Intro
Discover what PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) means, its benefits, and how it works, including network coverage, out-of-pocket costs, and healthcare provider choices, to make informed decisions about your health insurance plan.
The importance of understanding health insurance options cannot be overstated, especially in today's complex and often confusing healthcare landscape. One type of health insurance plan that has gained popularity over the years is the Preferred Provider Organization, commonly referred to as a PPO. In this article, we will delve into the details of what a PPO is, how it works, and its benefits and drawbacks, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of this health insurance option.
For individuals and families seeking flexible and comprehensive health coverage, PPOs have become a preferred choice. Unlike other types of health insurance plans, PPOs offer a unique blend of flexibility and cost savings, making them an attractive option for those who want to balance their healthcare needs with their budget. Whether you are an individual looking for personal health insurance or an employer seeking to provide health benefits to your employees, understanding PPOs can help you make informed decisions about your health insurance needs.
The concept of PPOs revolves around a network of healthcare providers who have agreed to offer discounted services to plan members. This network can include doctors, hospitals, and other healthcare professionals who have contracted with the insurance company to provide care at negotiated rates. By choosing to receive care from within the network, individuals can significantly reduce their out-of-pocket expenses, making healthcare more affordable and accessible. However, PPOs also offer the flexibility to seek care outside of the network, albeit at a higher cost, providing members with greater control over their healthcare choices.
How PPOs Work
PPOs operate on a simple yet effective principle: by creating a network of preferred providers, insurance companies can negotiate lower rates for healthcare services, which in turn reduces the cost of care for plan members. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how PPOs work:
- Network Establishment: The insurance company establishes a network of healthcare providers who agree to offer their services at discounted rates.
- Plan Enrollment: Individuals or families enroll in the PPO plan, typically through their employer or by purchasing it directly from the insurance company.
- In-Network Care: When plan members receive care from providers within the network, they pay a lower copayment or coinsurance rate.
- Out-of-Network Care: If members choose to receive care from providers outside the network, they pay a higher copayment or coinsurance rate, and sometimes the insurance company may not cover the full cost of the care.
- Claim Submission: After receiving care, the healthcare provider submits a claim to the insurance company for reimbursement.
- Reimbursement: The insurance company reimburses the provider according to the negotiated rate and pays the member's portion of the bill, if applicable.
Benefits of PPOs

The benefits of PPOs are numerous and significant, making them a popular choice among health insurance seekers. Some of the key advantages include:
- Flexibility: PPOs offer the flexibility to choose any healthcare provider, both in-network and out-of-network, giving members greater control over their healthcare decisions.
- Cost Savings: By receiving care from in-network providers, members can save money on copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles.
- Comprehensive Coverage: PPOs typically offer comprehensive coverage, including preventive care, hospital stays, surgical procedures, and prescription medications.
- No Referrals Needed: Unlike some other types of health insurance plans, PPOs do not require members to obtain a referral from a primary care physician to see a specialist.
PPO Plan Structures
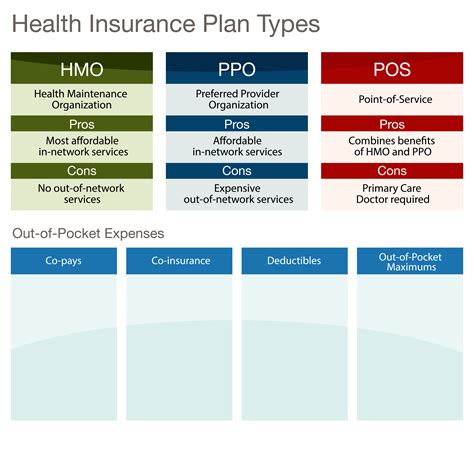
PPO plans can vary in structure, depending on the insurance company and the specific plan design. Some common features of PPO plans include:
- Deductibles: The amount members must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance company begins to pay its share of the costs.
- Copayments: A fixed amount members pay for each healthcare service, such as a doctor's visit or prescription medication.
- Coinsurance: A percentage of the healthcare costs that members pay after meeting the deductible.
- Out-of-Pocket Maximum: The maximum amount members pay for healthcare expenses in a given year, after which the insurance company pays 100% of eligible expenses.
Choosing the Right PPO Plan

