Intro
Intramuscular injections are a common medical procedure used to administer medications, vaccines, and other substances directly into the muscle tissue. This method of injection allows for faster absorption of the substance into the bloodstream, making it an effective way to deliver certain types of medications. However, administering an intramuscular injection requires proper technique and precautions to ensure the safety of both the person receiving the injection and the person giving it.
The importance of proper technique cannot be overstated, as incorrect administration can lead to complications such as nerve damage, infection, or ineffective medication absorption. Healthcare professionals and individuals who are trained to give injections must understand the anatomy of the injection site, the type of needle and syringe to use, and the steps to follow for a safe and effective injection. Moreover, the recipient's comfort and safety should always be the top priority, which includes explaining the procedure, addressing any concerns, and ensuring the environment is clean and suitable for the procedure.
Before proceeding with an intramuscular injection, it's crucial to assess the recipient's overall health and any potential allergies or sensitivities to the substance being administered. This assessment helps in identifying any contraindications and in selecting the most appropriate injection site. The most common sites for intramuscular injections are the deltoid muscle in the upper arm, the vastus lateralis muscle in the thigh, and the gluteus maximus muscle in the buttocks. Each site has specific guidelines for needle length and injection technique to ensure the medication is delivered into the muscle without causing undue discomfort or complications.
Preparation for Intramuscular Injection
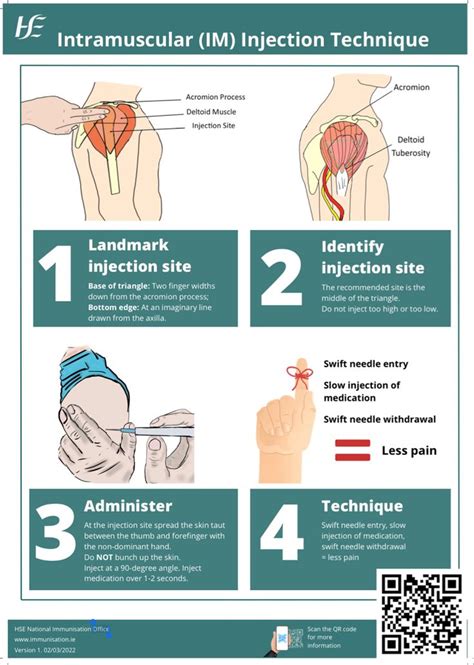
Preparation is key to a successful intramuscular injection. This involves gathering all necessary supplies, including the medication, a syringe, a needle of appropriate length and gauge, and alcohol wipes for skin preparation. The recipient should be positioned comfortably to allow easy access to the chosen injection site. For injections into the deltoid muscle, the recipient's arm should be relaxed and slightly bent. For injections into the vastus lateralis, the recipient should be sitting or lying down with the leg slightly bent. And for injections into the gluteus maximus, the recipient should be lying on their side with the injection site facing upwards.
Choosing the Right Equipment
The choice of needle and syringe is critical. The needle length should be sufficient to penetrate the skin and subcutaneous tissue to reach the muscle without causing discomfort or hitting the bone. Typically, needles for intramuscular injections are between 1 to 1.5 inches long for deltoid muscle injections in adults, and longer for gluteal injections. The gauge of the needle (its thickness) also matters, with thicker needles (lower gauge numbers) being used for thicker medications and thinner needles (higher gauge numbers) for more watery solutions.Technique for Administering Intramuscular Injections

The actual administration of an intramuscular injection involves several steps. First, the skin at the injection site should be cleaned with an alcohol wipe to reduce the risk of infection. The syringe should then be held at a 90-degree angle to the skin, and the needle should be inserted quickly and smoothly through the skin and into the muscle. Once the needle is in place, the plunger should be slowly pushed to inject the medication. After the injection is complete, the needle should be withdrawn quickly, and pressure should be applied to the site with a cotton ball or gauze for a few seconds to prevent bleeding.
Post-Injection Care
After the injection, the recipient should be monitored for any signs of adverse reaction, such as redness, swelling, or pain at the injection site. It's also important to provide instructions on how to manage any potential side effects and when to seek medical attention. The used needle and syringe should be disposed of safely in a sharps container to prevent injury and infection.Common Challenges and Complications

Despite the best techniques, complications can arise from intramuscular injections. These can range from minor issues like bruising or pain at the injection site to more serious problems such as nerve damage or infection. It's essential for healthcare providers to be aware of these potential complications and to take steps to prevent them, including using proper injection technique, ensuring the recipient's comfort and safety, and providing clear instructions for post-injection care.
Preventing Infection
Preventing infection is a critical aspect of intramuscular injection safety. This involves using sterile equipment, properly preparing the skin at the injection site, and ensuring that the environment is clean. Additionally, the recipient should be advised to monitor the injection site for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus, and to seek medical attention if any of these symptoms occur.Best Practices for Safe Intramuscular Injections

To ensure the safe administration of intramuscular injections, several best practices should be followed. These include:
- Using the correct needle length and gauge for the injection site and the recipient's body size.
- Ensuring the medication is at room temperature before injection to reduce discomfort.
- Not injecting into areas with scar tissue or where there has been a previous reaction.
- Documenting the injection, including the site, the medication administered, and any observations or reactions.
Training and Education
Proper training and education are essential for anyone who will be administering intramuscular injections. This training should cover the anatomy of the injection sites, the proper technique for administering injections, how to handle potential complications, and the importance of maintaining a clean and safe environment for the procedure. Ongoing education and practice can help ensure that skills are maintained and that the latest best practices are being followed.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, intramuscular injections are a valuable tool in medical treatment, offering a direct and effective way to administer medications and vaccines. However, their administration requires careful attention to detail, a thorough understanding of the proper technique, and a commitment to safety and hygiene. As medical science continues to evolve, it's likely that new techniques and technologies will emerge that can further improve the safety and efficacy of intramuscular injections. For now, adhering to established best practices and guidelines is crucial for minimizing risks and maximizing benefits.
Final Thoughts
The safety of intramuscular injections is a shared responsibility between healthcare providers and the recipients of these injections. By understanding the proper techniques, being aware of potential complications, and following best practices, we can work together to ensure that intramuscular injections are administered safely and effectively. Whether you are a healthcare professional or someone who will be receiving an intramuscular injection, taking the time to learn about this procedure can help alleviate fears and promote a smoother, more successful experience.What are the most common sites for intramuscular injections?
+The most common sites for intramuscular injections are the deltoid muscle in the upper arm, the vastus lateralis muscle in the thigh, and the gluteus maximus muscle in the buttocks.
How can I prevent infection after an intramuscular injection?
+To prevent infection, keep the injection site clean, avoid touching the area, and monitor for signs of infection such as redness, swelling, or increased pain.
What should I do if I experience pain or swelling after an intramuscular injection?
+If you experience significant pain or swelling, apply ice to the area, elevate it if possible, and contact your healthcare provider for further instructions.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with intramuscular injections. Your insights can help others understand the importance of proper technique and safety measures. If you have any questions or concerns, please don't hesitate to reach out. Together, we can promote safer and more effective use of intramuscular injections in medical care.
