Intro
Discover Zithromax uses and benefits, an antibiotic treating bacterial infections, with advantages including fast recovery, broad-spectrum efficacy, and convenience, for conditions like pneumonia, sinusitis, and bronchitis.
The world of antibiotics is vast and complex, with various medications designed to combat different types of bacterial infections. Among these, Zithromax has emerged as a widely prescribed and effective antibiotic. Its broad spectrum of activity and favorable pharmacokinetic profile make it an attractive option for treating a range of infections. Understanding the uses and benefits of Zithromax is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients, as it can significantly impact the management and outcome of bacterial infections.
Zithromax, also known by its generic name azithromycin, belongs to the macrolide class of antibiotics. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, which ultimately leads to the death of the bacterial cells. This antibiotic is particularly useful because it can be effective against a wide variety of bacterial infections, including those affecting the respiratory tract, skin, and soft tissues, among others. Moreover, its once-daily dosing regimen and relatively mild side effect profile contribute to its popularity and patient compliance.
The versatility of Zithromax is evident in its application across various medical specialties. From treating common infections like strep throat and pneumonia to more complex conditions such as Lyme disease and certain sexually transmitted infections, Zithromax has proven its efficacy. Its use extends beyond these examples, highlighting the importance of understanding its full range of applications to maximize its therapeutic potential. As with any antibiotic, the appropriate use of Zithromax is crucial to prevent resistance and ensure its continued effectiveness in treating bacterial infections.
Zithromax Mechanism of Action
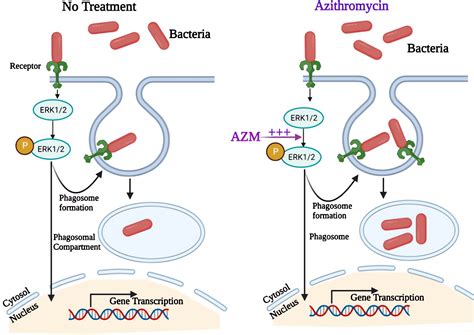
The mechanism of action of Zithromax involves binding to the bacterial ribosome, which is essential for protein synthesis. By inhibiting this process, Zithromax prevents the bacteria from producing vital proteins, leading to the cessation of bacterial growth and ultimately to the death of the bacterial cells. This action is bacteriostatic at lower concentrations and bactericidal at higher concentrations. Understanding how Zithromax works at a molecular level can provide insights into its effectiveness against various bacterial infections and its potential limitations.
Benefits of Using Zithromax

The benefits of using Zithromax are multifaceted. Its broad-spectrum activity allows it to be effective against a wide range of bacterial infections. Additionally, its pharmacokinetic properties, including high tissue penetration and a long half-life, enable once-daily dosing, which enhances patient compliance. Zithromax is also generally well-tolerated, with a mild side effect profile compared to other antibiotics. These benefits make Zithromax a preferred choice for many healthcare providers when treating bacterial infections.
Advantages in Specific Infections
Zithromax has shown particular advantages in treating certain types of infections. For respiratory tract infections, such as pneumonia and bronchitis, Zithromax's ability to penetrate into lung tissue effectively makes it a valuable option. Similarly, in the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections, its high concentration in these tissues contributes to its efficacy. The use of Zithromax in pediatric patients is also notable, given its safety profile and the convenience of its dosing regimen.Zithromax Side Effects and Precautions

While Zithromax is generally well-tolerated, it is not without side effects. Common adverse effects include gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain. Allergic reactions, although rare, can occur and range from mild to severe. It is also important to consider potential drug interactions, as Zithromax can interact with other medications, affecting their efficacy or increasing the risk of side effects. Precautions should be taken in patients with certain medical conditions, such as liver or kidney disease, and in pregnant or breastfeeding women, as the safety of Zithromax in these populations may be a concern.
Resistance and Stewardship
The issue of antibiotic resistance is a global health concern, and the use of Zithromax is not immune to this issue. The overuse or misuse of antibiotics, including Zithromax, can lead to the development of resistant bacterial strains, reducing the effectiveness of these drugs. Therefore, antibiotic stewardship is crucial, involving the appropriate selection of antibiotics, dosing, and duration of treatment to minimize the risk of resistance while effectively treating infections.Zithromax Dosage and Administration