With so many PPO plans available, choosing the right one can be overwhelming. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a PPO plan:
- Network: Check if your preferred healthcare providers are part of the plan's network.
- Cost: Compare the plan's premiums, deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance rates.
- Coverage: Ensure the plan covers the healthcare services you need, including prescription medications and specialist care.
- Maximum Out-of-Pocket: Consider the plan's out-of-pocket maximum to ensure it aligns with your budget.
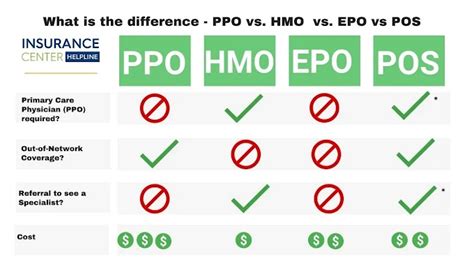
PPOs vs. Other Health Insurance Plans
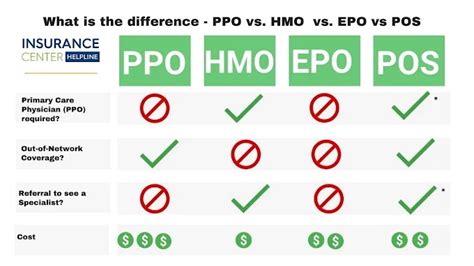
PPOs are just one type of health insurance plan, and there are other options available, including:
- HMOs (Health Maintenance Organizations): These plans require members to receive care from a specific network of providers and often require referrals to see specialists.
- EPOs (Exclusive Provider Organizations): These plans offer a network of providers, but members cannot receive care from out-of-network providers, except in emergency situations.
- HDHPs (High-Deductible Health Plans): These plans have higher deductibles and lower premiums, often paired with a Health Savings Account (HSA) to help members save for healthcare expenses.
PPOs and Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance

Many employers offer PPO plans as part of their employee benefits package. These plans can be an attractive option for employees, as they often provide comprehensive coverage and flexibility. Employers may also contribute to the plan's premiums, reducing the cost for employees.
PPOs and Individual Health Insurance
Individuals can also purchase PPO plans directly from insurance companies or through the health insurance marketplace. These plans can be more expensive than employer-sponsored plans, but they offer the same flexibility and comprehensive coverage.
PPOs and Medicare

Medicare beneficiaries can also enroll in PPO plans, known as Medicare Advantage PPOs. These plans offer additional benefits, such as dental, vision, and hearing coverage, and may have lower premiums than traditional Medicare.
What is a PPO, and how does it work?
+A PPO, or Preferred Provider Organization, is a type of health insurance plan that offers a network of healthcare providers who have agreed to offer discounted services to plan members. Members can receive care from in-network providers at a lower cost or from out-of-network providers at a higher cost.
What are the benefits of a PPO plan?
+The benefits of a PPO plan include flexibility, cost savings, comprehensive coverage, and no referrals needed to see specialists. Members can also choose to receive care from out-of-network providers, although at a higher cost.
How do I choose the right PPO plan for my needs?
+To choose the right PPO plan, consider factors such as the plan's network, cost, coverage, and maximum out-of-pocket. It's also essential to review the plan's summary of benefits and coverage to ensure it meets your healthcare needs.
In conclusion, PPOs offer a unique blend of flexibility, cost savings, and comprehensive coverage, making them a popular choice among health insurance seekers. By understanding how PPOs work, their benefits and drawbacks, and how to choose the right plan, individuals and families can make informed decisions about their health insurance needs. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with PPOs, ask questions, or seek guidance on choosing the right health insurance plan for their needs.
