Intro
The importance of testing for herpes cannot be overstated, as it is a highly prevalent and often asymptomatic infection that can have serious health consequences if left undiagnosed and untreated. Herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), which can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, mucous membranes, and nervous system. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 67% of people under the age of 50 worldwide are infected with HSV-1, while 11% are infected with HSV-2. The prevalence of herpes highlights the need for accurate and reliable testing methods to diagnose and manage the infection.
Testing for herpes is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions that may have similar symptoms. Secondly, it enables healthcare providers to develop an effective treatment plan and prevent the spread of the infection to others. Finally, testing for herpes can help to reduce the risk of complications, such as neonatal herpes, which can occur when an infected mother passes the virus to her baby during childbirth. With the advancement of medical technology, various testing methods are now available to diagnose herpes, including blood tests, swab tests, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests.
The availability of these testing methods has made it easier for individuals to get tested and take control of their health. However, many people are still unaware of the importance of testing for herpes or are hesitant to get tested due to fear, stigma, or lack of access to healthcare services. It is essential to raise awareness about the importance of testing for herpes and to promote education and prevention efforts to reduce the spread of the infection. By understanding the different testing methods and their benefits, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and take steps to protect themselves and others from the risks associated with herpes.
Types of Herpes Tests
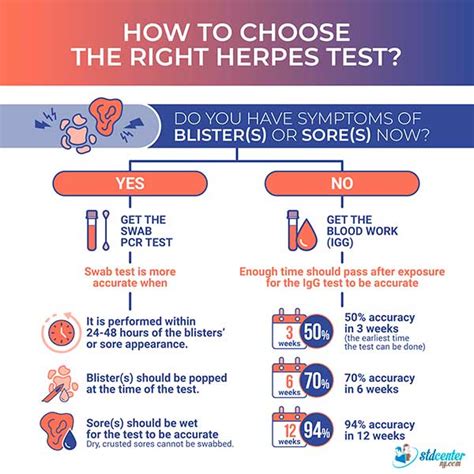
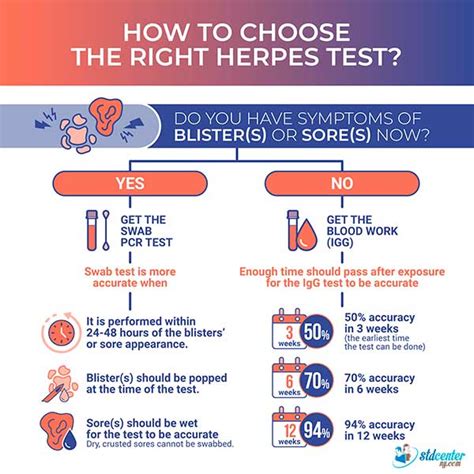
There are several types of tests available to diagnose herpes, each with its own advantages and limitations. The most commonly used tests include blood tests, swab tests, and PCR tests. Blood tests, also known as serology tests, detect the presence of antibodies against the herpes virus in the blood. These tests can identify whether an individual has been infected with herpes in the past, but they may not detect the virus during the early stages of infection. Swab tests, on the other hand, involve collecting a sample of cells or fluid from the affected area and testing it for the presence of the herpes virus. PCR tests are highly sensitive and can detect the virus in the blood, cerebrospinal fluid, or other bodily fluids.
Blood Tests for Herpes
Blood tests are widely used to diagnose herpes, as they are relatively inexpensive and easy to perform. There are two types of blood tests: type-specific and non-type-specific. Type-specific tests can distinguish between HSV-1 and HSV-2, while non-type-specific tests detect the presence of antibodies against the herpes virus without identifying the specific type. Blood tests are usually performed during the acute phase of infection, when the symptoms are most severe, and can provide a diagnosis within 1-2 weeks.Swab Tests for Herpes
Swab tests are used to collect a sample of cells or fluid from the affected area, such as the skin, mucous membranes, or genital areas. The sample is then tested for the presence of the herpes virus using a variety of techniques, including PCR, culture, or antigen detection. Swab tests are highly sensitive and can detect the virus during the early stages of infection, making them useful for diagnosing genital herpes and other types of herpes infections.How to Get Tested for Herpes
Getting tested for herpes is a straightforward process that involves visiting a healthcare provider or a testing center. The healthcare provider will typically ask questions about the individual's medical history, symptoms, and risk factors for herpes. A physical examination may also be performed to look for signs of infection, such as blisters, sores, or rashes. The healthcare provider will then collect a sample of blood, cells, or fluid from the affected area and send it to a laboratory for testing.
