Intro
Discover 5 ways a high bun blood test reveals kidney function issues, indicating urea buildup, dehydration, or kidney disease, and learn how to interpret bun blood test results for accurate diagnosis and treatment of related health conditions.
The high bun blood test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to assess kidney function and identify potential health issues. Elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels can indicate a range of conditions, from mild kidney impairment to life-threatening diseases. In this article, we will delve into the world of high BUN blood tests, exploring the causes, symptoms, and implications of elevated BUN levels.
A high BUN blood test can be a cause for concern, as it may signal underlying kidney problems or other health issues. The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood, and when they are not functioning properly, BUN levels can rise. There are several factors that can contribute to elevated BUN levels, including dehydration, kidney disease, and certain medications. Understanding the causes and implications of high BUN levels is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment.
The importance of monitoring BUN levels cannot be overstated, as it can help healthcare professionals identify potential health issues before they become severe. A high BUN blood test can be a warning sign for kidney disease, which can progress to end-stage renal disease if left untreated. Furthermore, elevated BUN levels can also indicate other health problems, such as heart failure, liver disease, and certain infections. By understanding the significance of high BUN levels, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their kidney health and overall well-being.
Understanding BUN Levels

Factors That Influence BUN Levels
Several factors can contribute to elevated BUN levels, including: * Dehydration: Inadequate fluid intake can cause a rise in BUN levels. * Kidney disease: Kidney impairment or disease can lead to elevated BUN levels. * Medications: Certain medications, such as antibiotics and diuretics, can increase BUN levels. * Diet: A high-protein diet can cause a rise in BUN levels. * Age: Older adults may have higher BUN levels due to decreased kidney function.Causes of High BUN Levels
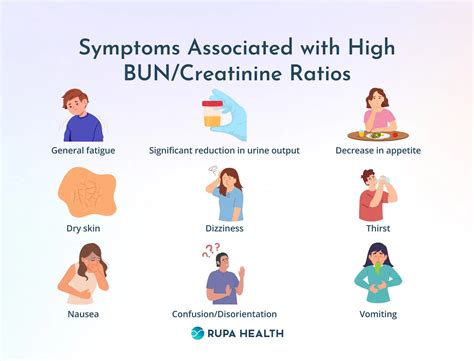
Symptoms of High BUN Levels
Individuals with high BUN levels may experience a range of symptoms, including: * Fatigue * Weakness * Shortness of breath * Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet * Nausea and vomiting * Abdominal painDiagnosing High BUN Levels

Treatment Options for High BUN Levels
Treatment for high BUN levels depends on the underlying cause. Healthcare professionals may recommend the following treatment options: * Medications: Medications can help manage underlying conditions, such as kidney disease or heart failure. * Lifestyle changes: Lifestyle changes, such as increasing fluid intake and reducing protein intake, can help manage high BUN levels. * Dialysis: In severe cases, dialysis may be necessary to remove waste and excess fluids from the blood.Preventing High BUN Levels

Complications of High BUN Levels
If left untreated, high BUN levels can lead to serious complications, including: * Kidney failure: Elevated BUN levels can progress to kidney failure if left untreated. * Heart failure: High BUN levels can increase the risk of heart failure. * Liver disease: Elevated BUN levels can increase the risk of liver disease. * Sepsis: Untreated high BUN levels can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening condition.Conclusion and Next Steps

We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with high BUN levels in the comments section below. Your feedback and insights can help others better understand the importance of kidney health and the implications of elevated BUN levels. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with your friends and family to raise awareness about kidney health and the importance of monitoring BUN levels.
What are the normal ranges for BUN levels?
+Normal BUN levels range from 6 to 24 mg/dL, but this can vary depending on age, sex, and other factors.
What are the symptoms of high BUN levels?
+Symptoms of high BUN levels can include fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet, nausea, and vomiting.
How can I prevent high BUN levels?
+To prevent high BUN levels, stay hydrated, eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and manage underlying conditions such as kidney disease or heart failure.
