Intro
Discover the Bone Marrow Examination Process, involving biopsy, aspiration, and smear tests to diagnose blood disorders, leukemia, and lymphoma, using advanced medical techniques and laboratory analysis for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
The process of examining bone marrow is a crucial diagnostic tool for various medical conditions, including blood disorders, cancer, and infections. Bone marrow examination, also known as bone marrow biopsy or aspiration, involves the removal of a small sample of bone marrow tissue or fluid from the body for laboratory analysis. This procedure can help doctors diagnose and monitor diseases, as well as develop effective treatment plans. The importance of bone marrow examination lies in its ability to provide valuable information about the production of blood cells, the presence of abnormal cells, and the overall health of the bone marrow.
Bone marrow examination is a relatively safe and straightforward procedure, but it can be uncomfortable and may cause some anxiety for patients. However, with the help of experienced medical professionals and modern technology, the process can be made as smooth and painless as possible. In this article, we will delve into the details of the bone marrow examination process, including its benefits, working mechanisms, steps, and other key information related to the topic.
The bone marrow examination process is a complex and highly specialized procedure that requires careful planning, precise technique, and attention to detail. The process typically begins with a thorough medical evaluation, including a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. This initial evaluation helps doctors determine the need for a bone marrow examination and identify potential risks or complications. Once the decision to proceed with the examination has been made, the patient is prepared for the procedure, which may involve receiving local anesthesia, sedation, or other medications to minimize discomfort and anxiety.
Bone Marrow Examination Procedure
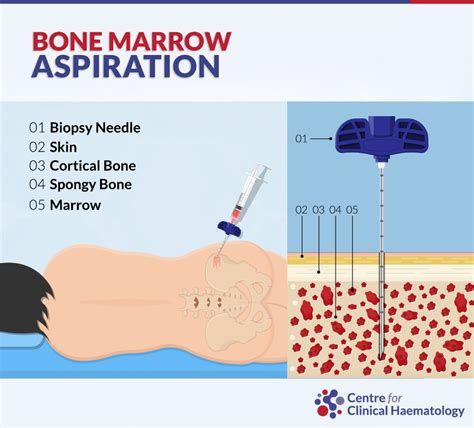
Benefits of Bone Marrow Examination
The benefits of bone marrow examination are numerous and significant. Some of the most important advantages of this procedure include: * Diagnosis of blood disorders, such as anemia, leukemia, and lymphoma * Monitoring of disease progression and response to treatment * Identification of abnormal cells, such as cancer cells or infectious agents * Evaluation of bone marrow function and production of blood cells * Development of effective treatment plans and management strategiesTypes of Bone Marrow Examination
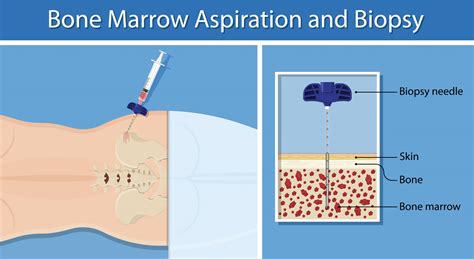
Preparation for Bone Marrow Examination
Preparation for bone marrow examination typically involves several steps, including: * Medical evaluation: A thorough medical evaluation, including a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, to determine the need for a bone marrow examination and identify potential risks or complications. * Informed consent: The patient must provide informed consent for the procedure, which involves understanding the risks, benefits, and alternatives to bone marrow examination. * Medications: The patient may be required to stop taking certain medications, such as blood thinners, before the procedure to minimize the risk of bleeding or other complications. * Sedation: The patient may be given sedation or other medications to minimize discomfort and anxiety during the procedure.Risks and Complications of Bone Marrow Examination

Aftercare and Follow-up
Aftercare and follow-up are essential components of the bone marrow examination process. Patients should follow their doctor's instructions for aftercare and follow-up, which may include: * Rest and relaxation: Patients should rest and avoid strenuous activities for several hours after the procedure. * Pain management: Patients should take medications as directed to manage pain and discomfort. * Follow-up appointments: Patients should attend follow-up appointments to monitor their condition and receive test results.Interpretation of Bone Marrow Examination Results
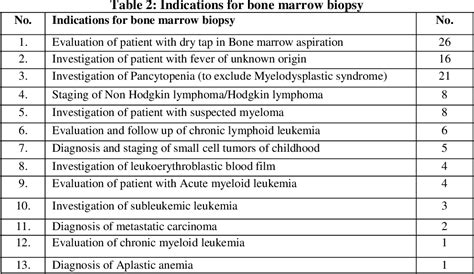
Common Applications of Bone Marrow Examination
Bone marrow examination has a range of common applications in medical practice, including: * Diagnosis of blood disorders: Bone marrow examination can help diagnose blood disorders, such as anemia, leukemia, and lymphoma. * Monitoring of disease progression: Bone marrow examination can help monitor disease progression and response to treatment. * Identification of abnormal cells: Bone marrow examination can help identify abnormal cells, such as cancer cells or infectious agents. * Evaluation of bone marrow function: Bone marrow examination can help evaluate bone marrow function and production of blood cells.Future Directions in Bone Marrow Examination
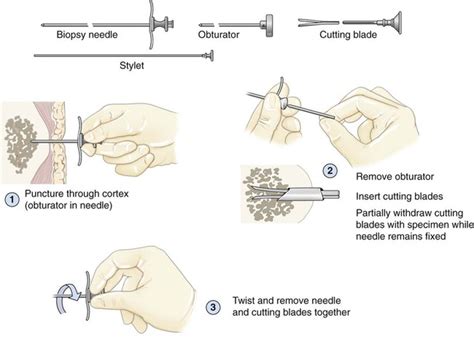
Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, bone marrow examination is a valuable diagnostic tool that can provide valuable information about the presence of abnormal cells, the production of blood cells, and the overall health of the bone marrow. While the procedure can be uncomfortable and may cause some anxiety for patients, it is a relatively safe and straightforward process that can be made as smooth and painless as possible with the help of experienced medical professionals and modern technology. We recommend that patients follow their doctor's instructions for aftercare and follow-up, and attend follow-up appointments to monitor their condition and receive test results.We invite readers to share their experiences and ask questions about bone marrow examination in the comments section below. If you have undergone a bone marrow examination, please share your story and any tips or advice you may have for others. If you have any questions or concerns about the procedure, please don't hesitate to ask.
What is bone marrow examination?
+Bone marrow examination is a diagnostic procedure that involves the removal of a small sample of bone marrow tissue or fluid from the body for laboratory analysis.
What are the benefits of bone marrow examination?
+The benefits of bone marrow examination include diagnosis of blood disorders, monitoring of disease progression, identification of abnormal cells, and evaluation of bone marrow function.
What are the risks and complications of bone marrow examination?
+The risks and complications of bone marrow examination include pain and discomfort, bleeding, infection, and nerve damage.
How is bone marrow examination performed?
+Bone marrow examination is typically performed under local anesthesia or sedation, and involves the removal of a small sample of bone marrow tissue or fluid using a needle and syringe or a special needle or drill.
What are the common applications of bone marrow examination?
+The common applications of bone marrow examination include diagnosis of blood disorders, monitoring of disease progression, identification of abnormal cells, and evaluation of bone marrow function.
