Intro
Discover 5 crucial TB skin test facts, including its purpose, procedure, and interpretation, to understand Tuberculosis diagnosis and treatment, featuring related terms like Mantoux test, PPD test, and Tuberculin skin test.
The TB skin test, also known as the Mantoux test, is a widely used method for detecting tuberculosis (TB) infection. It's a crucial tool in the fight against this infectious disease, which affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding how the TB skin test works, its benefits, and its limitations is essential for individuals, healthcare professionals, and public health organizations. In this article, we'll delve into the world of TB skin testing, exploring its importance, mechanisms, and practical applications.
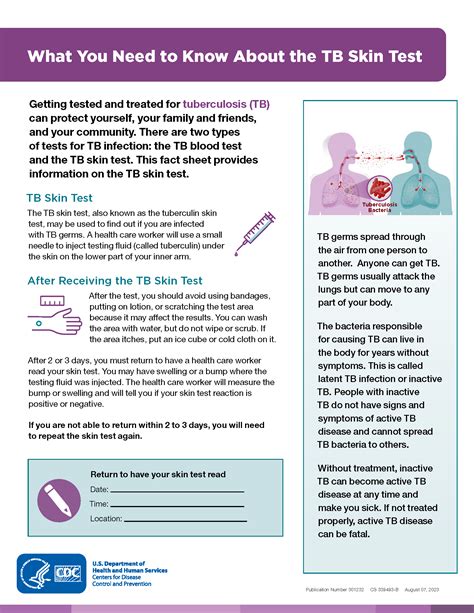
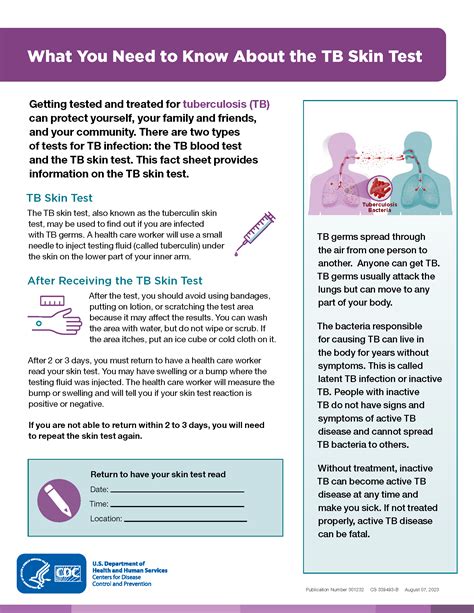
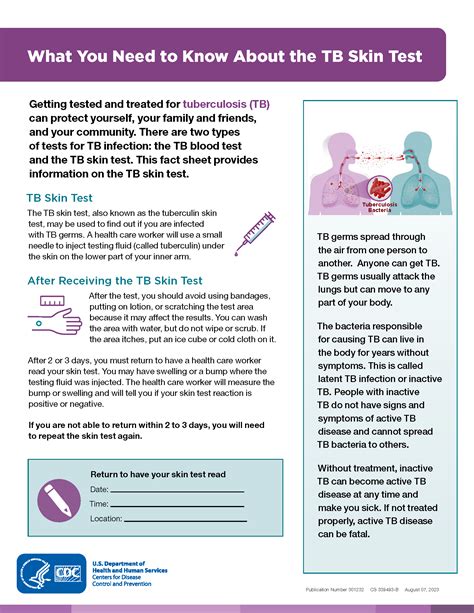
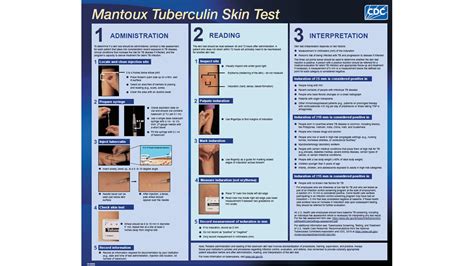
Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which primarily affects the lungs but can also spread to other parts of the body. The TB skin test is a simple, yet effective way to determine if someone has been infected with TB. The test involves injecting a small amount of purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin into the skin, usually on the forearm. After 48-72 hours, the skin is examined for a reaction, which can indicate the presence of TB infection.
The TB skin test has been a cornerstone of tuberculosis diagnosis for decades, and its significance extends beyond individual diagnosis. It plays a critical role in public health efforts to control and prevent the spread of TB. By identifying individuals with latent TB infection, healthcare providers can offer treatment to prevent the development of active TB disease. This not only improves individual health outcomes but also helps to reduce the transmission of TB in communities.
