Intro
Discover 5 ways to elevate blood glucose levels naturally, managing diabetes with balanced diets, exercise, and stress reduction, using glucose monitors and healthy lifestyle habits.
Managing blood glucose levels is crucial for maintaining overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Elevated blood glucose can lead to a variety of complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Therefore, understanding how to manage and regulate blood glucose levels is essential for preventing these complications and promoting overall well-being.
Effective management of blood glucose involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, medication. Lifestyle changes can significantly impact blood glucose levels, and simple adjustments to diet, exercise, and daily habits can make a substantial difference. For individuals looking to elevate their blood glucose levels in a healthy and sustainable manner, there are several strategies that can be employed.
It's also important to note that the goal is not to excessively elevate blood glucose but to maintain it within a healthy range. Both high and low blood glucose levels can be detrimental to health. Thus, any approach to managing blood glucose should aim at achieving a balance that supports overall health and reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Understanding Blood Glucose Regulation
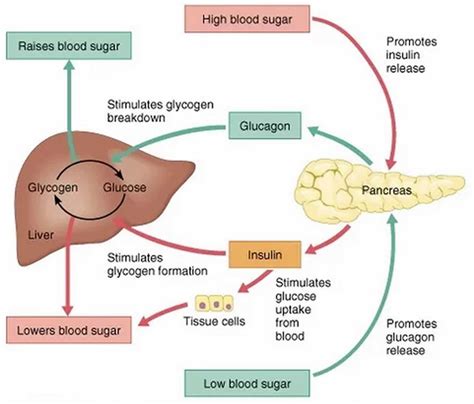
Blood glucose regulation is a complex process involving the pancreas, liver, and various hormones. The pancreas produces insulin and glucagon, hormones that play key roles in lowering and raising blood glucose levels, respectively. After a meal, the body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream, causing blood glucose levels to rise. In response, the pancreas releases insulin, facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells throughout the body, thereby lowering blood glucose levels. Conversely, when blood glucose levels drop, such as between meals or during fasting, the pancreas releases glucagon, which stimulates the liver to release stored glucose (glycogen) into the bloodstream, elevating blood glucose levels.
Importance of Balanced Blood Glucose Levels
Maintaining balanced blood glucose levels is vital for energy production, cellular function, and overall health. Imbalances, whether too high or too low, can lead to immediate and long-term health issues. High blood glucose levels over time can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, and neuropathy. On the other hand, low blood glucose (hypoglycemia) can cause immediate symptoms like shakiness, dizziness, and confusion, and if severe, can lead to loss of consciousness or even death.Dietary Interventions for Managing Blood Glucose
Diet plays a critical role in managing blood glucose levels. Certain foods can help regulate blood glucose, while others can cause spikes. Foods with a low glycemic index (GI) are digested more slowly, causing a gradual rise in blood glucose levels. These include whole grains, non-starchy vegetables, and most fruits. On the other hand, foods with a high GI, such as white bread, sugary snacks, and refined grains, cause a rapid increase in blood glucose levels.
Some key dietary interventions for managing blood glucose include:
- Increasing Fiber Intake: Fiber, particularly soluble fiber found in foods like oats, barley, and fruits, can slow the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream.
- Choosing Whole Grains: Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole-wheat bread provide sustained energy and fiber.
- Incorporating Protein and Healthy Fats: Protein and healthy fats, found in foods like lean meats, fish, avocados, and nuts, can help regulate the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, thereby affecting blood glucose levels.
Physical Activity and Blood Glucose Management
Regular physical activity is another crucial component of blood glucose management. Exercise increases the body's sensitivity to insulin, allowing glucose to enter cells more efficiently, which in turn lowers blood glucose levels. Both aerobic exercises, such as walking and cycling, and resistance training can be beneficial. For individuals with diabetes or at risk of developing diabetes, it's essential to incorporate physical activity into their daily routine, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.Stress Management Techniques

Stress can significantly impact blood glucose levels. When the body is under stress, it releases stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause blood glucose levels to rise. Engaging in stress-reducing activities can help mitigate this effect. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises have been shown to reduce stress and improve blood glucose control.
