Intro
Recognize 7 hypoglycemia signs, including dizziness, shakiness, and confusion, to manage low blood sugar levels, preventing severe symptoms like seizures and loss of consciousness, and maintain overall health and wellness.
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, is a common health issue that can affect anyone, particularly those with diabetes. It occurs when the level of glucose in the blood falls below a certain threshold, typically below 70 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Recognizing the signs of hypoglycemia is crucial, as prompt treatment can help prevent serious complications. In this article, we will delve into the importance of understanding hypoglycemia, its causes, and the 7 key signs that indicate low blood sugar levels.
The importance of recognizing hypoglycemia signs cannot be overstated. If left untreated, low blood sugar can lead to confusion, seizures, loss of consciousness, and even death. Therefore, it is essential to be aware of the warning signs and take immediate action when they occur. People with diabetes, especially those taking insulin or certain oral medications, are at a higher risk of developing hypoglycemia. However, it can also affect individuals without diabetes, particularly after intense exercise, fasting, or consuming excessive alcohol.
Understanding the causes of hypoglycemia is also vital in preventing and managing the condition. For individuals with diabetes, hypoglycemia can be caused by taking too much diabetes medication, skipping meals, or engaging in strenuous physical activity without adjusting medication or food intake. In people without diabetes, hypoglycemia can be triggered by certain medications, critical illnesses, or rare disorders that affect hormone production. By recognizing the underlying causes and being aware of the signs of hypoglycemia, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage the condition.
Introduction to Hypoglycemia

Causes of Hypoglycemia

Diabetic Causes of Hypoglycemia
Individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing hypoglycemia due to the medications they take to manage their condition. Insulin and certain oral medications can cause blood sugar levels to drop, particularly if taken in excess or without adequate food intake. Additionally, people with diabetes may experience hypoglycemia due to delayed or skipped meals, inadequate carbohydrate intake, or excessive physical activity without proper adjustments to medication or food.Non-Diabetic Causes of Hypoglycemia
In people without diabetes, hypoglycemia can be caused by various factors, including certain medications, critical illnesses, or rare disorders that affect hormone production. For example, some medications used to treat conditions such as cancer, HIV, or tuberculosis can cause hypoglycemia as a side effect. Critical illnesses, such as sepsis or severe burns, can also lead to hypoglycemia due to the body's increased glucose demands. Rare disorders, such as insulinoma or adrenal insufficiency, can cause hypoglycemia due to abnormal hormone production.7 Key Signs of Hypoglycemia

- Shakiness or Tremors: One of the earliest signs of hypoglycemia is shakiness or tremors, particularly in the hands. This is caused by the body's release of stress hormones, such as adrenaline, in response to low blood sugar.
- Sweating: Hypoglycemia can cause excessive sweating, particularly on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, and armpits. This is also a result of the body's stress response to low blood sugar.
- Hunger or Nausea: People with hypoglycemia often experience hunger or nausea, particularly after eating. This is because the body is unable to regulate blood sugar levels, leading to a rapid drop in glucose levels after meals.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Hypoglycemia can cause dizziness or lightheadedness, particularly when standing up or changing positions quickly. This is due to the brain's reduced ability to function properly with low blood sugar.
- Confusion or Disorientation: As hypoglycemia worsens, individuals may experience confusion or disorientation, making it difficult to concentrate or make decisions. This is a result of the brain's impaired function due to low blood sugar.
- Slurred Speech: Hypoglycemia can cause slurred speech, as the brain's ability to coordinate muscle movements is impaired. This can make it difficult for individuals to communicate effectively.
- Loss of Consciousness: In severe cases of hypoglycemia, individuals may lose consciousness, which can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. This is a result of the brain's complete inability to function with critically low blood sugar levels.
Treatment and Prevention of Hypoglycemia
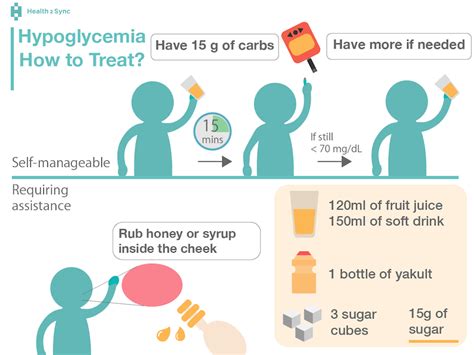
Preventing hypoglycemia is also crucial, particularly for individuals with diabetes. This can be achieved by:
- Eating regular meals and snacks to maintain stable blood sugar levels
- Adjusting medication or food intake in response to physical activity or changes in schedule
- Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly to detect early signs of hypoglycemia
- Carrying a fast-acting carbohydrate source, such as glucose tablets or juice, at all times
Conclusion and Next Steps

We encourage you to share this article with friends and family to raise awareness about hypoglycemia and its importance. If you have any questions or concerns, please comment below, and we will be happy to help. Remember, prompt recognition and treatment of hypoglycemia can save lives, so stay informed and take action today!
What are the most common causes of hypoglycemia in people with diabetes?
+The most common causes of hypoglycemia in people with diabetes include taking too much insulin or oral diabetes medications, skipping meals, and engaging in strenuous physical activity without adjusting medication or food intake.
Can hypoglycemia occur in people without diabetes?
+Yes, hypoglycemia can occur in people without diabetes, particularly after intense exercise, fasting, or consuming excessive alcohol. Certain medications, critical illnesses, or rare disorders that affect hormone production can also cause hypoglycemia in people without diabetes.
What is the best way to treat hypoglycemia?
+The most effective treatment for hypoglycemia is the "15-15 rule," which involves consuming 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets or juice, and re-checking blood sugar levels after 15 minutes. If blood sugar levels remain low, the process is repeated until levels return to normal.
How can I prevent hypoglycemia?
+Preventing hypoglycemia involves eating regular meals and snacks to maintain stable blood sugar levels, adjusting medication or food intake in response to physical activity or changes in schedule, monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, and carrying a fast-acting carbohydrate source at all times.
What are the symptoms of severe hypoglycemia?
+The symptoms of severe hypoglycemia include confusion, seizures, loss of consciousness, and even death if left untreated. It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms.