What is the TB Skin Test?
How Does the TB Skin Test Work?
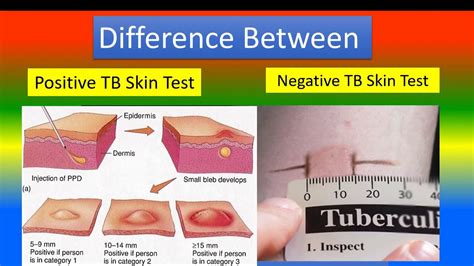
The TB skin test works by exploiting the body's immune response to TB infection. When an individual is infected with TB, their immune system recognizes the bacteria and mounts a response to fight the infection. The PPD tuberculin used in the skin test contains proteins from the TB bacteria, which stimulates this immune response. In individuals with TB infection, the immune system recognizes the PPD tuberculin and responds by causing inflammation at the injection site. This inflammation leads to the formation of induration, which is measured to determine the test result.Benefits of the TB Skin Test

Limitations of the TB Skin Test
While the TB skin test is a valuable tool, it also has some limitations. Some of the key limitations include: * False negatives: The TB skin test can produce false negative results in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or taking immunosuppressive medications. * False positives: The TB skin test can also produce false positive results in individuals who have been vaccinated with the BCG vaccine or have been exposed to non-tuberculous mycobacteria. * Variable interpretation: The interpretation of TB skin test results can vary depending on the individual's risk factors and the criteria used to define a positive result.Who Should Get a TB Skin Test?
How to Prepare for a TB Skin Test
Preparing for a TB skin test is relatively straightforward. Individuals should: * Avoid taking medications that may suppress the immune system, such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressive medications. * Inform their healthcare provider about any medical conditions or allergies they may have. * Wear loose-fitting clothing to allow easy access to the injection site. * Plan to return to the healthcare provider 48-72 hours after the test to have the results read.Interpreting TB Skin Test Results
What to Do After a Positive TB Skin Test
A positive TB skin test result indicates that an individual has been infected with TB. The next steps typically involve: * Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray is performed to determine if the individual has active TB disease. * Sputum tests: Sputum tests are performed to detect the presence of TB bacteria in the lungs. * Treatment: If the individual has active TB disease, treatment is initiated to cure the infection. If the individual has latent TB infection, treatment may be offered to prevent the development of active TB disease.TB Skin Test vs. Blood Tests
Advantages of Blood Tests
Blood tests have several advantages over the TB skin test, including: * Faster results: Blood tests can provide results in a matter of hours, whereas the TB skin test requires 48-72 hours to produce results. * Less invasive: Blood tests are less invasive than the TB skin test, as they do not require an injection. * More accurate: Blood tests may be more accurate than the TB skin test, as they are less subject to variability in interpretation.Common Misconceptions About the TB Skin Test
Debunking Myths About the TB Skin Test
It's essential to debunk myths and misconceptions about the TB skin test to ensure that individuals understand the importance of testing and the benefits of early detection. Some of the myths that need to be debunked include: * The TB skin test is only for individuals with active TB disease: The TB skin test is recommended for individuals with latent TB infection, as well as those with active TB disease. * The TB skin test is a vaccine: The TB skin test is not a vaccine and does not provide immunity against TB infection.What is the TB skin test used for?
+The TB skin test is used to detect infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacteria that causes tuberculosis (TB).
How is the TB skin test performed?
+The TB skin test involves injecting a small amount of purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin into the skin, usually on the forearm. The skin is then examined for a reaction 48-72 hours later.
What are the benefits of the TB skin test?
+The TB skin test is a simple, inexpensive, and widely available method for detecting TB infection. It is also highly sensitive and can detect TB infection in most individuals who have been exposed to the bacteria.
What are the limitations of the TB skin test?
+The TB skin test can produce false negative or false positive results, and its interpretation can vary depending on individual circumstances. It is also not suitable for individuals with weakened immune systems or those who have been vaccinated with the BCG vaccine.
Who should get a TB skin test?
+Individuals who are at high risk of TB infection, such as healthcare workers, individuals with HIV/AIDS, and close contacts of individuals with active TB disease, should get a TB skin test.
In conclusion, the TB skin test is a valuable tool in the diagnosis and management of tuberculosis. While it has its limitations, it remains a widely used and effective method for detecting TB infection. By understanding the importance of the TB skin test and its benefits, individuals can take an active role in protecting their health and preventing the spread of TB. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with the TB skin test and to ask questions about this important topic. Together, we can work towards a future where TB is no longer a major public health threat.
