Intro
Discover the implications of high C peptide levels, a marker of insulin resistance, and its connection to diabetes, blood sugar control, and pancreatic function, understanding the risks and management strategies for optimal health.
The importance of understanding high C peptide levels cannot be overstated, especially for individuals living with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. C peptide is a compound that the pancreas releases into the bloodstream in equal amounts to insulin. It plays a crucial role in diagnosing and managing diabetes, as well as in understanding the body's insulin production. In this article, we will delve into the world of high C peptide levels, exploring what they mean, how they are measured, and their implications for health.
High C peptide levels are often associated with insulin resistance, a condition where the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to increased glucose levels in the blood. This can be a precursor to type 2 diabetes, making it essential to monitor and manage C peptide levels. Moreover, high C peptide levels can also indicate other health issues, such as pancreas problems or the use of certain medications. As we navigate the complexities of high C peptide levels, it becomes clear that understanding this topic is vital for maintaining optimal health and preventing potential complications.
The relationship between C peptide and insulin is intricately linked, as both are produced in the pancreas and released into the bloodstream in tandem. When blood glucose levels rise, the pancreas responds by releasing more insulin and C peptide to facilitate glucose uptake in cells. However, in individuals with high C peptide levels, this delicate balance can be disrupted, leading to a range of health issues. As we explore the world of high C peptide levels, it becomes apparent that a comprehensive understanding of this topic is crucial for individuals seeking to manage their health and prevent potential complications.
What are High C Peptide Levels?
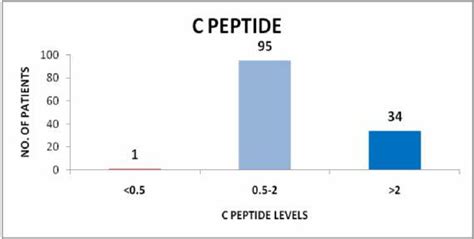
Causes of High C Peptide Levels
High C peptide levels can be caused by a range of factors, including: * Insulin resistance: When the body's cells become less responsive to insulin, the pancreas produces more insulin and C peptide to compensate, leading to elevated C peptide levels. * Pancreas problems: Certain conditions, such as pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer, can cause the pancreas to produce excessive amounts of C peptide. * Medications: Some medications, such as those used to treat type 2 diabetes, can increase C peptide levels. * Obesity: Excess weight, particularly around the abdominal area, can lead to insulin resistance and high C peptide levels.Measuring High C Peptide Levels
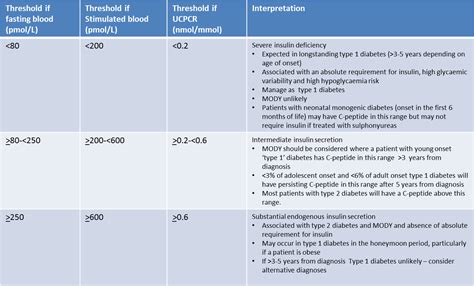
Interpreting C Peptide Test Results
Interpreting C peptide test results requires careful consideration of various factors, including: * Reference range: The reference range for C peptide levels can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's health status. * Insulin levels: C peptide levels are typically measured in conjunction with insulin to assess the body's insulin production and sensitivity. * Health status: Certain health conditions, such as kidney disease or liver disease, can affect C peptide levels.Implications of High C Peptide Levels
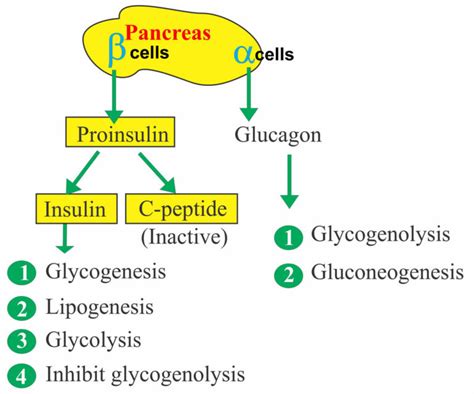
Managing High C Peptide Levels
Managing high C peptide levels typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical interventions, including: * Diet and exercise: A healthy diet and regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce C peptide levels. * Medications: Certain medications, such as metformin, can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce C peptide levels. * Monitoring: Regular monitoring of C peptide levels and other health markers can help identify potential health issues early on.Preventing High C Peptide Levels
Lifestyle Modifications for Preventing High C Peptide Levels
Lifestyle modifications can play a crucial role in preventing high C peptide levels, including: * Getting enough sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can increase the risk of insulin resistance and high C peptide levels. * Managing stress: Chronic stress can increase the risk of insulin resistance and high C peptide levels. * Quitting smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of insulin resistance and high C peptide levels.Conclusion and Next Steps

What are the symptoms of high C peptide levels?
+High C peptide levels may not always produce noticeable symptoms, but they can be associated with symptoms such as increased thirst and urination, fatigue, and blurred vision.
How can I lower my C peptide levels?
+Lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and eating a balanced diet can help lower C peptide levels. Additionally, certain medications such as metformin may be prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce C peptide levels.
What are the risks associated with high C peptide levels?
+High C peptide levels can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other health complications. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to manage and monitor C peptide levels to prevent these risks.
