Intro
Learn Flu A symptoms 2024, including fever, cough, and fatigue. Discover diagnosis, treatment, and prevention methods to manage influenza A virus infections effectively.
The flu, also known as influenza, is a highly contagious respiratory illness caused by the influenza virus. It can affect anyone, regardless of age or health status, and can lead to serious complications, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and people with certain chronic health conditions. With the ever-changing landscape of influenza viruses, it's essential to stay informed about the latest symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies. In this article, we'll delve into the world of Flu A symptoms, exploring what they are, how they manifest, and what you can do to protect yourself and your loved ones.
As we navigate the complexities of the flu season, it's crucial to understand the different types of influenza viruses and their characteristics. Influenza A viruses are one of the most common types of flu viruses and are known to cause more severe symptoms than Influenza B viruses. The symptoms of Flu A can vary from person to person, but they often include a combination of respiratory, systemic, and gastrointestinal symptoms. By recognizing the early warning signs of Flu A, you can seek medical attention promptly, reducing the risk of complications and promoting a faster recovery.
The flu season typically runs from October to May, with peak activity usually occurring between December and February. During this time, it's essential to be vigilant about your health, taking proactive steps to prevent the spread of the flu virus. This includes practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated, and avoiding close contact with people who are sick. By taking these precautions, you can significantly reduce your risk of contracting the flu and minimize the impact of Flu A symptoms on your daily life.
Understanding Flu A Symptoms
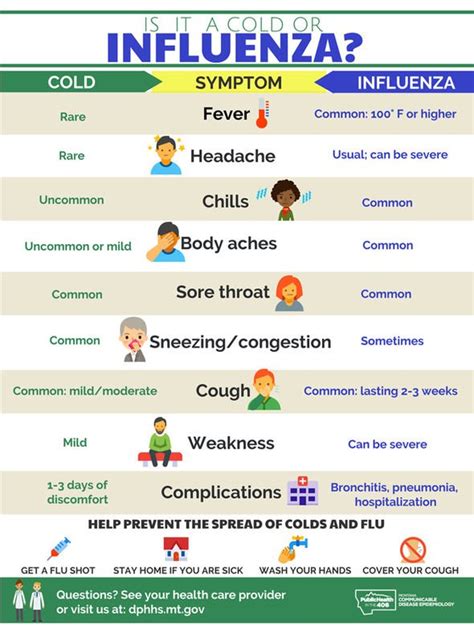
Flu A symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include a combination of the following:
- High fever, usually above 102°F (39°C)
- Chills and sweats
- Cough, often dry and hacking
- Sore throat
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Headache and fatigue
- Muscle and body aches
- Diarrhea and vomiting, especially in children
- Loss of appetite
- Chest discomfort or tightness
It's essential to note that not everyone with Flu A will exhibit all of these symptoms, and the severity of the symptoms can vary greatly from person to person. Some people may experience mild symptoms, while others may develop more severe complications, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, or sinus and ear infections.
Causes and Risk Factors
Influenza A viruses are highly contagious and can spread through:
- Airborne transmission, when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes
- Close contact with an infected person, such as touching or shaking hands
- Contaminated surfaces and objects, such as doorknobs, light switches, and countertops
Certain groups of people are at higher risk of developing severe Flu A symptoms, including:
- Older adults, especially those aged 65 and older
- Young children, especially those under the age of 5
- Pregnant women
- People with certain chronic health conditions, such as heart disease, lung disease, or diabetes
- People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect you have Flu A, it's essential to consult with your healthcare provider as soon as possible. They will perform a physical examination, take a medical history, and may conduct laboratory tests, such as a rapid influenza diagnostic test (RIDT) or a viral culture, to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment for Flu A typically involves a combination of:
- Antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu) or zanamivir (Relenza), which can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms
- Over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers, decongestants, and cough suppressants, to alleviate symptoms
- Rest and hydration to help your body recover
- Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and avoiding close contact with others, to prevent the spread of the virus
Prevention Strategies
Preventing the spread of Flu A requires a multi-faceted approach, including:
- Getting vaccinated annually, as the flu vaccine is updated to protect against the most common strains of the virus
- Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with others, and avoiding touching your eyes, nose, and mouth
- Avoiding close contact with people who are sick
- Staying home from work or school if you're experiencing flu-like symptoms
- Avoiding sharing personal items, such as utensils, drinks, or towels
- Cleaning and disinfecting surfaces and objects regularly
Complications and Long-Term Effects
In some cases, Flu A can lead to serious complications, such as:
- Pneumonia, an infection of the lungs that can be life-threatening
- Bronchitis, an inflammation of the bronchial tubes that can cause coughing and difficulty breathing
- Sinus and ear infections, which can cause pain, fever, and difficulty hearing
- Worsening of underlying chronic health conditions, such as heart disease, lung disease, or diabetes
In rare cases, Flu A can also lead to long-term effects, such as:
- Increased risk of heart attack or stroke
- Development of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Increased risk of respiratory failure
Managing Flu A Symptoms at Home

If you're experiencing mild Flu A symptoms, there are several steps you can take to manage them at home:
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids, such as water, clear broths, or electrolyte-rich beverages like sports drinks
- Rest and avoid strenuous activities to help your body recover
- Use over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers, decongestants, and cough suppressants, to alleviate symptoms
- Practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and avoiding close contact with others, to prevent the spread of the virus
- Use a humidifier to add moisture to the air, which can help relieve congestion and coughing
When to Seek Medical Attention

If you're experiencing severe Flu A symptoms or are at high risk of complications, it's essential to seek medical attention promptly. You should seek medical attention if you experience:
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Chest pain or pressure
- Severe headache or confusion
- Fever above 103°F (39.4°C)
- Vomiting or diarrhea that lasts more than 2 days
- Severe fatigue or weakness
- Worsening of underlying chronic health conditions
What are the most common symptoms of Flu A?
+The most common symptoms of Flu A include high fever, chills, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, headache, and fatigue.
How can I prevent the spread of Flu A?
+You can prevent the spread of Flu A by getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and staying home from work or school if you're experiencing flu-like symptoms.
What are the complications of Flu A?
+The complications of Flu A can include pneumonia, bronchitis, sinus and ear infections, and worsening of underlying chronic health conditions.
How can I manage Flu A symptoms at home?
+You can manage Flu A symptoms at home by staying hydrated, resting, using over-the-counter medications, practicing good hygiene, and using a humidifier to add moisture to the air.
When should I seek medical attention for Flu A?
+You should seek medical attention for Flu A if you're experiencing severe symptoms, are at high risk of complications, or have underlying chronic health conditions.
As we conclude our exploration of Flu A symptoms, it's essential to remember that prevention and early intervention are key to reducing the impact of the flu on your daily life. By staying informed, taking proactive steps to prevent the spread of the virus, and seeking medical attention when necessary, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from the risks associated with Flu A. We encourage you to share this article with others, providing them with the knowledge and tools they need to stay healthy and thrive during the flu season. Together, we can create a community that prioritizes health, wellness, and resilience in the face of illness.
