Intro
Learn about Fasting Glucose Test Levels, including normal ranges, blood sugar targets, and diagnostic criteria for prediabetes and diabetes, to understand your health and manage glucose levels effectively.
The importance of monitoring blood glucose levels cannot be overstated, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. One of the most common methods of checking blood glucose levels is through a fasting glucose test. This test provides valuable insights into how the body regulates blood sugar levels, helping healthcare professionals diagnose and manage diabetes. In this article, we will delve into the world of fasting glucose test levels, exploring what they mean, how they are interpreted, and their significance in maintaining good health.
Understanding blood glucose levels is crucial because they can have a significant impact on overall health. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose, thereby regulating blood sugar levels. However, for individuals with diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces, leading to elevated blood glucose levels. A fasting glucose test is a simple yet effective way to assess how well the body is managing blood sugar levels.
The fasting glucose test is typically conducted in the morning, after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours. During this time, individuals are not allowed to eat or drink anything except water. The test measures the level of glucose in the blood after this fasting period, providing a baseline reading of blood glucose levels. This test is critical for diagnosing diabetes, prediabetes, and monitoring the effectiveness of diabetes treatment plans. By understanding fasting glucose test levels, individuals can better manage their condition, make informed lifestyle choices, and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Fasting Glucose Test Levels
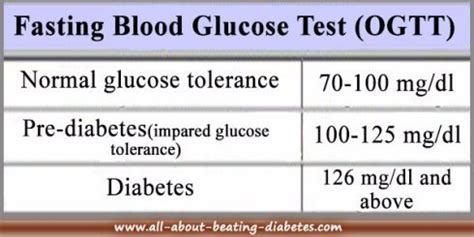
Normal Fasting Glucose Levels
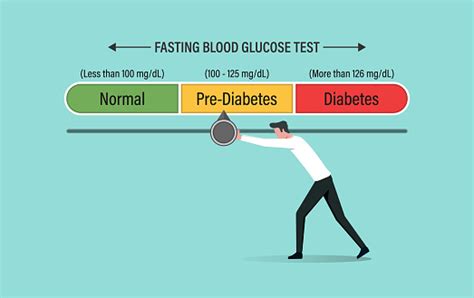
Individuals with normal fasting glucose levels have a lower risk of developing diabetes and its associated complications. Maintaining normal blood glucose levels is essential for overall health, as it reduces the risk of heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. A normal fasting glucose level is typically below 100 mg/dL. This range indicates that the body is effectively regulating blood sugar levels, and the risk of diabetes-related complications is minimal.Prediabetes and Impaired Fasting Glucose
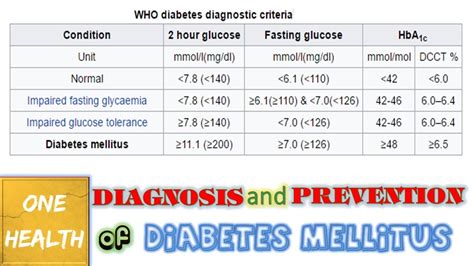
Diabetes Diagnosis
A fasting glucose level of 126 mg/dL or higher is indicative of diabetes. This diagnosis is typically confirmed through a second test on a different day, as recommended by healthcare professionals. Diabetes diagnosis marks the beginning of a management plan that includes monitoring blood glucose levels, adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and possibly using medications or insulin therapy to control blood sugar levels.Managing Fasting Glucose Levels
Lifestyle Interventions
Lifestyle interventions play a critical role in managing fasting glucose levels. Simple changes, such as increasing physical activity levels and improving dietary habits, can significantly impact blood glucose control. For example, studies have shown that regular aerobic exercise can improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Similarly, dietary patterns that emphasize whole, unprocessed foods can help regulate blood sugar levels and support overall health.The Role of Healthcare Professionals

Monitoring and Adjustments
Monitoring fasting glucose levels regularly is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of the management plan. Based on the results of fasting glucose tests, healthcare professionals may adjust medication dosages, recommend changes in diet or physical activity levels, or suggest additional tests to monitor for complications. This ongoing monitoring and adjustment process ensures that individuals with diabetes or prediabetes receive the care they need to manage their condition effectively.Conclusion and Next Steps

Final Thoughts
As we reflect on the significance of fasting glucose test levels, it is clear that they play a pivotal role in the management of diabetes and prediabetes. By staying informed, making healthy lifestyle choices, and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can effectively manage their fasting glucose levels and improve their overall health outcomes.What is the normal range for fasting glucose levels?
+Less than 100 mg/dL is considered normal.
What does a fasting glucose level between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL indicate?
+This range indicates impaired fasting glucose (IFG), also known as prediabetes.
What is the significance of monitoring fasting glucose levels for individuals with diabetes?
+Monitoring fasting glucose levels helps assess the effectiveness of the management plan and makes adjustments as necessary to prevent complications.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with managing fasting glucose levels. Your insights can help others understand the importance of this aspect of health management. Please feel free to comment below or share this article with someone who might benefit from this information. Together, we can promote better health outcomes and support those living with diabetes or prediabetes.
