Intro
Discover the 5 ways a sedimentation rate test measures inflammation, including ESR, blood tests, and medical diagnosis, to assess chronic disease risk and autoimmune disorders effectively.
The sedimentation rate test, also known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test, is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. The sedimentation rate test is a simple, yet effective tool used to diagnose and monitor various conditions, including inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. In this article, we will delve into the details of the sedimentation rate test, its importance, and its applications.
The sedimentation rate test is crucial in the medical field because it provides valuable information about the presence of inflammation in the body. Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system to injury or infection, but chronic inflammation can lead to various health problems. The test is often used to diagnose conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and other autoimmune disorders. It is also used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and to detect potential complications.
The sedimentation rate test is a non-invasive and relatively inexpensive procedure. A blood sample is taken from the patient, and the erythrocytes are allowed to settle in a test tube. The rate at which they settle is measured and compared to a standard value. The test results are usually available within a few hours, and they can provide valuable insights into the patient's condition. The sedimentation rate test is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests, such as the C-reactive protein (CRP) test, to confirm a diagnosis or to monitor the progression of a disease.
What is Sedimentation Rate Test
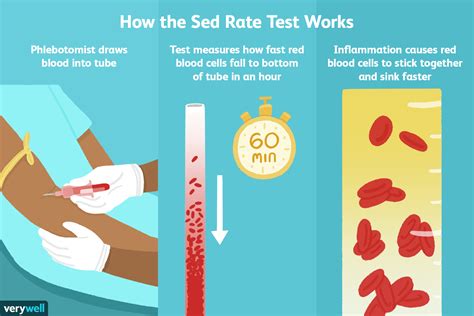
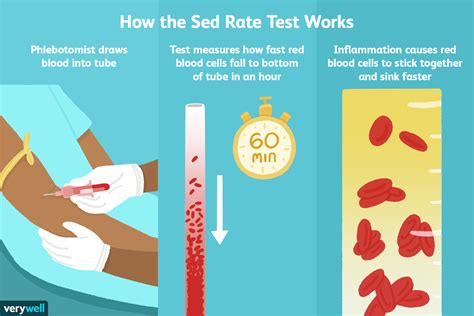
How Sedimentation Rate Test Works
The sedimentation rate test works by measuring the rate at which erythrocytes settle in a test tube. The test is based on the principle that erythrocytes settle more quickly in the presence of inflammation. When there is inflammation in the body, the liver produces more acute-phase proteins, such as fibrinogen and immunoglobulins. These proteins cause the erythrocytes to clump together, forming stacks called rouleaux. The rouleaux settle more quickly than individual erythrocytes, resulting in a higher sedimentation rate.Benefits of Sedimentation Rate Test
Applications of Sedimentation Rate Test
The sedimentation rate test has several applications, including: * Diagnosing inflammatory and autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. * Monitoring the effectiveness of treatment and detecting potential complications. * Detecting chronic inflammation, which can lead to various health problems. * Monitoring the progression of a disease and adjusting treatment accordingly. * Providing valuable information about the presence of inflammation in the body.How to Prepare for Sedimentation Rate Test

What to Expect During Sedimentation Rate Test
During the sedimentation rate test, patients can expect: * A blood sample to be taken from a vein in their arm. * The blood sample to be placed in a test tube and treated with an anticoagulant. * The erythrocytes to be allowed to settle for a specified period, usually one hour. * The distance the erythrocytes have settled to be measured and compared to a standard value. * The test results to be available within a few hours.Interpreting Sedimentation Rate Test Results

Limitations of Sedimentation Rate Test
The sedimentation rate test has several limitations, including: * It is not specific to any particular disease or condition. * It can be affected by various factors, such as age, sex, and medications. * It is not a definitive diagnostic test, but rather a tool to aid in diagnosis. * It should be used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests to confirm a diagnosis.Common Conditions Diagnosed with Sedimentation Rate Test

Monitoring Disease Progression with Sedimentation Rate Test
The sedimentation rate test can be used to monitor disease progression and adjust treatment accordingly. The test can help doctors: * Monitor the effectiveness of treatment. * Detect potential complications. * Adjust treatment to achieve optimal results. * Provide valuable information about the presence of inflammation in the body.What is the normal range for the sedimentation rate test?
+The normal range for the sedimentation rate test is 0-20 mm/h for men, 0-30 mm/h for women, and 0-15 mm/h for children.
What is the sedimentation rate test used for?
+The sedimentation rate test is used to diagnose conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and other autoimmune disorders. It is also used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment and to detect potential complications.
How is the sedimentation rate test performed?
+The sedimentation rate test is performed by taking a blood sample from a vein in the arm and placing it in a test tube. The erythrocytes are allowed to settle for a specified period, usually one hour, and the distance they have settled is measured and compared to a standard value.
In conclusion, the sedimentation rate test is a valuable tool used to diagnose and monitor various conditions, including inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. It provides valuable information about the presence of inflammation in the body and can help doctors diagnose conditions, monitor disease progression, and adjust treatment accordingly. By understanding the benefits, applications, and limitations of the sedimentation rate test, patients can better appreciate the importance of this test in maintaining their health. If you have any questions or concerns about the sedimentation rate test, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with others who may benefit from this information.
