Intro
Famotidine is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various gastrointestinal conditions. It is a type of histamine-2 (H2) blocker, which works by reducing the amount of stomach acid produced in the body. This decrease in stomach acid helps to alleviate symptoms such as heartburn, acid reflux, and stomach ulcers. Famotidine is commonly known by its brand name, Pepcid, and is available over-the-counter (OTC) as well as by prescription.
The importance of famotidine lies in its ability to provide quick and effective relief from gastrointestinal discomfort. Many people suffer from heartburn and acid reflux, which can be caused by a variety of factors, including eating spicy or fatty foods, lying down after eating, and having a hiatal hernia. Famotidine works by blocking the histamine receptors in the stomach, which in turn reduces the production of stomach acid. This decrease in acid production helps to heal and prevent stomach ulcers, as well as reduce the symptoms of heartburn and acid reflux.
Famotidine has been extensively studied and has been shown to be safe and effective for the treatment of various gastrointestinal conditions. It is often prescribed by doctors to patients who suffer from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, and stomach ulcers. Additionally, famotidine is also used to prevent stomach ulcers in patients who are taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which can increase the risk of stomach ulcers. With its proven track record and wide range of applications, famotidine has become a staple in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders.
Famotidine Mechanism of Action
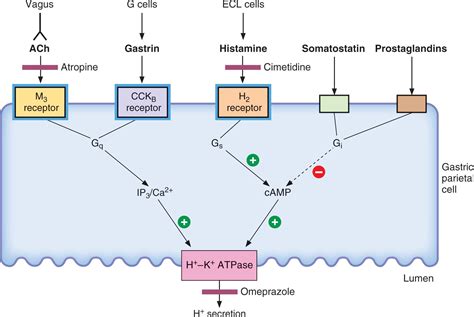
Famotidine works by blocking the histamine receptors in the stomach, which reduces the production of stomach acid. Histamine is a chemical that stimulates the stomach to produce acid, and by blocking its receptors, famotidine decreases the amount of acid produced. This decrease in acid production helps to heal and prevent stomach ulcers, as well as reduce the symptoms of heartburn and acid reflux. The mechanism of action of famotidine is as follows:
- Famotidine binds to the histamine receptors in the stomach, blocking the action of histamine.
- The binding of famotidine to the histamine receptors reduces the production of stomach acid.
- The decrease in stomach acid production helps to heal and prevent stomach ulcers, as well as reduce the symptoms of heartburn and acid reflux.
Famotidine Benefits
The benefits of famotidine are numerous and well-documented. Some of the key benefits include: * Quick and effective relief from heartburn and acid reflux symptoms * Healing and prevention of stomach ulcers * Reduction in the risk of stomach ulcers in patients taking NSAIDs * Safe and effective for long-term use * Available over-the-counter and by prescriptionFamotidine Side Effects

While famotidine is generally safe and well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects in some individuals. Some of the common side effects of famotidine include:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
Famotidine Interactions
Famotidine can interact with other medications, including: * Antacids: Famotidine can decrease the absorption of antacids, reducing their effectiveness. * Ketoconazole: Famotidine can increase the levels of ketoconazole in the body, increasing the risk of side effects. * Sucralfate: Famotidine can decrease the absorption of sucralfate, reducing its effectiveness. * Theophylline: Famotidine can increase the levels of theophylline in the body, increasing the risk of side effects.Famotidine Dosage

The dosage of famotidine varies depending on the condition being treated and the individual's response to the medication. The typical dosages of famotidine are:
- For heartburn and acid reflux: 10-20 mg twice a day
- For stomach ulcers: 20-40 mg twice a day
- For Zollinger-Ellison syndrome: 20-160 mg twice a day
Famotidine Overdose
While famotidine is generally safe, an overdose can occur if too much of the medication is taken. Symptoms of a famotidine overdose include: * Headache * Dizziness * Confusion * Abdominal pain * Nausea and vomitingFamotidine Contraindications
Famotidine is contraindicated in individuals with certain medical conditions, including:
- Hypersensitivity to famotidine or other H2 blockers
- Kidney or liver disease
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Famotidine Warnings
Famotidine can cause some warnings, including: * Increased risk of osteoporosis with long-term use * Increased risk of vitamin B12 deficiency with long-term use * Increased risk of diarrhea and abdominal pain with high dosesFamotidine Drug Interactions
Famotidine can interact with other medications, including:
- Antacids
- Ketoconazole
- Sucralfate
- Theophylline
- Warfarin
Famotidine Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of famotidine include: * Absorption: Famotidine is absorbed rapidly and completely after oral administration. * Distribution: Famotidine is distributed widely throughout the body, with high concentrations in the stomach and small intestine. * Metabolism: Famotidine is metabolized in the liver, with the majority of the dose excreted in the urine. * Elimination: Famotidine has a half-life of approximately 2.5-3.5 hours, with the majority of the dose eliminated within 24 hours.Famotidine Clinical Trials
Famotidine has been studied in numerous clinical trials, which have demonstrated its efficacy and safety in the treatment of various gastrointestinal conditions. Some of the key clinical trials include:
- A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, which demonstrated the efficacy of famotidine in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- A study published in the Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology, which demonstrated the efficacy of famotidine in the treatment of stomach ulcers.
- A study published in the American Journal of Gastroenterology, which demonstrated the safety and efficacy of famotidine in the treatment of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
Famotidine Future Directions
The future directions of famotidine include: * Development of new formulations, such as delayed-release and extended-release formulations. * Investigation of the use of famotidine in the treatment of other gastrointestinal conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease. * Study of the potential benefits of famotidine in the prevention of gastrointestinal complications, such as bleeding and perforation.What is famotidine used for?
+Famotidine is used to treat various gastrointestinal conditions, including heartburn, acid reflux, and stomach ulcers.
How does famotidine work?
+Famotidine works by blocking the histamine receptors in the stomach, reducing the production of stomach acid.
What are the common side effects of famotidine?
+The common side effects of famotidine include headache, dizziness, constipation, diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain.
In summary, famotidine is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various gastrointestinal conditions. Its mechanism of action, benefits, side effects, interactions, dosage, and contraindications have been extensively studied and documented. With its proven track record and wide range of applications, famotidine has become a staple in the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with famotidine, and to ask any questions you may have about this medication. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about famotidine and its uses.
