Intro
Learn about normal A1c levels, blood sugar control, and diabetes management, including target HbA1c ranges, glucose monitoring, and healthy lifestyle habits for optimal glycemic balance.
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes. One of the key metrics used to assess blood sugar control is the hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level. Understanding what normal A1c levels are and how they are measured can help individuals better manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications. In this article, we will delve into the details of normal A1c levels, their significance, and how they are used in clinical practice.
The HbA1c test is a blood test that measures the average level of glucose (sugar) in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months. It does this by assessing the percentage of hemoglobin molecules in red blood cells that have bonded with glucose. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to different parts of the body. When glucose is present in the blood, some of it binds to hemoglobin, forming glycosylated hemoglobin, or HbA1c. The higher the blood glucose levels, the more hemoglobin gets glycosylated. Therefore, the HbA1c level serves as a reliable indicator of how well diabetes is being managed.
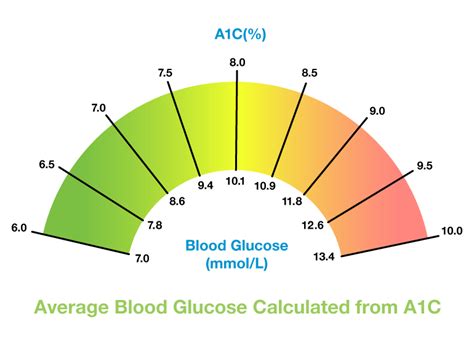
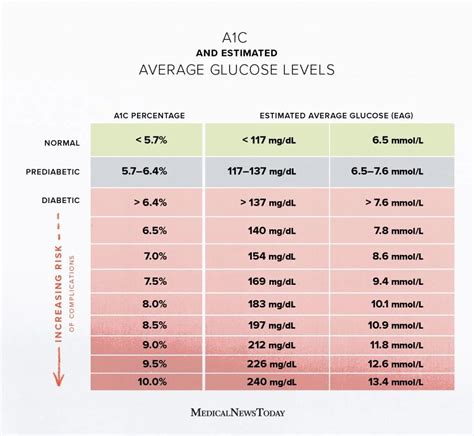
For individuals without diabetes, normal A1c levels typically fall below 5.7%. This value indicates that blood sugar levels have been within a healthy range over the preceding months. For people with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends aiming for an HbA1c level less than 7% to minimize the risk of complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage. However, targets can vary based on age, other health conditions, duration of diabetes, life expectancy, resources, and support system. It's essential for each individual with diabetes to work with their healthcare provider to set a personalized HbA1c goal.
Understanding HbA1c Measurements
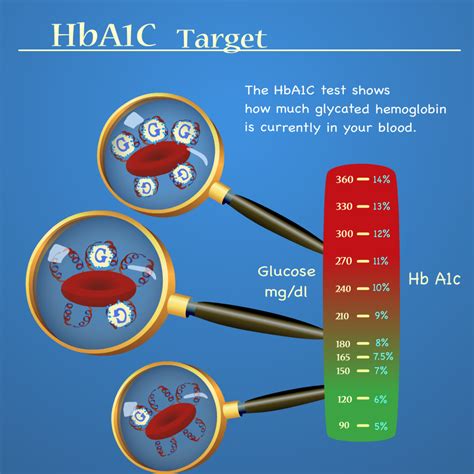
Understanding how HbA1c measurements are interpreted is vital for both healthcare providers and patients. The test results are usually reported as a percentage, and the interpretation is as follows:
- Below 5.7%: Normal
- 5.7% to 6.4%: Prediabetes
- 6.5% or higher: Diabetes
It's worth noting that HbA1c levels can be influenced by several factors, including the lifespan of red blood cells, which typically is about 120 days. Conditions that affect red blood cell turnover, such as anemia, blood transfusions, or certain nutritional deficiencies, can impact HbA1c results, potentially leading to misleading readings.
Benefits of Maintaining Normal A1c Levels
Maintaining normal A1c levels offers numerous benefits, especially for individuals with diabetes. These benefits include reduced risk of microvascular complications such as diabetic retinopathy (affecting the eyes), nephropathy (affecting the kidneys), and neuropathy (affecting the nerves). Additionally, good glycemic control can decrease the risk of macrovascular complications, including heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease. Beyond these specific benefits, achieving and maintaining target HbA1c levels can also improve overall quality of life by reducing symptoms of diabetes, such as fatigue, thirst, and frequent urination, thereby enhancing physical and mental well-being.
Steps to Achieve Normal A1c Levels
Achieving and maintaining normal A1c levels requires a multifaceted approach that includes:
- Healthy Diet: Focusing on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercises, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercises, or a combination of both, per week.
- Medication Adherence: For those with diabetes, taking medications as prescribed by their healthcare provider.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar: Regularly checking blood glucose levels to understand how different factors affect blood sugar and to make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
- Stress Management: Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga, as stress can raise blood sugar levels.
Challenges in Maintaining Normal A1c Levels
Despite the benefits, maintaining normal A1c levels can be challenging. Factors such as socioeconomic status, access to healthcare, the presence of other health conditions, and personal motivation can all impact an individual's ability to manage their blood sugar levels effectively. Additionally, the psychological aspect of living with a chronic condition should not be underestimated, as feelings of frustration, anxiety, and burnout can arise, affecting adherence to treatment plans.
Addressing Challenges
To overcome these challenges, it's essential to:
- Seek Support: Connect with family, friends, or support groups to share experiences and gain encouragement.
- Educate Yourself: Learn about diabetes management, including how to read food labels, understand medication, and recognize the signs of high or low blood sugar.
- Set Realistic Goals: Break down larger goals into smaller, achievable steps, celebrating successes along the way.
- Work with Healthcare Providers: Establish a collaborative relationship with healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to individual needs and circumstances.
Technological Advancements in A1c Monitoring

The field of diabetes management is constantly evolving, with technological advancements playing a significant role. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems and flash glucose monitoring devices allow for real-time tracking of blood glucose levels, providing detailed insights into glucose patterns and trends. These technologies can help identify periods of high or low blood sugar, enabling timely interventions and adjustments to treatment plans.
Future Directions
The future of A1c monitoring and diabetes management holds much promise, with ongoing research into areas such as:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Using AI to analyze glucose data and predict blood sugar levels, potentially automating insulin delivery.
- Implantable Devices: Developing implantable devices that can continuously monitor glucose levels and administer insulin as needed.
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring diabetes treatment to the individual, taking into account genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, maintaining normal A1c levels is a cornerstone of diabetes management, offering protection against the complications of diabetes and improving overall health and well-being. By understanding what normal A1c levels are, how they are measured, and the steps to achieve and maintain them, individuals can take control of their health. Whether through lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, or leveraging technological advancements, the journey to optimal blood sugar control is unique to each individual. It's crucial to stay informed, seek support when needed, and work closely with healthcare providers to navigate the complexities of diabetes management.
What is a normal A1c level for someone without diabetes?
+A normal A1c level for someone without diabetes is typically below 5.7%.
How often should I get my A1c levels checked if I have diabetes?
+The frequency of A1c checks depends on the type of diabetes and how well-controlled it is. Generally, the American Diabetes Association recommends checking A1c levels at least twice a year if diabetes is well-controlled, and more frequently if levels are not at goal or if changes are made to the treatment plan.
Can lifestyle changes alone lower my A1c levels?
+Yes, lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and weight loss can significantly lower A1c levels. For some individuals with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, these changes may be enough to achieve normal A1c levels. However, for others, medication may also be necessary.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with managing A1c levels and diabetes in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can promote better understanding and management of diabetes, leading to healthier lives for all.
