Intro
Identify concussion symptoms, signs, and treatment. Learn about traumatic brain injury, mild TBI, and head trauma effects, and when to seek medical help for a concussion diagnosis and recovery.
Concussions are a type of traumatic brain injury that can occur when the head is hit or shaken violently, causing the brain to move back and forth inside the skull. This can lead to a variety of symptoms, some of which may not appear immediately after the injury. It is essential to check for concussion symptoms after a head injury, as prompt medical attention can help prevent long-term damage and ensure proper recovery.
The importance of checking for concussion symptoms cannot be overstated. Concussions can affect anyone, regardless of age or activity level, and can have serious consequences if left untreated. In fact, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), concussions are a leading cause of brain injury in the United States, with over 1.6 million people suffering from a traumatic brain injury each year. By being aware of the signs and symptoms of concussions, individuals can take the necessary steps to protect themselves and others from the potential long-term effects of these injuries.
Checking for concussion symptoms is particularly crucial in sports and other high-risk activities, where head injuries are common. Coaches, trainers, and parents should be educated on the signs of concussions and take immediate action if they suspect that an athlete has suffered a head injury. This may involve removing the athlete from play, conducting a thorough medical evaluation, and providing ongoing monitoring and support to ensure a safe and successful recovery.
Understanding Concussion Symptoms
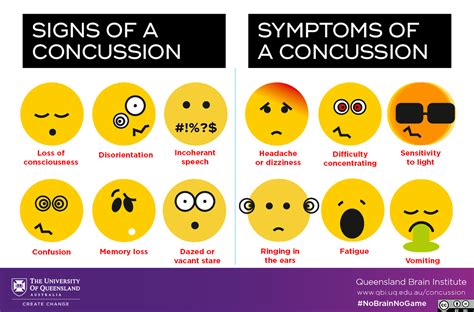
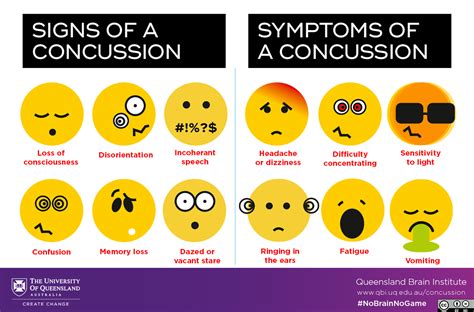
Concussion symptoms can vary widely from person to person and may not always be immediately apparent. Some common symptoms of concussions include headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. In more severe cases, concussions can cause seizures, difficulty speaking, weakness or numbness in the arms or legs, and loss of coordination or balance.
Physical Symptoms of Concussions
Physical symptoms of concussions can be divided into several categories, including cognitive, emotional, and physical symptoms. Cognitive symptoms may include difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and confusion, while emotional symptoms may include irritability, anxiety, and depression. Physical symptoms, on the other hand, may include headache, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting, as well as fatigue, sleep disturbances, and sensitivity to light and sound.Checking for Concussion Symptoms in Athletes
Checking for concussion symptoms in athletes is a critical step in preventing long-term brain damage and ensuring a safe return to play. Coaches, trainers, and parents should be educated on the signs of concussions and take immediate action if they suspect that an athlete has suffered a head injury. This may involve removing the athlete from play, conducting a thorough medical evaluation, and providing ongoing monitoring and support to ensure a safe and successful recovery.
Some common tools used to check for concussion symptoms in athletes include the Concussion Symptom Inventory, the Sport Concussion Assessment Tool (SCAT), and the Balance Error Scoring System (BESS). These tools can help healthcare professionals quickly and accurately assess an athlete's condition and make informed decisions about their return to play.
Return to Play Protocol
The return to play protocol is a critical step in ensuring that athletes who have suffered a concussion are able to safely return to their sport. This protocol typically involves a gradual progression of physical activity, starting with light exercise and gradually increasing in intensity and duration. Athletes must be symptom-free and have received medical clearance before returning to full contact practice or competition.Concussion Prevention and Treatment

Concussion prevention and treatment are critical components of any comprehensive concussion management plan. Prevention strategies may include educating athletes, coaches, and parents on the signs and symptoms of concussions, as well as teaching proper tackling and falling techniques. Treatment strategies, on the other hand, may include rest, physical therapy, and cognitive rehabilitation, as well as medication to manage symptoms such as headache and nausea.
Some common prevention strategies include:
- Wearing proper protective equipment, such as helmets and mouthguards
- Avoiding head-to-head contact and other high-risk behaviors
- Staying hydrated and fueled to prevent fatigue and other underlying conditions that may increase the risk of concussion
- Getting enough sleep and taking regular breaks to rest and recover
Cognitive Rehabilitation
Cognitive rehabilitation is an important component of concussion treatment, particularly for athletes who have suffered a severe or prolonged concussion. This type of rehabilitation typically involves a combination of cognitive training, physical therapy, and behavioral therapy, and is designed to help athletes regain their cognitive and physical function.Some common cognitive rehabilitation strategies include:
- Cognitive training, such as memory and attention exercises
- Physical therapy, such as balance and coordination exercises
- Behavioral therapy, such as stress management and relaxation techniques
- Educational support, such as tutoring and academic accommodations
Long-Term Effects of Concussions

The long-term effects of concussions can be serious and debilitating, particularly for athletes who have suffered multiple concussions or have a history of traumatic brain injury. Some common long-term effects of concussions include chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), dementia, depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
CTE is a degenerative brain disease that is caused by repeated blows to the head, and is characterized by memory loss, confusion, and difficulty with speech and language. Dementia, on the other hand, is a broad term that refers to a decline in cognitive function, including memory loss, difficulty with communication, and impaired judgment.
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
CTE is a serious and debilitating condition that is caused by repeated blows to the head. It is characterized by memory loss, confusion, and difficulty with speech and language, and can also cause mood changes, such as depression and anxiety.Some common symptoms of CTE include:
- Memory loss and difficulty with learning new information
- Difficulty with speech and language, including slurred speech and difficulty finding the right words
- Mood changes, such as depression, anxiety, and irritability
- Difficulty with coordination and balance, including trouble with walking and balance
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, checking for concussion symptoms is a critical step in preventing long-term brain damage and ensuring a safe return to play. By being aware of the signs and symptoms of concussions, individuals can take the necessary steps to protect themselves and others from the potential long-term effects of these injuries.
If you or someone you know has suffered a concussion, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. A healthcare professional can provide a thorough evaluation and develop a comprehensive treatment plan to ensure a safe and successful recovery.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with concussions in the comments below. Have you or someone you know suffered a concussion? What steps did you take to ensure a safe and successful recovery? Share your story and help raise awareness about the importance of concussion prevention and treatment.
What are the symptoms of a concussion?
+The symptoms of a concussion can vary widely from person to person, but may include headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
How can I prevent concussions?
+Concussions can be prevented by wearing proper protective equipment, avoiding head-to-head contact and other high-risk behaviors, staying hydrated and fueled, and getting enough sleep and taking regular breaks to rest and recover.
What is the return to play protocol for concussions?
+The return to play protocol for concussions typically involves a gradual progression of physical activity, starting with light exercise and gradually increasing in intensity and duration. Athletes must be symptom-free and have received medical clearance before returning to full contact practice or competition.
