Intro
Understand PT INR blood test results, including prothrombin time, international normalized ratio, and coagulation factors, to diagnose bleeding disorders and monitor anticoagulant therapy effectively.
The Prothrombin Time (PT) and International Normalized Ratio (INR) blood tests are crucial for evaluating the blood clotting process in individuals, particularly those taking anticoagulant medications. These tests help healthcare professionals assess the risk of bleeding or thrombosis, ensuring that patients receive appropriate treatment and care. Understanding PT and INR blood test results is vital for effective patient management and minimizing potential complications.
The PT and INR tests measure the time it takes for blood to clot, with PT focusing on the extrinsic coagulation pathway and INR providing a standardized measurement of blood clotting. Abnormal results can indicate an increased risk of bleeding or thrombosis, and it is essential to comprehend the underlying causes and implications of these results. In this article, we will delve into the world of PT and INR blood tests, exploring their significance, interpretation, and applications in clinical practice.
The importance of PT and INR blood tests cannot be overstated, as they play a critical role in monitoring patients with cardiovascular diseases, such as atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. Additionally, these tests are essential for individuals taking anticoagulant medications, like warfarin, to ensure that their blood clotting is within a safe range. By understanding PT and INR blood test results, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about patient care, adjusting treatment plans as needed to minimize the risk of adverse events.
Introduction to PT and INR Blood Tests
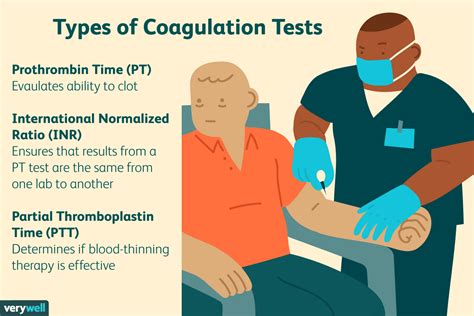
How PT and INR Blood Tests Work
The PT test measures the time it takes for blood to clot after adding tissue factor, a substance that initiates the extrinsic coagulation pathway. The result is reported in seconds, with normal values ranging from 11 to 13.5 seconds. The INR test, however, is calculated by dividing the patient's PT result by the normal PT result, and then raising it to the power of the International Sensitivity Index (ISI). This calculation provides a standardized measurement of blood clotting, allowing for comparison of results across different laboratories.Interpretation of PT and INR Blood Test Results
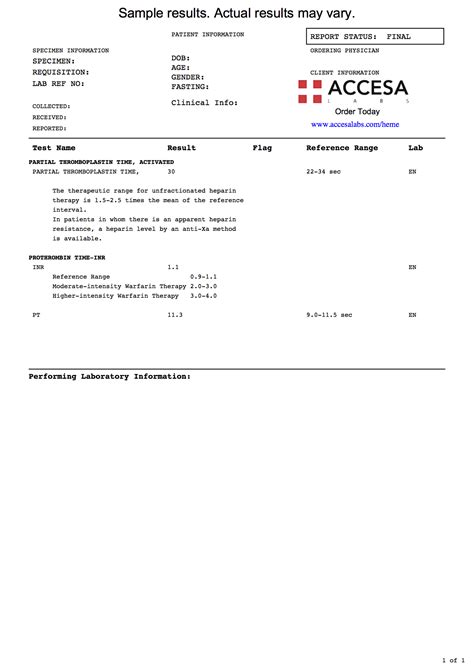
Normal and Abnormal PT and INR Values
Normal PT values typically range from 11 to 13.5 seconds, while normal INR values range from 0.8 to 1.2. Abnormal PT values can be categorized as follows: * Prolonged PT: >13.5 seconds * Shortened PT: <11 seconds Abnormal INR values can be categorized as follows: * Elevated INR: >1.2 * Decreased INR: <0.8Clinical Applications of PT and INR Blood Tests
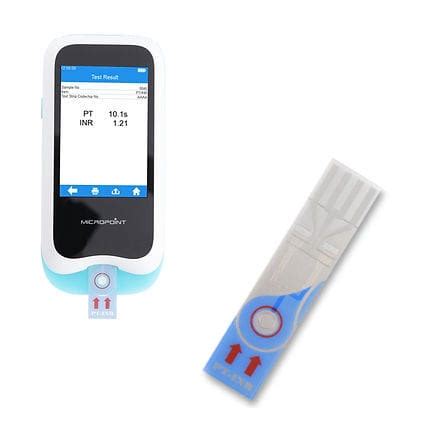

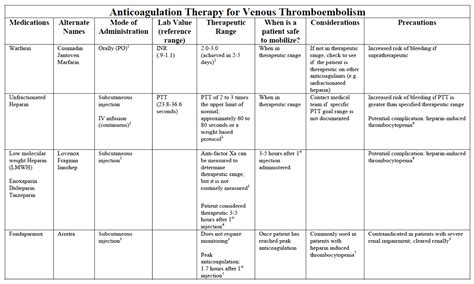
Monitoring Anticoagulation Therapy
PT and INR blood tests are crucial for monitoring patients on anticoagulation therapy, particularly those taking warfarin. The goal of anticoagulation therapy is to maintain an INR value between 2.0 and 3.0, which reduces the risk of thrombosis while minimizing the risk of bleeding. Regular PT and INR testing helps healthcare professionals adjust the dose of anticoagulant medication, ensuring that patients receive optimal treatment.Potential Complications and Limitations of PT and INR Blood Tests
Factors Affecting PT and INR Results
Several factors can affect PT and INR results, including: * Medications, such as anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, and certain antibiotics * Dietary factors, such as vitamin K intake * Underlying medical conditions, such as liver disease or kidney disease * Laboratory variability, including differences in thromboplastin reagents and testing methodsFuture Directions and Emerging Trends in PT and INR Blood Tests
Point-of-Care Testing Devices
Point-of-care testing devices are becoming increasingly popular, allowing healthcare professionals to perform PT and INR tests at the bedside or in outpatient settings. These devices offer improved convenience and rapid results, enabling healthcare professionals to make timely decisions about patient care.What is the normal range for PT and INR blood tests?
+Normal PT values typically range from 11 to 13.5 seconds, while normal INR values range from 0.8 to 1.2.
What are the potential complications of PT and INR blood tests?
+Potential complications and limitations include variability in thromboplastin reagents, interference from other medications or substances, and limited sensitivity and specificity.
How often should PT and INR blood tests be performed?
+The frequency of PT and INR blood tests depends on the individual patient's clinical context and medical history, but typically ranges from every 1-4 weeks for patients on anticoagulation therapy.
In conclusion, PT and INR blood tests are essential tools in clinical practice, providing valuable information about blood clotting and guiding treatment decisions. By understanding the significance, interpretation, and applications of these tests, healthcare professionals can optimize patient care and minimize the risk of complications. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with PT and INR blood tests, and to explore the latest developments and advancements in this field.
