Intro
Master glucose testing with 5 expert tips, including monitoring blood sugar levels, choosing the right glucose meter, and understanding test strips, to effectively manage diabetes and maintain healthy glucose control.
Monitoring blood glucose levels is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes and maintaining overall health. For individuals with diabetes, regular glucose testing is essential to ensure that their blood sugar levels remain within a healthy range. This not only helps in preventing complications associated with diabetes but also allows for timely adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication. The importance of accurate glucose testing cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts the effectiveness of diabetes management plans. Understanding how to properly conduct a glucose test and interpret its results is vital for both individuals with diabetes and healthcare providers. Moreover, advancements in glucose testing technologies have made the process more convenient and less invasive, encouraging more frequent monitoring and better health outcomes.
The process of glucose testing has evolved significantly over the years, from traditional methods that required a visit to a healthcare facility to the modern, portable glucose meters that allow for testing at home or on the go. This evolution has empowered individuals with diabetes to take a more proactive role in their health management. However, with the variety of glucose testing options available, it can be challenging to determine the best approach. Factors such as accuracy, ease of use, and cost must be considered. Furthermore, understanding the different types of glucose tests, including fasting glucose tests, postprandial tests, and continuous glucose monitoring, is essential for comprehensive diabetes care.
For those new to glucose testing, the array of available devices and testing strips can be overwhelming. It's crucial to select a glucose meter that meets individual needs, considering factors such as test strip cost, meter size, and additional features like data storage and Bluetooth connectivity for seamless tracking and sharing of results with healthcare providers. Moreover, proper technique in obtaining a blood sample and correctly using the glucose meter is key to obtaining accurate results. This includes preparing the skin properly before pricking, using the correct amount of blood, and ensuring the test strip is properly inserted into the meter. By mastering these skills and staying informed about the latest in glucose testing technology, individuals can better manage their diabetes and improve their quality of life.
Understanding Glucose Testing
Understanding the basics of glucose testing is the first step towards effective diabetes management. Glucose tests measure the amount of glucose in the blood, which is essential for assessing how well the body is managing blood sugar levels. This information is critical for making informed decisions about diet, physical activity, and medication. There are several types of glucose tests, each serving a different purpose. The fasting plasma glucose test, for example, measures blood glucose after an overnight fast and is commonly used for diagnosing diabetes and prediabetes. The oral glucose tolerance test, on the other hand, involves drinking a sugary drink and then measuring blood glucose levels over time, providing insights into how the body regulates blood sugar after consuming glucose.
Types of Glucose Tests
The variety of glucose tests available allows healthcare providers to tailor diabetes management plans to individual patient needs. Continuous glucose monitoring systems, for instance, provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day, offering detailed insights into glucose levels and trends. This information can be particularly useful for identifying patterns and making adjustments to treatment plans. Additionally, understanding the normal ranges for blood glucose levels and how they vary throughout the day is essential for interpreting test results accurately.Preparing for a Glucose Test

Preparation is key to ensuring accurate and reliable glucose test results. For fasting glucose tests, this typically involves abstaining from food and drink (except water) for at least 8 hours before the test. It's also important to avoid strenuous exercise and smoking, as these can affect blood glucose levels. Understanding the specific requirements for each type of glucose test, including the timing of meals and physical activity, helps in obtaining accurate results. Moreover, being well-hydrated and avoiding caffeine and alcohol before a glucose test can help ensure that results reflect typical blood glucose levels.
Importance of Accurate Results
Accurate glucose test results are foundational to effective diabetes management. They provide the data needed to adjust medication, diet, and exercise regimens, helping to maintain blood glucose levels within a target range. This, in turn, reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. By ensuring that glucose testing is conducted correctly and regularly, individuals with diabetes can better control their condition and improve their overall health and well-being.Interpreting Glucose Test Results
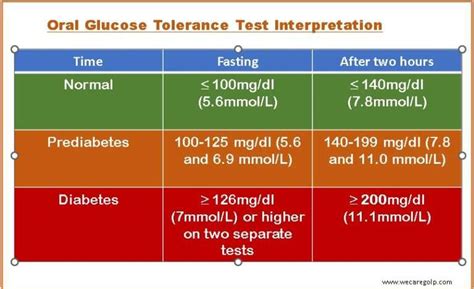
Interpreting glucose test results requires understanding the target ranges for blood glucose levels. For individuals with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends a fasting plasma glucose level of less than 130 mg/dl and a postprandial (after meal) glucose level of less than 180 mg/dl. Results that fall outside these ranges may indicate the need for adjustments to the diabetes management plan. It's also important to consider trends in glucose levels over time, as these can provide insights into the effectiveness of current treatments and the need for potential changes.
Using Results to Adjust Treatment Plans
Glucose test results are a powerful tool for managing diabetes. By analyzing these results, individuals and their healthcare providers can identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication. For example, if postprandial glucose levels are consistently high, adjustments might include changing the timing or dosage of medications, altering meal plans to reduce carbohydrate intake, or increasing physical activity after meals. Regular review and adjustment of the diabetes management plan, based on glucose test results, are crucial for maintaining good glycemic control and preventing long-term complications.Advancements in Glucose Testing Technology

