Intro
Discover the meaning of a high leukocyte count, its causes, and implications on health, including infection, inflammation, and immune response, to understand elevated white blood cell counts and their effects on overall wellbeing.
A high leukocyte count, also known as leukocytosis, is a condition where the body has an elevated number of white blood cells, which are a crucial part of the immune system. White blood cells, or leukocytes, play a vital role in protecting the body against infections and diseases. An abnormal increase in the number of white blood cells can be an indication of an underlying health issue. In this article, we will delve into the meaning of a high leukocyte count, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
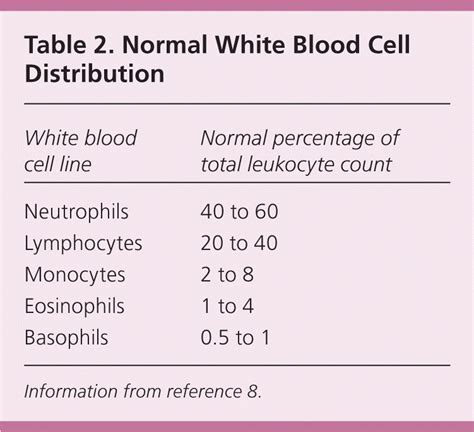
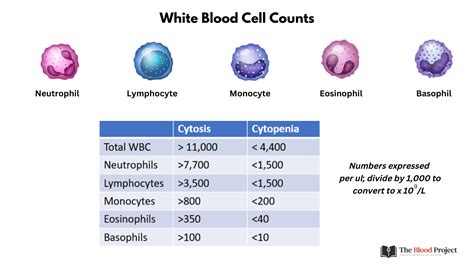
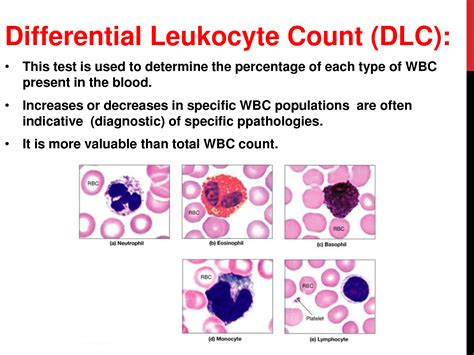
The immune system is a complex mechanism that helps the body fight off infections and diseases. White blood cells are a key component of the immune system, and they work tirelessly to protect the body against harm. There are several types of white blood cells, including neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Each type of white blood cell has a unique function, and an imbalance in the number of any of these cells can lead to health problems. A high leukocyte count can be a sign of an underlying infection, inflammation, or disease, and it is essential to understand the causes and symptoms of this condition.
A high leukocyte count can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, inflammatory diseases, and blood disorders. Infections such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and sepsis can cause a significant increase in the number of white blood cells. Inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Crohn's disease can also lead to an elevated white blood cell count. Additionally, blood disorders like leukemia and lymphoma can cause an abnormal increase in the number of white blood cells. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional if you have a high leukocyte count to determine the underlying cause and receive proper treatment.
What is a High Leukocyte Count?
Causes of a High Leukocyte Count
A high leukocyte count can be caused by a variety of factors, including: * Infections such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and sepsis * Inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Crohn's disease * Blood disorders like leukemia and lymphoma * Allergic reactions * Stress and anxiety * Certain medicationsSymptoms of a High Leukocyte Count
Treatment Options for a High Leukocyte Count
The treatment for a high leukocyte count depends on the underlying cause. If the high leukocyte count is caused by an infection, antibiotics or antiviral medications may be prescribed. If the high leukocyte count is caused by an inflammatory disease, anti-inflammatory medications or immunosuppressants may be prescribed. In some cases, blood transfusions or bone marrow transplants may be necessary.Diagnosis of a High Leukocyte Count
Risk Factors for a High Leukocyte Count
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing a high leukocyte count, including: * Age: Older adults are more likely to develop a high leukocyte count * Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are more likely to develop a high leukocyte count * Certain medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, can increase the risk of developing a high leukocyte count * Family history: A family history of blood disorders or inflammatory diseases can increase the risk of developing a high leukocyte countComplications of a High Leukocyte Count

Prevention of a High Leukocyte Count
There are several steps that can be taken to prevent a high leukocyte count, including: * Practicing good hygiene: Washing hands regularly and avoiding close contact with people who are sick can help prevent infections * Getting vaccinated: Getting vaccinated against infections such as pneumonia and influenza can help prevent a high leukocyte count * Managing stress: Managing stress and anxiety through techniques such as meditation and exercise can help prevent a high leukocyte count * Avoiding certain medications: Avoiding certain medications, such as corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, can help prevent a high leukocyte countConclusion and Next Steps
Final Thoughts
A high leukocyte count can be a sign of an underlying health issue, and it is essential to take it seriously. By understanding the causes and symptoms of this condition, you can take steps to prevent it and seek medical attention if necessary. Remember to stay informed and educated about your health, and don't hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional if you have any questions or concerns.What is a normal leukocyte count?
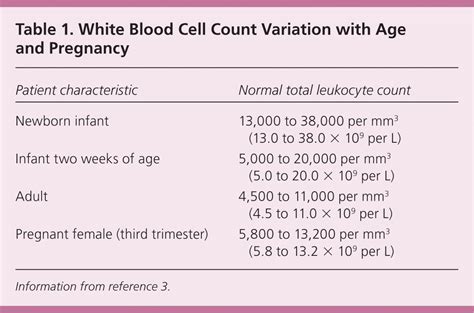
+A normal leukocyte count is between 4,000 and 11,000 cells per microliter of blood.
What are the symptoms of a high leukocyte count?
+The symptoms of a high leukocyte count can include fever, chills, fatigue, weakness, headache, muscle and joint pain, swollen lymph nodes, and weight loss.
How is a high leukocyte count diagnosed?
+A high leukocyte count is typically diagnosed through a blood test that measures the number of white blood cells in the blood.
What are the treatment options for a high leukocyte count?
+The treatment for a high leukocyte count depends on the underlying cause and can include antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, immunosuppressants, blood transfusions, or bone marrow transplants.
Can a high leukocyte count be prevented?
+Yes, a high leukocyte count can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, getting vaccinated, managing stress, and avoiding certain medications.