The dosage and administration of Zithromax can vary depending on the type and severity of the infection being treated, as well as the patient's age and weight. For most infections, Zithromax is administered orally, once daily, for a period ranging from 3 to 5 days, although this can extend up to 12 days for certain conditions. It is essential to follow the prescribed dosing regimen to ensure the effective treatment of the infection and to minimize the risk of side effects.
Special Considerations
In certain patient populations, such as the elderly or those with renal or hepatic impairment, dose adjustments may be necessary to avoid accumulation of the drug and potential toxicity. Additionally, in pediatric patients, the dose is often calculated based on body weight to ensure appropriate drug exposure. These considerations highlight the importance of individualizing treatment with Zithromax to optimize its benefits and minimize risks.Zithromax Interactions and Contraindications
Zithromax can interact with various medications, either by enhancing their effects or increasing the risk of side effects. For example, it can interact with warfarin, increasing the risk of bleeding, and with certain antacids, which can reduce its absorption. Contraindications to the use of Zithromax include known hypersensitivity to azithromycin or other macrolide antibiotics. Caution is also advised in patients with certain heart conditions, as Zithromax can prolong the QT interval, potentially leading to serious cardiac arrhythmias.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
During treatment with Zithromax, patients should be monitored for signs of infection improvement or worsening, as well as for potential side effects. Follow-up appointments may be necessary to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and to adjust the regimen as needed. This monitoring is particularly important in patients with underlying health conditions or those taking multiple medications.Zithromax in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding

The use of Zithromax during pregnancy and breastfeeding requires careful consideration. While animal studies have not shown evidence of harm to the fetus, there are limited data on its use in pregnant women. As a result, Zithromax should only be used during pregnancy if clearly needed. In breastfeeding women, Zithromax is excreted into breast milk, but the amounts are generally considered to be low and not expected to cause significant effects in the infant. However, caution is advised, and the decision to use Zithromax should be made after weighing the potential benefits against the potential risks.
Pediatric and Geriatric Use
In pediatric patients, Zithromax is used to treat various bacterial infections, with dosing based on weight. The safety and efficacy of Zithromax in children have been established, making it a valuable treatment option in this population. In geriatric patients, Zithromax can be used with caution, taking into account the potential for decreased renal or hepatic function, which may require dose adjustments.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, Zithromax is a valuable antibiotic with a broad spectrum of activity and a favorable pharmacokinetic profile, making it suitable for treating a wide range of bacterial infections. Its benefits, including once-daily dosing and a mild side effect profile, contribute to its popularity. However, the potential for resistance and the importance of antibiotic stewardship must be considered to ensure the continued effectiveness of Zithromax. Future directions may involve the development of new macrolide antibiotics with improved properties or the investigation of Zithromax in combination with other antibiotics to combat resistant infections.
As we move forward, it is essential to continue monitoring the efficacy and safety of Zithromax, as well as its potential interactions and contraindications. By doing so, we can maximize the benefits of this antibiotic while minimizing its risks, ultimately improving patient outcomes in the treatment of bacterial infections.
What is Zithromax used for?
+Zithromax is used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and certain sexually transmitted infections.
How does Zithromax work?
+Zithromax works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, which ultimately leads to the death of the bacterial cells.
What are the common side effects of Zithromax?
+Common side effects of Zithromax include gastrointestinal disturbances such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal pain, as well as allergic reactions.
Can Zithromax be used in pregnant or breastfeeding women?
+Zithromax should only be used during pregnancy if clearly needed, and with caution in breastfeeding women, as it is excreted into breast milk.
How can antibiotic resistance be prevented when using Zithromax?
+Antibiotic resistance can be prevented by using Zithromax appropriately, following the prescribed dosing regimen, and avoiding unnecessary use of antibiotics.
We hope this comprehensive overview of Zithromax has provided you with valuable insights into its uses, benefits, and considerations. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with Zithromax, please feel free to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, we encourage you to share it with others who may benefit from this information. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us create more informative and helpful content in the future.
