Intro
Discover the ultimate Hepatitis B Testing Guide, covering diagnosis, symptoms, and treatment options, with expert insights on viral hepatitis, liver disease, and vaccination protocols.
Hepatitis B is a serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) that can lead to severe health complications, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 257 million people worldwide are living with chronic hepatitis B, and nearly 900,000 people die each year from complications related to the infection. In the United States alone, it is estimated that over 2 million people are infected with HBV, with many more at risk of infection. Given the significant public health burden of hepatitis B, accurate and timely testing is crucial for identifying infected individuals, preventing transmission, and initiating effective treatment.
The importance of hepatitis B testing cannot be overstated, as it is a critical step in the diagnosis, management, and prevention of the infection. Without testing, many individuals may remain unaware of their infection status, putting themselves and others at risk of transmission. Moreover, hepatitis B testing can help identify individuals who are at risk of developing severe health complications, such as liver disease and liver cancer, allowing for early intervention and treatment. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive guide to hepatitis B testing, including the different types of tests, testing procedures, and interpretation of test results.
Hepatitis B testing is a complex process that involves several different tests, each with its own specific purpose and application. The most common types of hepatitis B tests include the hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) test, the hepatitis B surface antibody (HBsAb) test, the hepatitis B core antibody (HBcAb) test, and the hepatitis B viral load (HBV DNA) test. These tests can be used to diagnose acute and chronic hepatitis B infection, monitor the effectiveness of treatment, and assess the risk of transmission. In addition to these tests, other diagnostic procedures, such as liver function tests and imaging studies, may be used to evaluate the extent of liver damage and disease progression.
Hepatitis B Testing Types
HBsAg Test
The HBsAg test is the most commonly used test for diagnosing hepatitis B infection. This test detects the presence of the HBsAg protein on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. A positive result indicates that the individual is infected with HBV, while a negative result indicates that the individual is not infected. The HBsAg test is typically performed on a blood sample, and results are usually available within a few days.HBsAb Test
The HBsAb test is used to detect the presence of antibodies against the HBsAg protein. A positive result indicates that the individual has developed immunity to HBV, either through vaccination or previous infection. The HBsAb test is typically performed on a blood sample, and results are usually available within a few days.Hepatitis B Testing Procedure

Pre-Test Preparation
Before undergoing hepatitis B testing, individuals should prepare by: * Avoiding food and drink for at least 8 hours before the test * Avoiding strenuous exercise for at least 24 hours before the test * Informing their healthcare provider of any medications they are taking * Informing their healthcare provider of any underlying medical conditionsPost-Test Care
After undergoing hepatitis B testing, individuals should: * Follow their healthcare provider's instructions for follow-up testing or treatment * Practice good hygiene, such as washing their hands frequently, to prevent transmission of the infection * Avoid sharing personal items, such as toothbrushes or razors, to prevent transmission of the infectionHepatitis B Test Result Interpretation
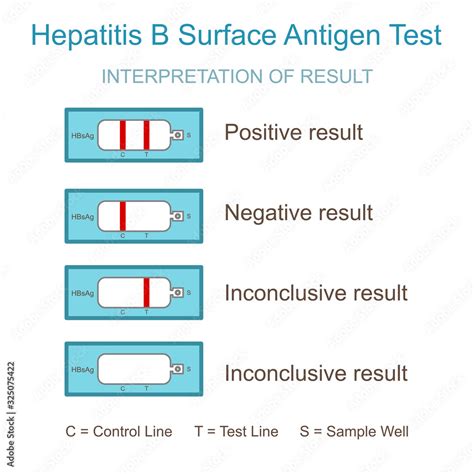
Test Result Limitations
It is essential to note that hepatitis B test results are not always 100% accurate. False-positive and false-negative results can occur due to various factors, such as: * Laboratory error * Contamination of the blood sample * Interference from other medical conditions or medications * Recent vaccination or infectionHepatitis B Testing in Special Populations
Pregnant Women
Pregnant women should undergo hepatitis B testing as part of their routine prenatal care. This is to prevent mother-to-child transmission of the infection, which can occur during childbirth or breastfeeding.Newborns
Newborns should undergo hepatitis B testing to diagnose congenital hepatitis B infection. This is essential to prevent the development of chronic hepatitis B infection and its associated complications.Hepatitis B Prevention and Treatment

Vaccination
The hepatitis B vaccine is the most effective way to prevent hepatitis B infection. The vaccine is typically administered in three doses, with the first dose given at birth, the second dose given at 1-2 months of age, and the third dose given at 6-18 months of age.Antiviral Therapy
Antiviral therapy is used to treat chronic hepatitis B infection. The goal of treatment is to reduce the viral load, prevent disease progression, and reduce the risk of transmission.What is hepatitis B?
+Hepatitis B is a serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) that can lead to severe health complications, including liver cancer and cirrhosis.
How is hepatitis B transmitted?
+Hepatitis B is transmitted through contact with infected blood, semen, or other bodily fluids, as well as through mother-to-child transmission during childbirth or breastfeeding.
What are the symptoms of hepatitis B?
+The symptoms of hepatitis B can vary, but may include fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, and yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice).
How is hepatitis B diagnosed?
+Hepatitis B is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
What is the treatment for hepatitis B?
+The treatment for hepatitis B depends on the severity of the infection and may include antiviral therapy, interferon therapy, and liver transplantation in severe cases.
