Intro
Understand Hemoglobin A1c levels with our comprehensive chart guide, featuring normal, prediabetic, and diabetic ranges, plus tips to manage blood sugar and HbA1c test results for better health outcomes.
Understanding and managing hemoglobin A1c levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Hemoglobin A1c, also known as HbA1c or glycated hemoglobin, is a blood test that measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months. It's an essential tool for diagnosing diabetes, monitoring blood sugar control, and preventing complications. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the importance of hemoglobin A1c levels, how to interpret the results, and provide a detailed chart to help you understand your numbers.
The importance of monitoring hemoglobin A1c levels cannot be overstated. For individuals with diabetes, regular testing helps to identify trends in blood sugar control, allowing for timely adjustments to medication, diet, or exercise routines. It also helps to prevent long-term complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage, which are associated with poorly controlled diabetes. Moreover, for those without diabetes, knowing their hemoglobin A1c levels can help identify prediabetes, a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes.
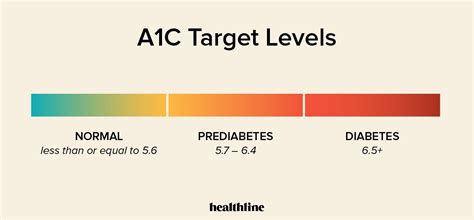
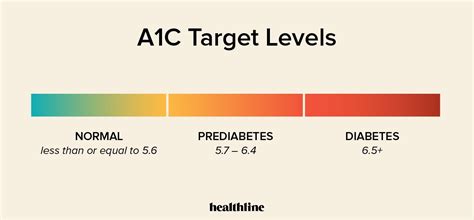
The hemoglobin A1c test is a simple blood draw that can be performed in a doctor's office or laboratory. The results are usually available within a few days and are expressed as a percentage. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following hemoglobin A1c targets: less than 5.7% for people without diabetes, 5.7% to 6.4% for people with prediabetes, and less than 7% for people with diabetes. However, these targets may vary depending on individual factors, such as age, health status, and the presence of other medical conditions.
Understanding Hemoglobin A1c Levels
To better understand hemoglobin A1c levels, it's essential to know how the test works. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to different parts of the body. When glucose is present in the blood, it binds to hemoglobin, forming glycated hemoglobin. The more glucose in the blood, the more hemoglobin gets glycated. The HbA1c test measures the percentage of glycated hemoglobin in the blood, providing an average of blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months.
Interpreting Hemoglobin A1c Results

Interpreting hemoglobin A1c results requires careful consideration of individual factors, such as age, health status, and the presence of other medical conditions. The following chart provides a general guide to understanding hemoglobin A1c levels:
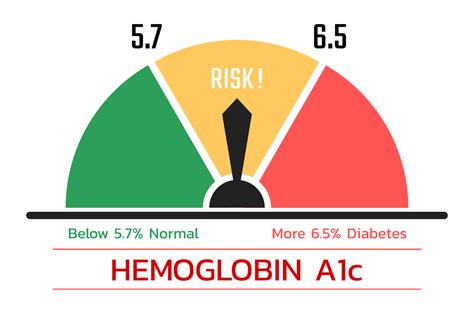
- Less than 5.7%: Normal
- 5.7% to 6.4%: Prediabetes
- 6.5% or higher: Diabetes
- Less than 7%: Good control for people with diabetes
- 7% to 8%: Fair control for people with diabetes
- Above 8%: Poor control for people with diabetes
Hemoglobin A1c Levels Chart
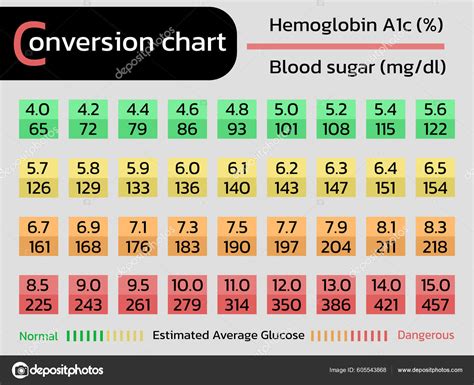
The following chart provides a detailed guide to understanding hemoglobin A1c levels:
| HbA1c Level | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Less than 5.7% | Normal |
| 5.7% to 6.0% | Prediabetes (low risk) |
| 6.1% to 6.4% | Prediabetes (high risk) |
| 6.5% to 7.0% | Diabetes (good control) |
| 7.1% to 8.0% | Diabetes (fair control) |
| 8.1% to 9.0% | Diabetes (poor control) |
| Above 9.0% | Diabetes (very poor control) |
Factors That Affect Hemoglobin A1c Levels

Several factors can affect hemoglobin A1c levels, including:
- Age: Hemoglobin A1c levels tend to increase with age.
