Intro
Discover foods high in purine, including seafood, meat, and vegetables, and learn how to manage purine intake for gout prevention and uric acid balance, with a list of low-purine diet options and purine-rich foods to avoid.
The importance of understanding foods high in purine cannot be overstated, particularly for individuals who suffer from gout or are at risk of developing kidney stones. Purines are naturally occurring substances found in the body and in certain foods, and when they are broken down, they form uric acid. Elevated levels of uric acid can lead to various health issues, including gout, a form of arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness in one or more joints, most often in the big toe. Managing dietary intake of purine-rich foods is a crucial aspect of preventing and managing these conditions.
For individuals who are prone to gout or kidney stones, it is essential to be aware of the foods that are high in purine. This knowledge enables them to make informed dietary choices, potentially reducing the risk of these conditions or alleviating their symptoms. Foods high in purine are not inherently bad and can be part of a healthy diet when consumed in moderation. However, for those with specific health concerns, understanding which foods to limit is vital. This awareness also underscores the importance of a balanced diet, emphasizing the variety of food choices that can help maintain overall health and well-being.
Understanding the impact of dietary purines on health involves recognizing the body's metabolic processes and how certain foods can influence uric acid levels. While the body naturally produces uric acid, consuming foods high in purine can increase uric acid production, potentially leading to hyperuricemia, a condition characterized by elevated uric acid levels in the blood. This condition is a precursor to gout and can also contribute to the formation of kidney stones. By being mindful of dietary purine intake, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health and reduce the risk of associated complications.
Foods High in Purine
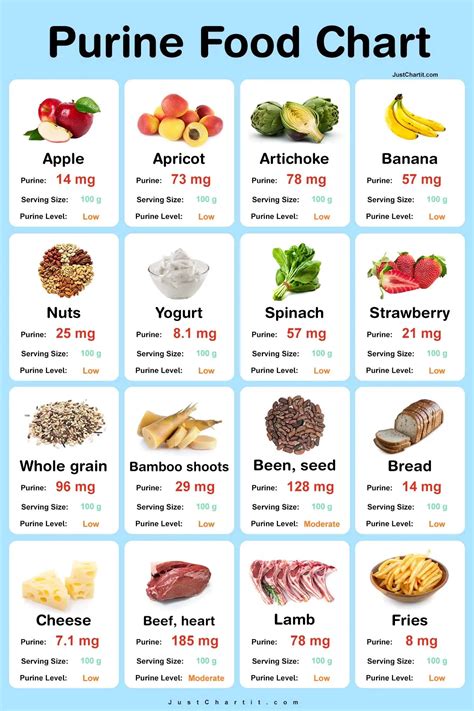
Foods high in purine are categorized into several groups, including organ meats, certain seafood, and some vegetables. Organ meats like liver, kidney, and sweetbreads are particularly high in purine. Seafood such as anchovies, sardines, mussels, and scallops also contain significant amounts of purine. Among vegetables, asparagus, mushrooms, and spinach are notable for their purine content. Understanding these categories helps individuals make informed choices about their diet, allowing them to manage their purine intake effectively.
Organ Meats and Seafood
Organ meats and certain types of seafood are among the richest sources of purine. These foods can be particularly problematic for individuals with gout or those at risk of developing kidney stones. Organ meats like liver and kidney are not only high in purine but also rich in iron and other essential nutrients, making them a double-edged sword for health-conscious individuals. Similarly, seafood like anchovies and mussels, while nutritious, are high in purine, necessitating moderation in their consumption.Dietary Management of Purine Intake
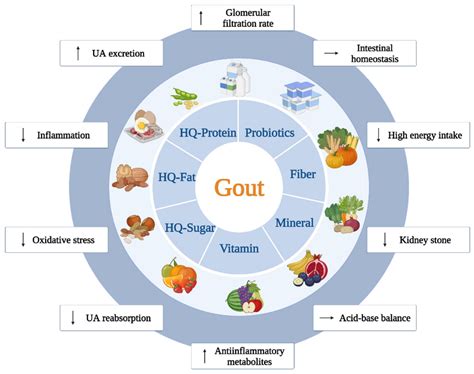
Managing dietary purine intake involves a combination of limiting foods high in purine and incorporating foods that can help reduce uric acid levels. Drinking plenty of water is essential to help the kidneys flush out uric acid. Additionally, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide necessary fiber, vitamins, and minerals while keeping purine intake in check. Foods with anti-inflammatory properties, such as berries and omega-3 rich foods, can also be beneficial in managing gout symptoms.
