Intro
Learn optimal blood sugar levels and management with our comprehensive guide, covering normal ranges, glucose monitoring, and healthy targets to maintain stable blood glucose, preventing diabetes and related complications.
Maintaining ideal blood sugar levels is crucial for overall health and well-being. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When blood sugar levels are too high or too low, it can lead to various health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, and nerve damage. Understanding the importance of blood sugar control can help individuals take proactive steps to manage their levels and reduce the risk of related health issues.
The human body is designed to regulate blood sugar levels within a specific range. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose from the blood. As glucose enters the cells, blood sugar levels decrease. On the other hand, when blood sugar levels drop, the pancreas releases glucagon, a hormone that stimulates the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream. This delicate balance is essential for maintaining ideal blood sugar levels.
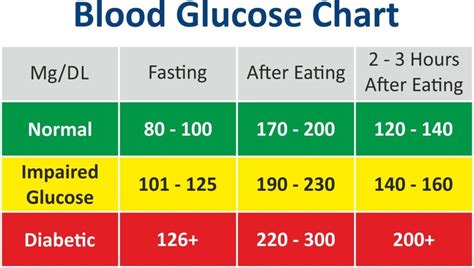
Ideal blood sugar levels can vary depending on factors such as age, medication, and overall health. However, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) provides general guidelines for blood sugar targets. For people without diabetes, a normal blood sugar level is typically between 70 and 99 mg/dL before meals and less than 140 mg/dL after meals. Understanding these guidelines can help individuals make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and lifestyle habits to maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
Blood Sugar Basics

Blood sugar management involves understanding the factors that affect blood sugar levels. Carbohydrates, protein, and fat are the three main macronutrients that impact blood sugar. Carbohydrates have the most significant effect, as they are broken down into glucose during digestion. The glycemic index (GI) is a measure of how quickly a carbohydrate raises blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GI, such as white bread and sugary snacks, cause a rapid increase in blood sugar, while foods with a low GI, such as whole grains and non-starchy vegetables, have a more gradual effect.
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including: * Diet: The type and amount of carbohydrates consumed can significantly impact blood sugar levels. * Physical activity: Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. * Stress: Stress can raise blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. * Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood sugar regulation and insulin sensitivity. * Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and some psychiatric medications, can affect blood sugar levels.Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
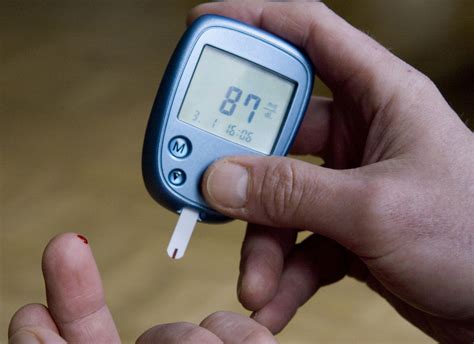
Monitoring blood sugar levels is essential for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. There are several ways to check blood sugar levels, including:
- Fingertip testing: This involves pricking the fingertip with a lancet to collect a blood sample, which is then tested using a glucose meter.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM): CGM devices track blood sugar levels throughout the day and night, providing real-time data and trends.
- Laboratory tests: Healthcare providers may order laboratory tests, such as the hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test, to assess average blood sugar control over a period of time.
Understanding Blood Sugar Test Results
Interpreting blood sugar test results can be complex, but understanding the different metrics can help individuals make informed decisions about their care. The HbA1c test, for example, measures the percentage of glucose that has bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells over the past 2-3 months. An HbA1c level of less than 5.7% is considered normal, while a level of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes.Maintaining Ideal Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining ideal blood sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications. The following strategies can help:
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
- Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Benefits of Maintaining Ideal Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining ideal blood sugar levels can have numerous benefits, including: * Reduced risk of chronic diseases: High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. * Improved energy levels: Stable blood sugar levels can help regulate energy production and reduce fatigue. * Enhanced cognitive function: Maintaining ideal blood sugar levels can support brain health and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.Common Blood Sugar Mistakes

