Intro
Discover effective Staph Infection Treatment options, including antibiotics, home remedies, and prevention methods to combat MRSA, boils, and cellulitis, and learn how to manage symptoms and promote healing with our comprehensive guide.
Staph infections are a type of bacterial infection caused by Staphylococcus bacteria, which can be found on the skin and in the noses of healthy individuals. However, when these bacteria enter the body through cuts or other openings, they can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe. In recent years, the rise of antibiotic-resistant staph bacteria, such as MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), has made treatment more challenging. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for staph infections is crucial for effective management and prevention.
The importance of addressing staph infections lies in their potential to cause serious health complications, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly, young children, and those with chronic illnesses. Prompt and appropriate treatment can significantly reduce the risk of complications and improve outcomes. Moreover, with the increasing concern about antibiotic resistance, it's essential to use antibiotics judiciously and explore alternative treatments where possible.
Staph infections can manifest in various forms, including skin infections, respiratory infections, and food poisoning, among others. Each type of infection requires a tailored approach to treatment, emphasizing the need for accurate diagnosis. Healthcare professionals play a critical role in diagnosing staph infections, often through a combination of physical examination, laboratory tests, and medical history. Early detection and treatment are key to preventing the spread of infection and reducing the risk of severe complications.
Understanding Staph Infections
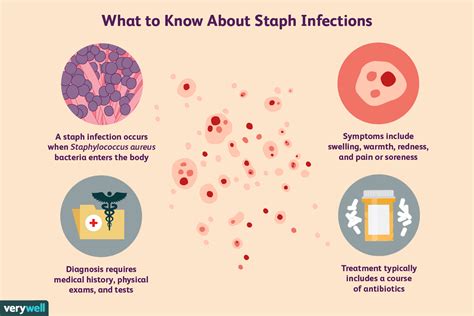
Understanding the basics of staph infections is the first step towards effective management. Staphylococcus bacteria are commonly found on the skin and mucous membranes of humans and animals. While they are typically harmless, they can cause infection if they enter the body through a cut or other opening. The symptoms of a staph infection can vary widely, depending on the location and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include redness, swelling, and pain at the site of infection, as well as fever and general feeling of illness.
Types of Staph Infections
Staph infections can be categorized into several types, based on the location and severity of the infection. Skin infections, such as boils, impetigo, and cellulitis, are the most common types of staph infections. These infections can range from mild to severe and may require antibiotic treatment. Respiratory infections, such as pneumonia, can also be caused by staph bacteria, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems. Food poisoning is another common type of staph infection, often caused by eating foods contaminated with staph bacteria.Treatment Options for Staph Infections

The treatment of staph infections depends on the severity and location of the infection, as well as the type of bacteria causing the infection. For mild skin infections, treatment may involve applying warm compresses to the affected area and keeping the area clean and dry. For more severe infections, antibiotic treatment may be necessary. However, with the rise of antibiotic-resistant staph bacteria, treatment can be challenging. In such cases, healthcare professionals may need to use alternative antibiotics or combinations of antibiotics to effectively treat the infection.
Antibiotic Treatment
Antibiotic treatment is often necessary for staph infections, particularly for severe or widespread infections. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type of bacteria causing the infection and the severity of the infection. For MRSA infections, alternative antibiotics such as vancomycin or linezolid may be used. It's essential to complete the full course of antibiotic treatment, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication, to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.Prevention and Management

Preventing staph infections is crucial, especially in healthcare settings and among individuals with weakened immune systems. Good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing and proper wound care, can significantly reduce the risk of infection. Avoiding close contact with individuals who have staph infections can also help prevent the spread of infection. In healthcare settings, strict infection control measures, including the use of personal protective equipment and proper cleaning and disinfection of surfaces, are essential for preventing the spread of staph infections.
Home Remedies and Self-Care
For mild staph infections, home remedies and self-care measures can be effective in managing symptoms and promoting healing. Applying warm compresses to the affected area, keeping the area clean and dry, and using over-the-counter pain relievers can help alleviate symptoms. It's also essential to practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, to prevent the spread of infection.Complications and Risks
If left untreated or inadequately treated, staph infections can lead to serious complications, including sepsis, endocarditis, and osteomyelitis. Sepsis, a life-threatening condition that occurs when the infection spreads to the bloodstream, requires prompt medical attention. Endocarditis, an infection of the heart valves, can be a complication of staph infections, particularly in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions. Osteomyelitis, an infection of the bone, can occur when staph bacteria spread to the bone, often through the bloodstream.
Risk Factors
Certain individuals are at higher risk of developing staph infections, including those with weakened immune systems, such as the elderly, young children, and individuals with chronic illnesses. Athletes and individuals who participate in contact sports are also at higher risk, as are individuals who have undergone surgery or have medical devices, such as catheters or prosthetic joints.Current Research and Developments

Researchers are continually working to develop new treatments and prevention strategies for staph infections. The development of new antibiotics and alternative therapies, such as bacteriophage therapy, offers hope for more effective treatment of antibiotic-resistant staph infections. Additionally, research into the genetic mechanisms of staph bacteria and the development of vaccines against staph infections is ongoing.
Future Directions
As the concern about antibiotic resistance continues to grow, it's essential to explore alternative approaches to treating staph infections. The development of new antibiotics and therapies, as well as the use of existing antibiotics in a more judicious and responsible manner, will be crucial in the future management of staph infections. Public awareness and education about the risks of antibiotic resistance and the importance of proper hygiene and infection control practices will also play a vital role in preventing the spread of staph infections.Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, staph infections are a significant public health concern, requiring prompt and effective treatment to prevent serious complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for staph infections, individuals can take steps to protect themselves and their loved ones. It's essential to practice good hygiene, seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen, and adhere to antibiotic treatment regimens as prescribed by healthcare professionals.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with staph infections in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards preventing the spread of staph infections and promoting effective management and treatment.
What are the symptoms of a staph infection?
+The symptoms of a staph infection can vary widely, depending on the location and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include redness, swelling, and pain at the site of infection, as well as fever and general feeling of illness.
How are staph infections treated?
+The treatment of staph infections depends on the severity and location of the infection, as well as the type of bacteria causing the infection. For mild skin infections, treatment may involve applying warm compresses to the affected area and keeping the area clean and dry. For more severe infections, antibiotic treatment may be necessary.
How can I prevent staph infections?
+Preventing staph infections is crucial, especially in healthcare settings and among individuals with weakened immune systems. Good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing and proper wound care, can significantly reduce the risk of infection. Avoiding close contact with individuals who have staph infections can also help prevent the spread of infection.
What are the complications of untreated staph infections?
+If left untreated or inadequately treated, staph infections can lead to serious complications, including sepsis, endocarditis, and osteomyelitis. Sepsis, a life-threatening condition that occurs when the infection spreads to the bloodstream, requires prompt medical attention.
Are there any new developments in the treatment of staph infections?
+Researchers are continually working to develop new treatments and prevention strategies for staph infections. The development of new antibiotics and alternative therapies, such as bacteriophage therapy, offers hope for more effective treatment of antibiotic-resistant staph infections.
