Intro
Discover the Lupus condition, a chronic autoimmune disease causing inflammation, joint pain, and fatigue. Learn about lupus symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for managing this complex condition.
The lupus condition is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, brain, and other organs. It is a complex and multifaceted disease that can be challenging to diagnose and treat. Despite its complexity, lupus is a relatively rare disease, affecting approximately 1.5 million people in the United States alone. The exact cause of lupus is still not fully understood, but research suggests that it is a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors that trigger the disease.
Lupus is often referred to as a "silent killer" because its symptoms can be subtle and nonspecific, making it difficult to diagnose. The disease can affect anyone, regardless of age, sex, or ethnicity, although it is more common in women, particularly those of African American, Hispanic, and Asian descent. Lupus can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe, including joint pain and inflammation, skin rashes, fever, fatigue, and kidney damage. If left untreated, lupus can lead to serious complications, such as kidney failure, heart disease, and increased risk of infections.
The importance of understanding lupus cannot be overstated. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing the disease and preventing long-term damage to organs and tissues. Additionally, lupus research has led to a greater understanding of the immune system and the development of new treatments for other autoimmune diseases. Furthermore, raising awareness about lupus can help reduce stigma and promote support for those affected by the disease. By learning more about lupus, we can work towards improving the quality of life for individuals with the disease and ultimately finding a cure.
What is Lupus?
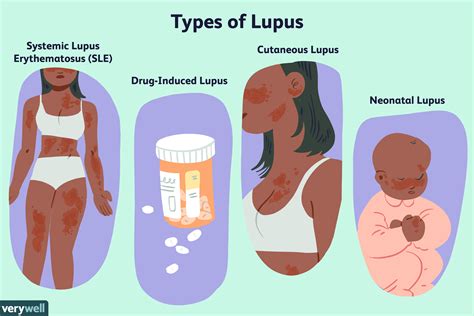
Types of Lupus
There are several types of lupus, including: * Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): This is the most common type of lupus and can affect multiple organs and tissues. * Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE): This type of lupus primarily affects the skin and can cause skin rashes and lesions. * Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE): This type of lupus is a rare form of lupus that affects the skin and can cause skin rashes and lesions. * Neonatal lupus: This is a rare form of lupus that affects newborn babies and is caused by the transfer of autoantibodies from the mother to the baby during pregnancy.Symptoms of Lupus
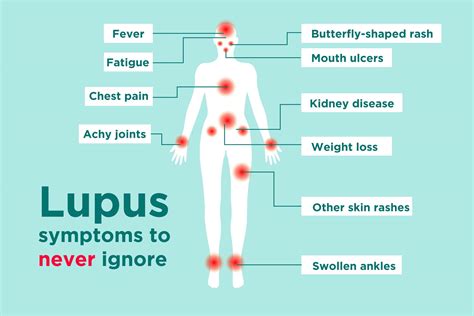
Lupus Symptoms in Women
Women with lupus may experience additional symptoms, including: * Menstrual irregularities * Miscarriage * Premature birth * Fertility problemsCauses of Lupus
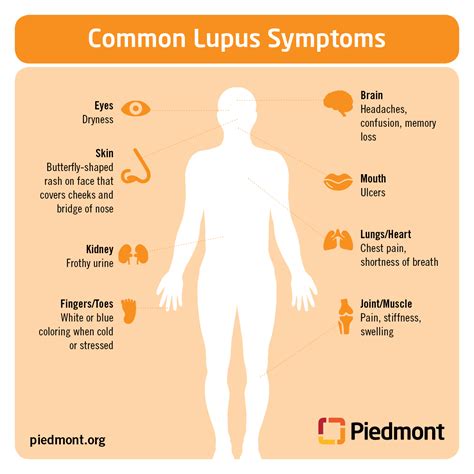
Lupus Triggers
Some common triggers of lupus include: * Ultraviolet light * Stress * Certain medications * Infections * Hormonal changesDiagnosis of Lupus

Lupus Diagnostic Criteria
The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) has established a set of diagnostic criteria for lupus, which includes: * Malar rash * Discoid rash * Photosensitivity * Oral ulcers * Arthritis * Serositis * Kidney disorder * Neurological disorder * Hematologic disorderTreatment of Lupus
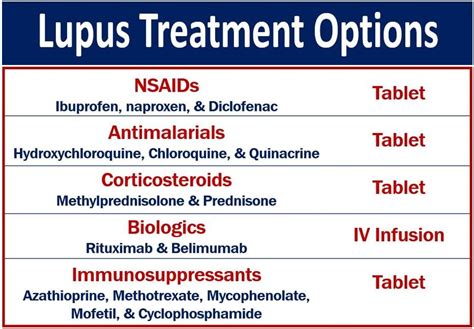
Lupus Management
In addition to medical treatment, individuals with lupus can manage their symptoms by: * Getting regular exercise * Eating a healthy diet * Getting enough sleep * Reducing stress * Avoiding triggersComplications of Lupus
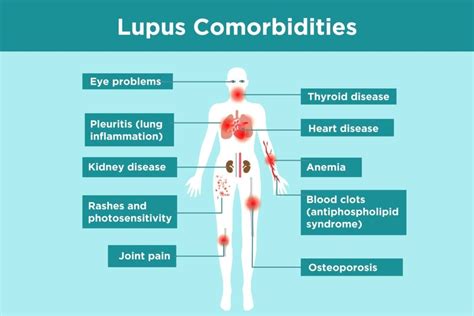
Lupus and Pregnancy
Women with lupus who become pregnant are at increased risk of complications, including: * Miscarriage * Premature birth * Fetal growth restriction * PreeclampsiaWhat is the prognosis for individuals with lupus?
+The prognosis for individuals with lupus varies depending on the severity of the disease and the organs affected. With proper treatment and management, many individuals with lupus can lead active and productive lives.
Can lupus be cured?
+Currently, there is no cure for lupus, but researchers are working towards developing new treatments and therapies to manage the disease.
How can I reduce my risk of developing lupus?
+While there is no guaranteed way to prevent lupus, reducing stress, getting regular exercise, and eating a healthy diet may help reduce the risk of developing the disease.
What are the most common symptoms of lupus?
+The most common symptoms of lupus include joint pain and inflammation, skin rashes, fever, fatigue, and kidney damage.
Can lupus affect other parts of the body besides the skin and joints?
+Yes, lupus can affect other parts of the body, including the kidneys, brain, and other organs.
In conclusion, lupus is a complex and multifaceted disease that requires early diagnosis and treatment to manage its symptoms and prevent long-term damage. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for lupus, individuals can take control of their health and work towards improving their quality of life. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may be affected by lupus, and to support ongoing research and awareness efforts to combat this disease.
