Intro
Discover causes of low MPV blood count, including thrombocytopenia, anemia, and bone marrow disorders, and learn about related conditions like platelet count and mean platelet volume.
Mean platelet volume (MPV) is a measure of the average size of platelets in the blood. Platelets are small cells that play a crucial role in blood clotting, and their size can be an indicator of various health conditions. A low MPV blood count, also known as thrombocytopenia, occurs when the platelet count is below the normal range, which is typically between 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. In this article, we will delve into the causes of a low MPV blood count, its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
A low MPV blood count can be caused by various factors, including bone marrow disorders, autoimmune diseases, certain medications, and infections. When the bone marrow is not producing enough platelets, it can lead to a low MPV blood count. This can be due to conditions such as leukemia, lymphoma, or aplastic anemia. Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Hashimoto's thyroiditis can also cause the immune system to attack and destroy platelets, leading to a low MPV blood count.
Certain medications, such as heparin, aspirin, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can also cause a low MPV blood count by interfering with platelet production or function. Infections like sepsis, malaria, and dengue fever can also lead to a low MPV blood count by causing the bone marrow to produce fewer platelets or by increasing the destruction of platelets.
Causes of Low MPV Blood Count
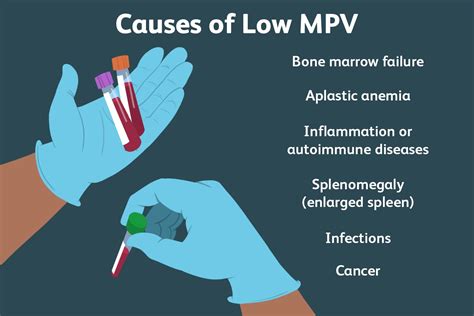
A low MPV blood count can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Bone marrow disorders: Conditions like leukemia, lymphoma, and aplastic anemia can affect the bone marrow's ability to produce platelets.
- Autoimmune diseases: Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and Hashimoto's thyroiditis can cause the immune system to attack and destroy platelets.
- Certain medications: Medications like heparin, aspirin, and NSAIDs can interfere with platelet production or function.
- Infections: Infections like sepsis, malaria, and dengue fever can cause the bone marrow to produce fewer platelets or increase the destruction of platelets.
- Vitamin deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamins like B12 and folate can affect the production of platelets.
- Chronic diseases: Conditions like kidney disease, liver disease, and HIV/AIDS can increase the risk of a low MPV blood count.
Symptoms of Low MPV Blood Count
The symptoms of a low MPV blood count can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include: * Easy bruising and bleeding * Prolonged bleeding from cuts or wounds * Petechiae (small red or purple spots on the skin) * Purpura (large purple spots on the skin) * Heavy menstrual bleeding in women * Nosebleeds * Gastrointestinal bleedingDiagnosis of Low MPV Blood Count
Diagnosing a low MPV blood count typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The following tests may be used to diagnose a low MPV blood count:
- Complete blood count (CBC): This test measures the levels of different blood cells, including platelets.
- Blood smear: This test involves examining a sample of blood under a microscope to look for abnormalities in platelets.
- Bone marrow biopsy: This test involves removing a sample of bone marrow tissue to examine for abnormalities in platelet production.
- Platelet count: This test measures the number of platelets in the blood.
Treatment Options for Low MPV Blood Count
The treatment for a low MPV blood count depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. The following are some common treatment options: * Medications: Medications like corticosteroids and immunoglobulins can help increase platelet production or reduce the destruction of platelets. * Platelet transfusions: In severe cases, platelet transfusions may be necessary to increase the number of platelets in the blood. * Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the spleen, which can help increase platelet production. * Lifestyle changes: Making lifestyle changes like avoiding certain medications, eating a healthy diet, and managing stress can help manage a low MPV blood count.Complications of Low MPV Blood Count
A low MPV blood count can increase the risk of several complications, including:
- Bleeding disorders: A low MPV blood count can increase the risk of bleeding disorders like hemophilia.
- Infections: A low MPV blood count can increase the risk of infections, particularly those that affect the bone marrow.
- Anemia: A low MPV blood count can increase the risk of anemia, which can lead to fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
- Organ damage: In severe cases, a low MPV blood count can cause damage to organs like the kidneys, liver, and spleen.
Prevention of Low MPV Blood Count
Preventing a low MPV blood count involves managing the underlying cause and making lifestyle changes to promote healthy platelet production. The following are some ways to prevent a low MPV blood count: * Avoiding certain medications: Avoiding medications that can interfere with platelet production or function can help prevent a low MPV blood count. * Eating a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help promote healthy platelet production. * Managing stress: Managing stress through techniques like meditation and yoga can help reduce the risk of a low MPV blood count. * Getting regular check-ups: Getting regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect a low MPV blood count early, when it is easier to treat.Living with Low MPV Blood Count
Living with a low MPV blood count requires careful management and lifestyle changes to prevent complications. The following are some tips for living with a low MPV blood count:
- Avoiding heavy lifting and bending: Avoiding heavy lifting and bending can help reduce the risk of bleeding and bruising.
- Avoiding certain medications: Avoiding medications that can interfere with platelet production or function can help prevent a low MPV blood count.
- Eating a healthy diet: Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help promote healthy platelet production.
- Getting regular check-ups: Getting regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect any changes in the condition and prevent complications.
Conclusion and Next Steps
A low MPV blood count is a condition that requires careful management and lifestyle changes to prevent complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, individuals can take steps to manage the condition and improve their quality of life. If you have a low MPV blood count, it is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan and make lifestyle changes to promote healthy platelet production.What is a low MPV blood count?
+A low MPV blood count, also known as thrombocytopenia, occurs when the platelet count is below the normal range, which is typically between 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood.
What are the symptoms of a low MPV blood count?
+The symptoms of a low MPV blood count can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, but common symptoms include easy bruising and bleeding, prolonged bleeding from cuts or wounds, and petechiae.
How is a low MPV blood count diagnosed?
+Diagnosing a low MPV blood count typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, including a complete blood count, blood smear, and bone marrow biopsy.
What are the treatment options for a low MPV blood count?
+The treatment for a low MPV blood count depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, but common treatment options include medications, platelet transfusions, and surgery.
Can a low MPV blood count be prevented?
+Preventing a low MPV blood count involves managing the underlying cause and making lifestyle changes to promote healthy platelet production, such as avoiding certain medications, eating a healthy diet, and managing stress.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of low MPV blood count causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may find it helpful. Remember to always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment.