- Health status: Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, can affect hemoglobin A1c levels.
- Medications: Some medications, such as erythropoietin, can affect hemoglobin A1c levels.
- Diet: A diet high in carbohydrates can increase hemoglobin A1c levels.
- Exercise: Regular exercise can help lower hemoglobin A1c levels.
Managing Hemoglobin A1c Levels
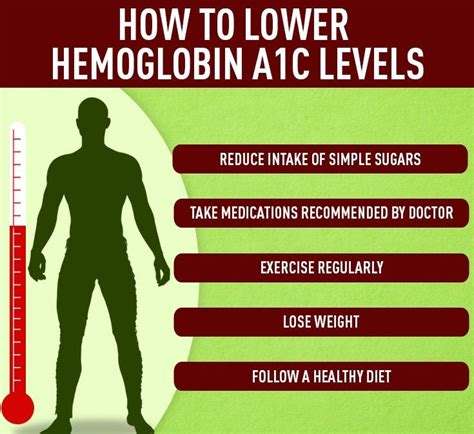
Managing hemoglobin A1c levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes:
- Healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet that is low in carbohydrates and rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, or swimming.
- Medications: Taking medications as prescribed by your doctor to control blood sugar levels.
- Monitoring: Regularly monitoring hemoglobin A1c levels to track progress and make adjustments to your treatment plan.
Tips for Lowering Hemoglobin A1c Levels
The following tips can help lower hemoglobin A1c levels:
- Eat a healthy breakfast to start your day off right.
- Choose whole grains over refined carbohydrates.
- Incorporate physical activity into your daily routine.
- Get enough sleep each night to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Manage stress through techniques such as meditation or deep breathing.
Hemoglobin A1c Levels and Complications
High hemoglobin A1c levels can increase the risk of complications, such as:
- Heart disease: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels and nerves that control the heart.
- Kidney disease: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney failure.
- Nerve damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, causing numbness, tingling, and pain.
- Blindness: High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, causing blindness.
Preventing Complications
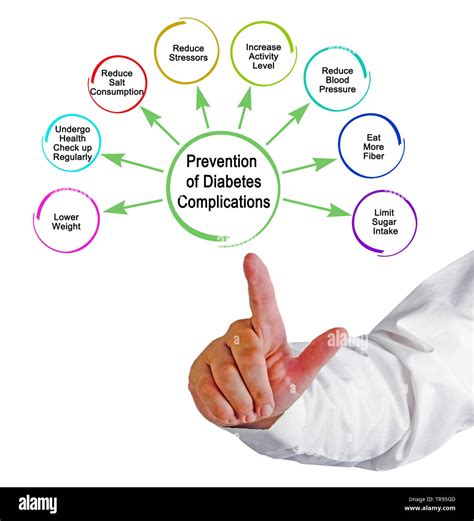
Preventing complications requires careful management of hemoglobin A1c levels, including:
- Regular monitoring: Regularly monitoring hemoglobin A1c levels to track progress and make adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Medications: Taking medications as prescribed by your doctor to control blood sugar levels.
- Regular check-ups: Regularly visiting your doctor to monitor for complications and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
What is the normal range for hemoglobin A1c levels?
+The normal range for hemoglobin A1c levels is less than 5.7%.
What are the risks of high hemoglobin A1c levels?
+High hemoglobin A1c levels can increase the risk of complications, such as heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and blindness.
How often should I get my hemoglobin A1c levels checked?
+The frequency of hemoglobin A1c level checks depends on individual factors, such as age, health status, and the presence of other medical conditions. Generally, it is recommended to get your hemoglobin A1c levels checked every 3 to 6 months.
In conclusion, understanding and managing hemoglobin A1c levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the risk of complications. We encourage readers to share their experiences and tips for managing hemoglobin A1c levels in the comments below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can promote healthy lifestyles and improve overall health outcomes.