Avoiding common blood sugar mistakes can help individuals maintain ideal levels and reduce the risk of related health issues. Some common mistakes include:
- Skipping meals: Skipping meals can lead to low blood sugar levels and increased cravings for unhealthy snacks.
- Eating too many carbohydrates: Consuming high amounts of carbohydrates can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels.
- Not staying hydrated: Inadequate hydration can disrupt blood sugar regulation and lead to complications.
Avoiding Blood Sugar Mistakes
To avoid common blood sugar mistakes, individuals can: * Eat regular, balanced meals: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods and include a source of protein, healthy fat, and complex carbohydrates at each meal. * Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day and limit sugary drinks. * Monitor blood sugar levels: Regularly check blood sugar levels to identify patterns and make informed decisions about diet and lifestyle habits.Blood Sugar and Exercise
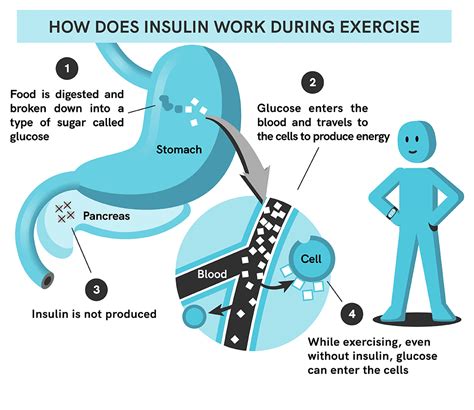
Exercise is a crucial component of blood sugar management. Regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce blood sugar levels, and enhance overall health. The following exercises can be beneficial for blood sugar control:
- Aerobic exercises: Activities like brisk walking, cycling, and swimming can help improve cardiovascular health and reduce blood sugar levels.
- Resistance training: Building muscle through resistance exercises can improve insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake.
- High-intensity interval training (HIIT): HIIT involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by periods of rest and can be effective for improving insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
Exercise and Blood Sugar Tips
To get the most out of exercise for blood sugar control, individuals can: * Consult with a healthcare provider: Before starting a new exercise program, consult with a healthcare provider to discuss any concerns or limitations. * Start slowly: Gradually increase exercise intensity and duration to avoid burnout and prevent low blood sugar levels. * Monitor blood sugar levels: Regularly check blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to identify patterns and make informed decisions about diet and lifestyle habits.Blood Sugar and Nutrition
Nutrition plays a critical role in blood sugar management. A balanced diet that includes a variety of whole, unprocessed foods can help regulate blood sugar levels and provide essential nutrients. The following nutrients can be beneficial for blood sugar control:
- Fiber: Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats, barley, and fruits, can help slow the absorption of glucose and reduce blood sugar levels.
- Protein: Including a source of protein at each meal can help regulate blood sugar levels and provide a feeling of fullness and satisfaction.
- Healthy fats: Foods high in healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation.
Nutrition and Blood Sugar Tips
To make the most of nutrition for blood sugar control, individuals can: * Focus on whole foods: Emphasize whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. * Read labels: Be aware of added sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats in packaged foods. * Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help regulate blood sugar levels and prevent dehydration.Managing Blood Sugar Levels with Medication

For individuals with diabetes or those who require medication to manage blood sugar levels, it is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan. The following medications can be used to manage blood sugar levels:
- Metformin: A common medication for type 2 diabetes that helps improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose production in the liver.
- Sulfonylureas: Medications that stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin.
- Insulin: Hormone replacement therapy for individuals with type 1 diabetes or those with type 2 diabetes who require insulin therapy.
Medication and Blood Sugar Tips
To get the most out of medication for blood sugar control, individuals can: * Take medication as directed: Follow the prescribed dosage and timing to ensure optimal effectiveness. * Monitor blood sugar levels: Regularly check blood sugar levels to identify patterns and make informed decisions about diet and lifestyle habits. * Attend regular check-ups: Schedule regular appointments with a healthcare provider to monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed.What are the ideal blood sugar levels for people without diabetes?
+For people without diabetes, a normal blood sugar level is typically between 70 and 99 mg/dL before meals and less than 140 mg/dL after meals.
How can I maintain ideal blood sugar levels through diet and exercise?
+Maintaining ideal blood sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates a balanced diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, stay hydrated, and engage in regular physical activity to help regulate blood sugar levels.
What are the benefits of maintaining ideal blood sugar levels?
+Maintaining ideal blood sugar levels can have numerous benefits, including reduced risk of chronic diseases, improved energy levels, and enhanced cognitive function.
How can I avoid common blood sugar mistakes?
+To avoid common blood sugar mistakes, individuals can eat regular, balanced meals, stay hydrated, and monitor blood sugar levels regularly. It is also essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan.
What role does exercise play in blood sugar management?
+Exercise is a crucial component of blood sugar management. Regular physical activity can help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce blood sugar levels, and enhance overall health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
In conclusion, maintaining ideal blood sugar levels is essential for overall health and well-being. By understanding the factors that affect blood sugar levels, monitoring levels regularly, and making informed decisions about diet and lifestyle habits, individuals can reduce the risk of related health issues and improve their quality of life. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and experiences with blood sugar management in the comments below and to explore our website for more information on this topic.
