumatoid arthritis * Gout * Overuse or traumaKnee Effusion Symptoms and Diagnosis

Diagnosing Knee Effusion
Diagnosing knee effusion involves: * Physical examination * Medical history * Imaging tests (X-rays or MRI scans) * Arthrocentesis (draining excess fluid)Treatment Options for Knee Effusion
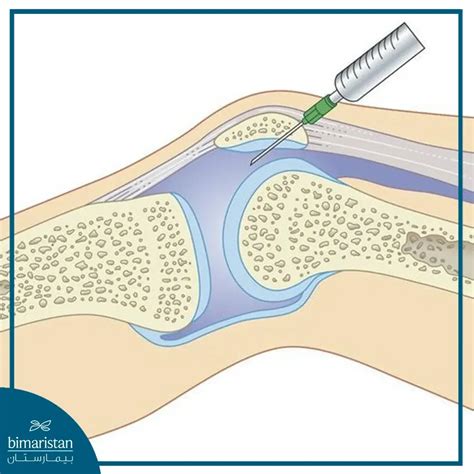
Treatment Options for Knee Effusion
Treatment options for knee effusion include: * Drainage of excess fluid * Medication (pain relief, anti-inflammatory) * Physical therapy * Surgery (in severe cases)Managing Knee Effusion with Lifestyle Changes
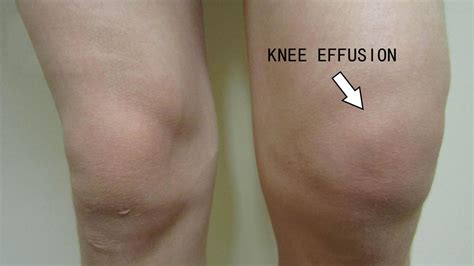
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Knee Effusion
Lifestyle changes for managing knee effusion include: * Maintaining a healthy weight * Engaging in regular exercise * Avoiding high-impact activities * Using proper techniques when lifting or bending * Taking regular breaks to rest the kneePreventing Knee Effusion
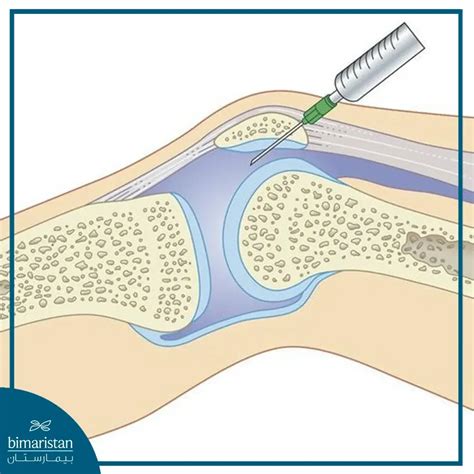
Preventing Knee Effusion
Preventing knee effusion involves: * Engaging in regular exercise * Maintaining a healthy weight * Using proper techniques when lifting or bending * Taking regular breaks to rest the knee * Using protective gear to reduce the risk of injuryKnee Effusion Complications and Prognosis
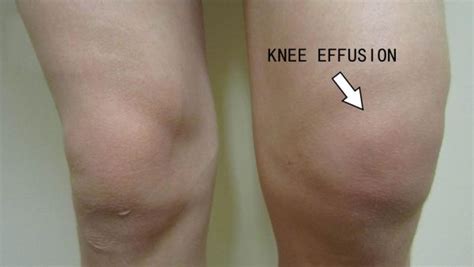
Knee Effusion Complications and Prognosis
Complications and prognosis for knee effusion include: * Chronic pain * Limited range of motion * Increased risk of infection * Permanent damage to the knee joint (in severe cases) * Surgical intervention (in severe cases)Knee Effusion and Related Conditions
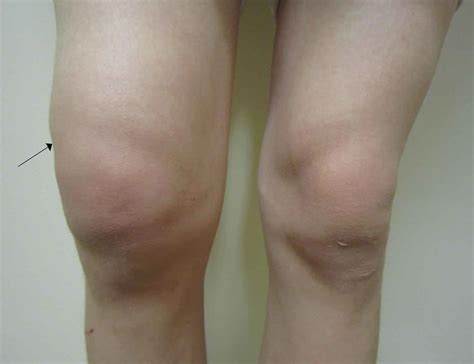
Knee Effusion and Related Conditions
Related conditions to knee effusion include: * Osteoarthritis * Rheumatoid arthritis * Gout * Other inflammatory or degenerative conditionsFuture Directions in Knee Effusion Treatment
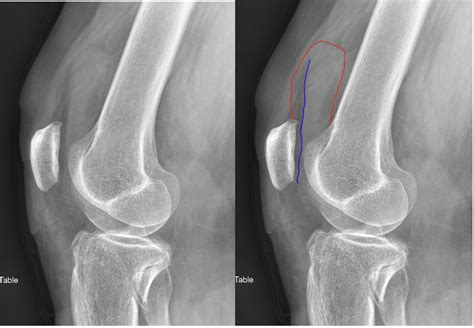
Future Directions in Knee Effusion Treatment
Future directions in knee effusion treatment include: * Stem cell therapy * Gene therapy * Other advanced technologies * Emerging treatments to reduce pain and inflammation * Improving range of motion and preventing further complicationsWhat is knee effusion?
+Knee effusion, also known as water on the knee, is a condition where excess fluid accumulates in the knee joint.
What are the symptoms of knee effusion?
+The symptoms of knee effusion can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, but common symptoms include swelling, pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion.
How is knee effusion diagnosed?
+Diagnosis of knee effusion typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans.
What are the treatment options for knee effusion?
+Treatment for knee effusion depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, but may involve drainage of the excess fluid, medication, physical therapy, or surgery in severe cases.
Can knee effusion be prevented?
+Yes, knee effusion can be prevented by taking proactive steps such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and using proper techniques when lifting or bending.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of knee effusion, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may find it helpful. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment. By working together, we can manage knee effusion and improve overall health and well-being.