Where to Get Tested for Herpes
There are several options for getting tested for herpes, including healthcare provider offices, clinics, and testing centers. Many healthcare providers offer herpes testing as part of their routine services, while others may specialize in sexually transmitted infections (STIs) or infectious diseases. Testing centers, such as those operated by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), may also offer free or low-cost testing for herpes and other STIs.What to Expect During a Herpes Test
During a herpes test, the healthcare provider will typically collect a sample of blood, cells, or fluid from the affected area. The sample may be collected using a swab, needle, or other medical device. The healthcare provider may also perform a physical examination to look for signs of infection. The test results are usually available within 1-2 weeks, although some tests may provide faster results.Interpreting Herpes Test Results
Interpreting herpes test results can be complex, as the results may indicate the presence of antibodies against the herpes virus, the presence of the virus itself, or the presence of other conditions that may have similar symptoms. A positive test result indicates that the individual has been infected with herpes, while a negative test result indicates that the individual has not been infected. However, a negative test result does not necessarily rule out the presence of herpes, as the virus may not be detectable during the early stages of infection.
Understanding False Negatives and False Positives
False negatives and false positives are possible with herpes testing, as with any medical test. A false negative occurs when the test result is negative, but the individual is actually infected with herpes. A false positive occurs when the test result is positive, but the individual is not infected with herpes. False negatives and false positives can occur due to a variety of factors, including the timing of the test, the type of test used, and the presence of other conditions that may interfere with the test results.What to Do If You Test Positive for Herpes
If you test positive for herpes, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to discuss treatment options and prevent the spread of the infection to others. The healthcare provider may prescribe antiviral medications to reduce the severity and frequency of symptoms, as well as to prevent the transmission of the virus to others. It is also essential to practice safe sex, use condoms, and avoid sharing personal items to reduce the risk of transmission.Preventing the Spread of Herpes

Preventing the spread of herpes is crucial to reducing the risk of transmission and protecting others from infection. The most effective way to prevent the spread of herpes is to practice safe sex, use condoms, and avoid sharing personal items. It is also essential to avoid touching the affected area and to wash your hands frequently to prevent the spread of the virus.
Reducing the Risk of Transmission
Reducing the risk of transmission is essential to preventing the spread of herpes. This can be achieved by practicing safe sex, using condoms, and avoiding sharing personal items. It is also essential to avoid touching the affected area and to wash your hands frequently to prevent the spread of the virus. Additionally, individuals with herpes should inform their partners about their condition and take steps to prevent transmission, such as using condoms and avoiding sex during outbreaks.Living with Herpes
Living with herpes can be challenging, but it is manageable with the right treatment and support. Individuals with herpes should consult with a healthcare provider to discuss treatment options and prevent the spread of the infection to others. It is also essential to practice self-care, manage stress, and maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce the severity and frequency of symptoms.What are the symptoms of herpes?
+The symptoms of herpes may include blisters, sores, or rashes on the skin or mucous membranes, as well as fever, headache, and fatigue.
How is herpes transmitted?
+Herpes is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact with an infected person, including sexual contact, kissing, or touching the affected area.
Can herpes be cured?
+Herpes cannot be cured, but it can be managed with antiviral medications and lifestyle changes to reduce the severity and frequency of symptoms.
How can I prevent the spread of herpes?
+Preventing the spread of herpes can be achieved by practicing safe sex, using condoms, and avoiding sharing personal items, as well as avoiding touching the affected area and washing your hands frequently.
What are the complications of herpes?
+The complications of herpes may include neonatal herpes, encephalitis, and meningitis, as well as increased risk of HIV transmission and other STIs.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of herpes testing and its importance in preventing the spread of the infection. If you have any questions or concerns about herpes testing, please do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider or a testing center. Remember, getting tested for herpes is the first step towards taking control of your health and protecting yourself and others from the risks associated with this infection. Share this article with your friends and family to raise awareness about the importance of herpes testing and to promote education and prevention efforts. Together, we can reduce the spread of herpes and create a healthier and safer community for everyone.