The field of glucose testing has seen significant advancements in recent years, with a focus on making testing more convenient, less invasive, and more accurate. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), for example, use a small sensor inserted under the skin to track glucose levels throughout the day, providing real-time data and trends. Flash glucose monitoring systems offer another option, using a small sensor worn on the back of the upper arm to measure glucose levels. These technologies have revolutionized diabetes management, enabling individuals to make more informed decisions about their health and reducing the burden of frequent fingerstick tests.
Impact on Diabetes Management
The impact of advancements in glucose testing technology on diabetes management cannot be overstated. These innovations have empowered individuals with diabetes to take a more active role in their health care, enabling them to monitor their glucose levels more frequently and make timely adjustments to their treatment plans. Moreover, the detailed insights provided by these technologies have allowed healthcare providers to tailor diabetes management plans more precisely to individual needs, leading to better health outcomes. As technology continues to evolve, it's likely that glucose testing will become even more integrated into daily life, further improving the management of diabetes.Best Practices for Glucose Testing
Adhering to best practices for glucose testing is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of test results. This includes following the manufacturer's instructions for the glucose meter and test strips, properly preparing the skin before obtaining a blood sample, and correctly coding the meter if using test strips with lot-specific codes. Regular calibration of the glucose meter, as recommended by the manufacturer, is also important. Furthermore, maintaining good hygiene practices, such as washing hands before testing and using a new lancet for each test, helps prevent infection and ensures accurate results.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Despite the importance of glucose testing, there are common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate results or unnecessary complications. These include not following the proper technique for obtaining a blood sample, failing to code the meter correctly when using lot-specific test strips, and not storing test strips and the glucose meter according to the manufacturer's instructions. Being aware of these potential pitfalls and taking steps to avoid them can significantly improve the effectiveness of glucose testing and overall diabetes management.Future of Glucose Testing

The future of glucose testing holds much promise, with ongoing research and development focused on making testing more convenient, accurate, and non-invasive. Emerging technologies, such as non-invasive glucose monitors that use optical or electrical signals to measure glucose levels, are being explored. These advancements have the potential to revolutionize diabetes management, reducing the burden of frequent blood glucose monitoring and improving health outcomes. Additionally, the integration of glucose testing with other health monitoring technologies, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, could further enhance the management of diabetes and other health conditions.
Implications for Diabetes Care
The implications of future advancements in glucose testing for diabetes care are profound. More accurate and convenient glucose monitoring could lead to better glycemic control, reduced risk of complications, and improved quality of life for individuals with diabetes. Moreover, these technologies could facilitate more personalized diabetes management, allowing for real-time adjustments to treatment plans based on individual responses to diet, exercise, and medication. As the field continues to evolve, it's essential for healthcare providers, individuals with diabetes, and technology developers to work together to ensure that these innovations are accessible, affordable, and integrated into comprehensive diabetes care plans.In conclusion, glucose testing is a critical component of diabetes management, offering valuable insights into blood glucose levels and trends. By understanding the importance of glucose testing, the different types of tests available, and how to properly conduct and interpret these tests, individuals with diabetes can better manage their condition. As technology continues to advance, it's likely that glucose testing will become even more integral to daily life, enabling more precise and personalized diabetes care. Whether through traditional glucose meters or the latest in continuous glucose monitoring systems, the goal remains the same: to empower individuals with diabetes to take control of their health and live full, active lives.
What is the importance of glucose testing in diabetes management?
+Glucose testing is crucial for managing diabetes as it provides the data needed to adjust medication, diet, and exercise regimens, helping to maintain blood glucose levels within a target range and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
How often should I conduct glucose tests?
+The frequency of glucose testing depends on the type of diabetes, the treatment plan, and the individual's health status. Generally, individuals with type 1 diabetes or those using insulin may need to test more frequently than those with type 2 diabetes managed through diet and oral medications.
What are the different types of glucose tests available?
+There are several types of glucose tests, including fasting plasma glucose tests, oral glucose tolerance tests, random plasma glucose tests, and continuous glucose monitoring. Each type of test serves a different purpose and is used in various scenarios for diagnosing and managing diabetes.
As you explore the world of glucose testing and diabetes management, remember that knowledge is power. By staying informed about the latest technologies, best practices, and research findings, you can take a more active role in your health care and work towards achieving better glycemic control and a higher quality of life. Whether you're just starting your journey with diabetes or have been managing the condition for years, there's always more to learn and discover. Share your experiences, ask questions, and seek out resources to continue educating yourself about glucose testing and diabetes care. Together, we can work towards a future where diabetes is more manageable, and health outcomes are improved for all.
