Intro
Discover the truth about Hydrocodone, a medication containing Codeine, and its effects, interactions, and risks, including opioid addiction and overdose, to make informed decisions about pain management and treatment options.
The importance of understanding the composition of medications cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to prescription drugs like hydrocodone. Hydrocodone is a widely prescribed opioid medication used for managing pain and coughs. However, there's a common misconception that hydrocodone contains codeine, which is another type of opioid. This confusion can stem from the fact that both hydrocodone and codeine are used for similar medical purposes and are classified under the opioid category. Understanding the difference and the actual composition of hydrocodone is crucial for patients, medical professionals, and anyone interested in pharmacology.
The medical field relies heavily on the precise classification and understanding of drugs to ensure safety and efficacy. Hydrocodone and codeine, while both opioids, have distinct differences in their chemical structure, usage, and effects on the body. Codeine is often used for mild to moderate pain relief and is known for its antitussive (cough suppressant) properties. On the other hand, hydrocodone is more potent and is commonly prescribed for moderate to severe pain. It's also used in combination with other ingredients in cough medicines.
Despite their differences, both hydrocodone and codeine are subject to strict regulation due to their potential for abuse and dependence. The misconception that hydrocodone contains codeine may arise from the fact that hydrocodone is sometimes compared to codeine in terms of its effects and potency. However, hydrocodone is a semi-synthetic opioid derived from codeine, meaning it is manufactured from codeine but has distinct chemical and pharmacological properties. This derivation process involves chemical modifications that result in a compound with different properties and uses.
Understanding Hydrocodone
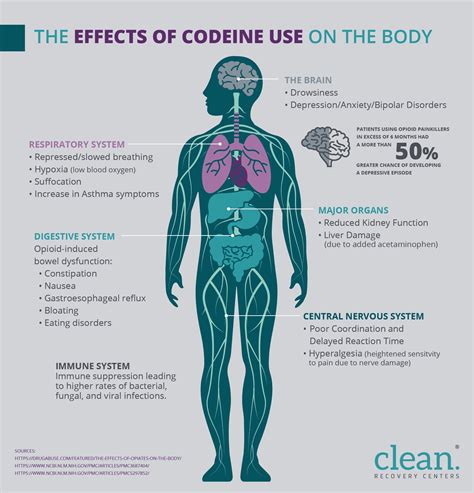
Hydrocodone works by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, altering the perception of and response to pain. It is often combined with other pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen to enhance its pain-relieving effects. The combination of hydrocodone with other medications is common in prescription pain management regimens. Understanding how hydrocodone works and its potential interactions with other drugs is essential for safe and effective use.
Benefits and Risks of Hydrocodone
The benefits of hydrocodone include its effectiveness in managing moderate to severe pain, which can significantly improve the quality of life for patients suffering from chronic pain or recovering from surgery. However, like all opioid medications, hydrocodone carries the risk of dependence, addiction, and overdose. These risks necessitate careful monitoring and adherence to prescribed dosages.Codeine and Its Uses
Codeine is used for the treatment of mild to moderate pain and as a cough suppressant. It is less potent than hydrocodone and is often used in over-the-counter (OTC) medications. Codeine's antitussive effects make it particularly useful in relieving dry, irritating coughs. However, its use is also subject to caution due to the risk of dependence and side effects such as constipation, drowsiness, and nausea.
Differences Between Hydrocodone and Codeine
Key differences between hydrocodone and codeine include their potency, with hydrocodone being significantly stronger, and their usage, with hydrocodone typically prescribed for more severe pain. While codeine is used for mild pain and cough suppression, hydrocodone is reserved for more serious pain management needs. Understanding these differences is crucial for healthcare providers to make informed decisions about patient care and for patients to understand their treatment plans.Working Mechanisms of Opioids
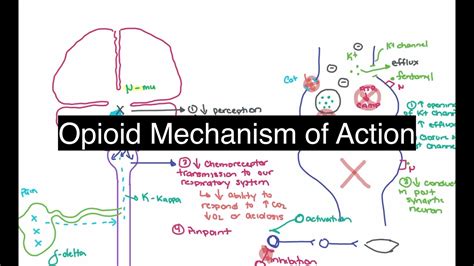
Opioids, including hydrocodone and codeine, work by interacting with opioid receptors in the body. These receptors are found in the brain, spinal cord, and other areas, and they play a role in pain perception and emotional response. When an opioid binds to these receptors, it can block the transmission of pain signals to the brain, providing relief. This mechanism is the basis for the therapeutic effects of opioids but also underlies their potential for abuse and dependence.
Steps for Safe Use
For safe use of hydrocodone or codeine, patients should: - Follow the prescription instructions carefully. - Not exceed the recommended dose. - Be aware of potential interactions with other medications. - Monitor for signs of dependence or addiction. - Seek medical help if experiencing side effects or concerns.Practical Examples and Statistical Data

The importance of understanding and properly managing opioid use is underscored by statistical data on opioid misuse and overdose. For example, according to various health reports, the misuse of prescription opioids is a significant public health concern, leading to thousands of deaths annually. Practical examples of safe opioid use include adhering to prescribed dosages, storing medications securely, and disposing of unused pills properly.
Benefits of Proper Management
Proper management of opioids like hydrocodone and codeine can lead to effective pain relief without the risks associated with misuse. This includes benefits such as improved quality of life for patients, reduced risk of addiction, and decreased incidence of opioid-related emergencies.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, while hydrocodone does not contain codeine, understanding the differences and similarities between these two opioids is crucial for safe and effective use. Future directions in pain management may include the development of new, safer opioids or alternative therapies that can provide relief without the risk of dependence. As research continues, it's essential for patients, healthcare providers, and policymakers to work together to address the complexities of opioid use and misuse.
Call to Action
Readers are encouraged to share their thoughts and experiences with opioid use and management in the comments below. By engaging in open and informed discussions, we can work towards a better understanding of these medications and their role in healthcare. Additionally, readers can support initiatives aimed at improving pain management practices and reducing the risks associated with opioid misuse.What is the main difference between hydrocodone and codeine?
+Hydrocodone and codeine differ in potency and usage, with hydrocodone being stronger and used for more severe pain, while codeine is used for mild to moderate pain and as a cough suppressant.
Can hydrocodone be used for cough suppression?
+Yes, hydrocodone can be used for cough suppression, especially in combination with other ingredients, but it is generally reserved for more severe cases where codeine may not be sufficient.
How can I safely use opioids like hydrocodone or codeine?
+To safely use opioids, follow your prescription carefully, do not exceed the recommended dose, be aware of potential interactions with other medications, and monitor for signs of dependence or addiction.