Sleep and Blood Glucose Regulation
Adequate sleep is also essential for maintaining healthy blood glucose levels. During sleep, the body regulates the balance of hormones that control glucose metabolism. Lack of sleep or poor sleep quality can disrupt this balance, leading to higher blood glucose levels and insulin resistance. Adults should aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to support overall health and blood glucose regulation.Monitoring and Medication
For individuals with diabetes, monitoring blood glucose levels regularly is crucial for managing the condition. This involves using a glucometer to check blood glucose levels at different times of the day, which helps in understanding how different factors like diet, exercise, and medication affect blood glucose levels. Based on these readings, adjustments can be made to the treatment plan to achieve better blood glucose control.
In some cases, medication may be necessary to manage blood glucose levels. This can include metformin, sulfonylureas, and insulin therapy, among others. The choice of medication depends on the type of diabetes, the severity of the condition, and the presence of other health conditions.
Importance of Regular Health Check-Ups
Regular health check-ups are vital for individuals managing blood glucose levels. These visits provide an opportunity for healthcare providers to monitor blood glucose control, adjust treatment plans as necessary, and screen for potential complications. They also offer a chance for patients to ask questions, discuss concerns, and learn more about managing their condition effectively.Lifestyle Modifications for Long-Term Management
Lifestyle modifications are fundamental to the long-term management of blood glucose levels. These modifications not only help in achieving and maintaining healthy blood glucose levels but also contribute to overall health and well-being. Key lifestyle modifications include:
- Healthy Eating: Focus on consuming a balanced diet that is rich in whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Regular Physical Activity: Aim for a combination of aerobic exercise and strength training to improve insulin sensitivity and overall health.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly improve blood glucose control and reduce the risk of complications.
- Stress Reduction: Engage in stress-reducing activities to minimize the impact of stress on blood glucose levels.
- Adequate Sleep: Prioritize getting enough sleep each night to support blood glucose regulation and overall health.
Support Systems and Education
Having a support system and being educated about diabetes and blood glucose management can make a significant difference in an individual's ability to manage their condition effectively. Support from family, friends, and support groups can provide emotional encouragement and practical help. Additionally, understanding the condition, its management, and the importance of adherence to the treatment plan is crucial for achieving good blood glucose control.Future Directions in Blood Glucose Management

The field of blood glucose management is continuously evolving, with ongoing research focused on developing new treatments, improving existing ones, and enhancing our understanding of the condition. Advances in technology, such as continuous glucose monitoring systems and insulin pumps, have already made significant impacts on the management of diabetes. Future directions may include the development of more sophisticated technologies, new medications, and a greater emphasis on personalized medicine approaches.
Personalized Approach to Blood Glucose Management
A personalized approach to blood glucose management, taking into account an individual's specific needs, lifestyle, and health status, is likely to become more prominent. This could involve tailored diet and exercise plans, as well as personalized medication regimens. The use of genetic information and other biomarkers may also play a role in developing targeted treatments.In conclusion, managing blood glucose levels effectively requires a multifaceted approach that includes dietary interventions, regular physical activity, stress management, adequate sleep, and, when necessary, medication. By understanding the importance of maintaining healthy blood glucose levels and implementing lifestyle modifications, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing complications associated with diabetes and promote overall well-being.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on managing blood glucose levels. Your insights can help others understand the importance of this aspect of health and how to approach it in a proactive and positive manner. If you have any questions or would like to learn more about a specific topic related to blood glucose management, please do not hesitate to ask.
What are the symptoms of high blood glucose levels?
+Symptoms of high blood glucose levels can include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and cuts or wounds that are slow to heal.
How often should I check my blood glucose levels?
+The frequency of checking blood glucose levels depends on the type of diabetes and the treatment plan. Generally, individuals with diabetes should check their levels at least once a day, but this can vary based on specific needs and healthcare provider recommendations.
Can lifestyle changes alone manage blood glucose levels?
+For some individuals, especially those with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise can be enough to manage blood glucose levels. However, for others, particularly those with type 1 diabetes, medication will also be necessary.
