Intro
Lidocaine works quickly as a local anesthetic, providing rapid pain relief and numbing effects, ideal for minor procedures, injections, and topical applications, with fast-acting properties and minimal side effects, making it a popular choice for medical professionals and patients alike.
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic that has been widely used in the medical field for its rapid and effective pain relief properties. It works by blocking the nerve signals in the body, which are responsible for transmitting pain sensations to the brain. This results in a numbing effect, making it an ideal solution for various medical procedures, including injections, skin grafts, and minor surgeries. The quick action of lidocaine makes it a preferred choice among medical professionals, as it enables them to perform procedures with minimal discomfort to the patient.
The importance of lidocaine lies in its ability to provide rapid pain relief, which is essential in emergency situations or when treating acute injuries. Its fast-acting properties also make it suitable for use in outpatient procedures, where patients can be treated and discharged quickly. Furthermore, lidocaine has a relatively long duration of action, which can last from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the dosage and method of administration. This prolonged effect helps to reduce the need for repeated doses, making it a convenient option for both patients and healthcare providers.
Lidocaine's mechanism of action is based on its ability to interfere with the transmission of nerve impulses. It does this by blocking the sodium channels in the nerve cells, which are responsible for generating the electrical signals that transmit pain sensations. By inhibiting these channels, lidocaine effectively numbs the area, preventing the brain from receiving pain signals. This makes it an effective solution for managing pain in various medical settings, including dentistry, dermatology, and emergency medicine.
Lidocaine Administration Methods
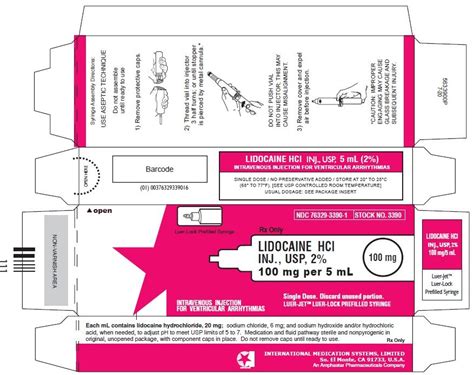
Lidocaine can be administered through various methods, including topical application, injection, and infiltration. Topical application involves applying a lidocaine cream or gel directly to the skin, which is then absorbed into the tissue to produce a numbing effect. This method is commonly used for minor procedures, such as skin biopsies or cosmetic treatments. Injection involves administering lidocaine directly into the tissue, which is typically used for more invasive procedures, such as surgeries or dental procedures. Infiltration involves injecting lidocaine into the tissue surrounding a wound or incision, which helps to reduce pain and discomfort during the healing process.
Benefits of Lidocaine
The benefits of lidocaine are numerous, making it a widely used and versatile local anesthetic. Some of the key benefits include: * Rapid onset of action, providing quick pain relief * Long duration of action, reducing the need for repeated doses * Effective in managing pain in various medical settings * Can be administered through various methods, including topical application, injection, and infiltration * Relatively safe and well-tolerated, with minimal side effectsLidocaine Uses

Lidocaine has a wide range of uses in the medical field, including:
- Local anesthesia for minor procedures, such as skin biopsies or cosmetic treatments
- Pain management in emergency situations, such as acute injuries or trauma
- Anesthesia for dental procedures, such as fillings or extractions
- Numbing agent for minor surgeries, such as skin grafts or mole removals
- Treatment of certain medical conditions, such as arrhythmias or epilepsy
Lidocaine Side Effects
While lidocaine is generally safe and well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects, including: * Numbness or tingling at the injection site * Redness or swelling at the injection site * Dizziness or lightheadedness * Headache or nausea * Allergic reactions, such as hives or itchingLidocaine Dosage
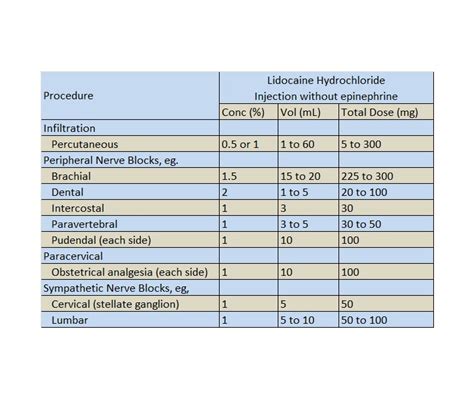
The dosage of lidocaine varies depending on the method of administration, the patient's weight, and the intended use. Typical dosages range from 0.5% to 2% lidocaine, with a maximum dose of 4.5 mg/kg. It is essential to follow the recommended dosage guidelines to minimize the risk of side effects and ensure effective pain relief.
Lidocaine Interactions
Lidocaine can interact with other medications, including: * Beta-blockers, which can increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias * Calcium channel blockers, which can increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias * Anti-arrhythmic medications, which can increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias * Certain antibiotics, such as erythromycin or clarithromycin, which can increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmiasLidocaine Precautions
When using lidocaine, it is essential to take certain precautions, including:
- Avoiding use in patients with a history of allergic reactions to lidocaine or other local anesthetics
- Avoiding use in patients with certain medical conditions, such as heart disease or epilepsy
- Monitoring patients for signs of toxicity, such as numbness or tingling
- Avoiding use in patients who are taking certain medications, such as beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers
Lidocaine Storage
Lidocaine should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. It is essential to follow the recommended storage guidelines to ensure the stability and effectiveness of the medication.Lidocaine Disposal

Lidocaine should be disposed of properly, following the recommended guidelines for hazardous waste disposal. It is essential to dispose of the medication and any associated materials, such as needles or syringes, in a safe and responsible manner.
Lidocaine Alternatives
There are several alternatives to lidocaine, including: * Benzocaine, which is commonly used as a topical anesthetic * Tetracaine, which is commonly used as a topical anesthetic * Mepivacaine, which is commonly used as a local anesthetic * Articaine, which is commonly used as a local anestheticLidocaine Future Directions

Research is ongoing to develop new and improved formulations of lidocaine, including:
- Sustained-release formulations, which can provide longer-lasting pain relief
- Topical formulations, which can provide rapid and effective pain relief
- Combination formulations, which can provide enhanced pain relief and reduced side effects
Lidocaine Conclusion and Recommendations
In conclusion, lidocaine is a widely used and effective local anesthetic that provides rapid and long-lasting pain relief. Its benefits, including rapid onset of action, long duration of action, and minimal side effects, make it a preferred choice among medical professionals. However, it is essential to follow the recommended dosage guidelines, take necessary precautions, and monitor patients for signs of toxicity. Further research is needed to develop new and improved formulations of lidocaine, which can provide enhanced pain relief and reduced side effects.What is lidocaine used for?
+Lidocaine is used as a local anesthetic to provide rapid and effective pain relief in various medical settings, including minor procedures, emergency situations, and dental procedures.
How does lidocaine work?
+Lidocaine works by blocking the nerve signals in the body, which are responsible for transmitting pain sensations to the brain, resulting in a numbing effect.
What are the side effects of lidocaine?
+The side effects of lidocaine include numbness or tingling at the injection site, redness or swelling at the injection site, dizziness or lightheadedness, headache or nausea, and allergic reactions.
How is lidocaine administered?
+Lidocaine can be administered through various methods, including topical application, injection, and infiltration, depending on the intended use and patient's needs.
What are the precautions when using lidocaine?
+Precautions when using lidocaine include avoiding use in patients with a history of allergic reactions, certain medical conditions, or taking certain medications, and monitoring patients for signs of toxicity.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of lidocaine, its uses, benefits, and precautions. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with lidocaine, please feel free to comment below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
