Intro
Discover 5 ways kidney disease is diagnosed, including urine tests, blood work, and imaging scans, to detect kidney damage, kidney failure, and chronic kidney disease, and learn about diagnosis methods and treatment options.
Kidney disease is a serious medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is essential to diagnose kidney disease early to prevent further damage and improve treatment outcomes. There are several ways to diagnose kidney disease, and understanding these methods can help individuals take proactive steps to protect their kidney health. In this article, we will explore the importance of diagnosing kidney disease and the various methods used to detect this condition.
Diagnosing kidney disease is crucial because it allows healthcare providers to identify individuals who are at risk of developing kidney failure or other complications. Early detection also enables timely intervention, which can help slow or halt the progression of the disease. Furthermore, diagnosing kidney disease can help individuals make informed decisions about their lifestyle and treatment options. With the rising prevalence of kidney disease, it is essential to raise awareness about the importance of early detection and the various methods used to diagnose this condition.
Kidney disease can be diagnosed using a combination of physical examinations, medical history, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Healthcare providers use these methods to assess kidney function, identify underlying causes of kidney damage, and monitor the progression of the disease. By understanding the different diagnostic methods, individuals can better appreciate the importance of regular health check-ups and the need to seek medical attention if they experience any symptoms of kidney disease.
Introduction to Kidney Disease Diagnosis
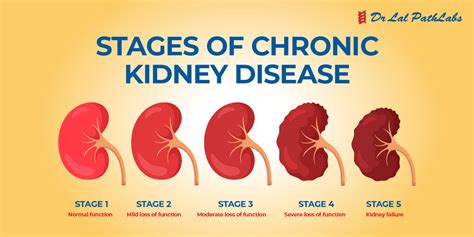
Kidney disease diagnosis involves a comprehensive evaluation of an individual's overall health, medical history, and laboratory results. Healthcare providers use this information to assess kidney function, identify potential causes of kidney damage, and develop an effective treatment plan. The diagnostic process typically begins with a physical examination, during which the healthcare provider will check for signs of kidney disease, such as high blood pressure, swelling, or abnormal heart sounds.
Physical Examination and Medical History

A physical examination is a crucial component of kidney disease diagnosis. During the examination, the healthcare provider will check for signs of kidney disease, such as swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet. They will also assess blood pressure, which is a significant risk factor for kidney disease. Additionally, the healthcare provider will review the individual's medical history, including any pre-existing conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, which can increase the risk of kidney disease.
Importance of Medical History
A thorough medical history is essential for diagnosing kidney disease. The healthcare provider will ask questions about the individual's family history, lifestyle, and any previous illnesses or injuries that may have affected the kidneys. This information helps the healthcare provider identify potential risk factors and develop a personalized treatment plan. For example, individuals with a family history of kidney disease or those who have been diagnosed with diabetes or high blood pressure are at a higher risk of developing kidney disease.Laboratory Tests for Kidney Disease

Laboratory tests are a critical component of kidney disease diagnosis. These tests help healthcare providers assess kidney function, identify underlying causes of kidney damage, and monitor the progression of the disease. Some common laboratory tests used to diagnose kidney disease include:
- Blood tests: to measure waste products, such as creatinine and urea, which can build up in the blood when the kidneys are not functioning properly.
- Urine tests: to check for protein, blood, or other abnormalities in the urine that may indicate kidney damage.
- Imaging tests: such as ultrasound or CT scans, to visualize the kidneys and identify any structural abnormalities.
Types of Laboratory Tests
There are several types of laboratory tests used to diagnose kidney disease. These include: * Creatinine test: to measure the level of creatinine in the blood, which can indicate kidney function. * Urea test: to measure the level of urea in the blood, which can also indicate kidney function. * Electrolyte test: to measure the level of electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, in the blood, which can help identify any imbalances that may be affecting kidney function.Imaging Studies for Kidney Disease
Imaging studies are an essential component of kidney disease diagnosis. These tests help healthcare providers visualize the kidneys and identify any structural abnormalities that may be affecting kidney function. Some common imaging studies used to diagnose kidney disease include:
- Ultrasound: to visualize the kidneys and identify any abnormalities, such as cysts or tumors.
- CT scan: to provide detailed images of the kidneys and identify any structural abnormalities.
- MRI: to provide detailed images of the kidneys and identify any structural abnormalities.
Benefits of Imaging Studies
Imaging studies offer several benefits for diagnosing kidney disease. These include: * Accurate diagnosis: imaging studies can help healthcare providers accurately diagnose kidney disease and identify any underlying causes of kidney damage. * Monitoring disease progression: imaging studies can help healthcare providers monitor the progression of kidney disease and adjust treatment plans accordingly. * Guiding treatment: imaging studies can help healthcare providers guide treatment and ensure that the individual receives the most effective care possible.Treatment Options for Kidney Disease

Treatment options for kidney disease depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some common treatment options include:
- Medications: to control blood pressure, reduce proteinuria, and slow the progression of kidney disease.
- Lifestyle modifications: such as dietary changes, exercise, and stress reduction, to help manage kidney disease and slow its progression.
- Dialysis: to filter waste products from the blood when the kidneys are no longer able to perform this function.
- Kidney transplant: to replace a damaged kidney with a healthy one from a donor.
Importance of Early Treatment
Early treatment is essential for managing kidney disease and preventing further damage. By seeking medical attention at the first sign of symptoms, individuals can help slow the progression of kidney disease and improve treatment outcomes. Additionally, early treatment can help individuals manage any underlying conditions that may be contributing to kidney disease, such as diabetes or high blood pressure.What are the symptoms of kidney disease?
+The symptoms of kidney disease can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include fatigue, swelling, and changes in urination. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention.
How is kidney disease diagnosed?
+Kidney disease is diagnosed using a combination of physical examinations, medical history, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. These tests help healthcare providers assess kidney function, identify underlying causes of kidney damage, and monitor the progression of the disease.
What are the treatment options for kidney disease?
+Treatment options for kidney disease depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common treatment options include medications, lifestyle modifications, dialysis, and kidney transplant. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan.
In conclusion, diagnosing kidney disease is a complex process that involves a combination of physical examinations, medical history, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. By understanding the different diagnostic methods and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their kidney health and manage kidney disease. If you have any questions or concerns about kidney disease, we encourage you to comment below or share this article with others who may be interested. Additionally, we invite you to explore our website for more information on kidney disease and other health-related topics.