Low-Purine Diet
A low-purine diet is recommended for individuals with gout or kidney stones. This dietary approach focuses on reducing the intake of purine-rich foods while emphasizing foods that are low in purine. Foods that are considered low in purine include dairy products, eggs, and most fruits and vegetables, excluding those high in purine like asparagus and mushrooms. Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread, are also good choices. Understanding the principles of a low-purine diet enables individuals to make dietary adjustments that can significantly impact their health and well-being.Benefits of a Balanced Diet

A balanced diet offers numerous benefits, particularly for individuals managing purine intake. By focusing on a variety of whole, unprocessed foods, individuals can ensure they are getting the nutrients they need while minimizing their consumption of purine-rich foods. A balanced diet also supports overall health, reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Furthermore, maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet can reduce the risk of gout and other health issues associated with obesity.
Nutritional Considerations
Nutritional considerations play a crucial role in managing purine intake. Individuals need to be aware not only of the purine content in foods but also of their overall nutritional value. For example, while organ meats are high in purine, they are also rich in iron and other essential nutrients. Similarly, seafood provides important omega-3 fatty acids. By considering the nutritional benefits and drawbacks of various foods, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet, ensuring they meet their nutritional needs while managing their purine intake.Practical Tips for Managing Purine Intake

Practical tips for managing purine intake include keeping a food diary to track purine consumption, drinking plenty of water, and limiting alcohol intake, especially beer and liquor, which can raise uric acid levels. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can also help manage uric acid production. Additionally, choosing low-fat or fat-free dairy products and incorporating plant-based protein sources can be beneficial. These practical strategies can help individuals effectively manage their purine intake and reduce the risk of associated health issues.
Importance of Hydration
Hydration plays a critical role in managing purine intake and reducing the risk of gout and kidney stones. Drinking enough water helps the kidneys function properly, facilitating the removal of uric acid from the body. Individuals with gout or at risk of kidney stones should aim to drink at least eight glasses of water a day, adjusting their intake based on their activity level and climate. Staying hydrated is a simple yet effective way to support overall health and manage purine-related health issues.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, understanding and managing dietary purine intake is crucial for individuals at risk of gout, kidney stones, and other health issues associated with elevated uric acid levels. By being aware of foods high in purine, adopting a balanced diet, and staying hydrated, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health. Future directions in dietary management may include further research into the effects of specific nutrients and dietary patterns on uric acid levels and the development of personalized dietary recommendations based on genetic and metabolic profiles. As our understanding of the relationship between diet and health evolves, so too will our approaches to managing purine intake and preventing associated health issues.
Final Thoughts
In final thoughts, the management of dietary purine intake is a multifaceted approach that involves awareness, moderation, and a commitment to overall health and wellness. By embracing a balanced diet, staying informed about the purine content of foods, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can effectively manage their purine intake and reduce the risk of associated health complications. This proactive approach to health not only benefits those with specific dietary concerns but also promotes overall well-being, underscoring the importance of informed dietary choices in maintaining health and preventing disease.What are the primary sources of purine in the diet?
+The primary sources of purine in the diet include organ meats like liver and kidney, certain seafood such as anchovies and mussels, and some vegetables like asparagus and mushrooms.
How can I manage my purine intake to prevent gout attacks?
+To manage your purine intake and prevent gout attacks, focus on a balanced diet that limits foods high in purine, stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, and consider consulting with a healthcare provider or dietitian for personalized dietary advice.
Are there any specific foods that can help reduce uric acid levels?
+Yes, foods with anti-inflammatory properties, such as berries and omega-3 rich foods, can help reduce uric acid levels and alleviate gout symptoms. Additionally, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential fiber, vitamins, and minerals that support overall health and help manage uric acid production.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with managing purine intake and its impact on your health. Your insights can help others who are navigating similar dietary challenges. Please feel free to comment below, and consider sharing this article with anyone who might benefit from this information. Together, we can promote healthier dietary habits and support each other in our journeys towards wellness.
