Intro
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a type of cancer that affects the stomach, which is a vital part of the digestive system. The stomach is responsible for breaking down food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and utilized by the body. Stomach cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the stomach lining grow and multiply uncontrollably, forming a tumor. This type of cancer is more common in certain parts of the world, such as Asia, and is often associated with a poor diet, smoking, and infection with the bacteria Helicobacter pylori.
The importance of understanding stomach cancer cannot be overstated, as it is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), stomach cancer is the fifth most common type of cancer and the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths globally. The disease is often asymptomatic in its early stages, making it difficult to detect and diagnose. As a result, many people are not aware that they have stomach cancer until it has reached an advanced stage, at which point treatment options may be limited.
Stomach cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease that requires a comprehensive approach to prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Research has shown that a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors contribute to the development of stomach cancer. For example, a diet high in salted and smoked foods, as well as a lack of fruits and vegetables, can increase the risk of developing stomach cancer. Additionally, smoking and infection with Helicobacter pylori can also increase the risk of developing the disease. Understanding these risk factors and taking steps to mitigate them can help reduce the incidence of stomach cancer.
Types of Stomach Cancer
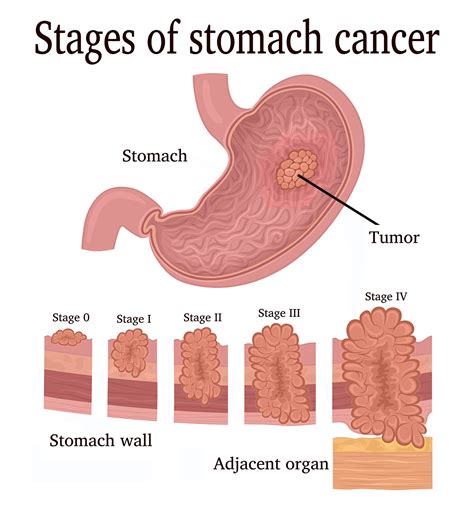
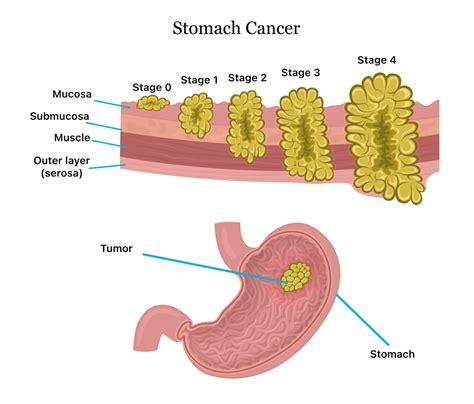
There are several types of stomach cancer, each with distinct characteristics and treatment options. The most common type of stomach cancer is adenocarcinoma, which accounts for about 90% of all stomach cancer cases. Adenocarcinoma arises from the glandular cells in the stomach lining and can be further divided into several subtypes, including intestinal-type and diffuse-type adenocarcinoma. Other types of stomach cancer include lymphoma, which arises from the immune cells in the stomach, and gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), which arises from the connective tissue in the stomach.
Risk Factors for Stomach Cancer
The risk of developing stomach cancer is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Some of the key risk factors for stomach cancer include:- Age: Stomach cancer is more common in older adults, with most cases occurring in people over the age of 50.
- Sex: Men are more likely to develop stomach cancer than women.
- Family history: A family history of stomach cancer can increase the risk of developing the disease.
- Diet: A diet high in salted and smoked foods, as well as a lack of fruits and vegetables, can increase the risk of developing stomach cancer.
- Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of developing stomach cancer.
- Infection with Helicobacter pylori: Infection with this bacteria can increase the risk of developing stomach cancer.
Symptoms of Stomach Cancer
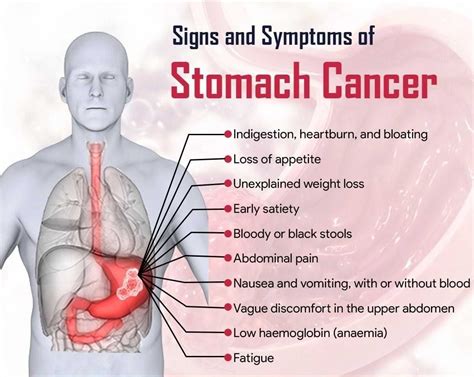
The symptoms of stomach cancer can vary depending on the stage and location of the tumor. Some common symptoms of stomach cancer include:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Bloating and gas
- Difficulty swallowing
Diagnosis of Stomach Cancer
The diagnosis of stomach cancer typically involves a combination of imaging tests, endoscopy, and biopsy. Imaging tests such as computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans can help identify the location and size of the tumor. Endoscopy involves the use of a flexible tube with a camera to visualize the inside of the stomach and take tissue samples. Biopsy involves the examination of tissue samples under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer cells.Treatment Options for Stomach Cancer
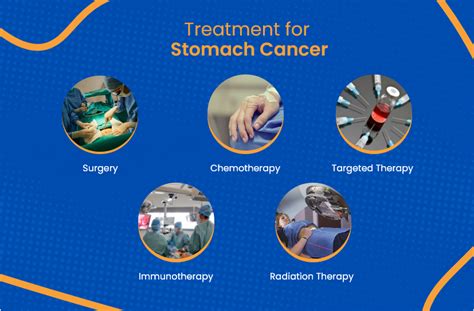
The treatment of stomach cancer depends on the stage and location of the tumor, as well as the overall health of the patient. Some common treatment options for stomach cancer include:
- Surgery: Surgery is often the primary treatment for stomach cancer, involving the removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of medications to kill cancer cells and can be used before or after surgery.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy involves the use of high-energy rays to kill cancer cells and can be used before or after surgery.
- Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy involves the use of medications that specifically target cancer cells and can be used in combination with chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Prevention of Stomach Cancer
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent stomach cancer, there are several steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing the disease. Some of these steps include:- Eating a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce the risk of developing stomach cancer.
- Avoiding smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of developing stomach cancer, so avoiding smoking or quitting if you already smoke can help reduce this risk.
- Getting regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with your doctor can help identify any potential health problems early on, including stomach cancer.
- Avoiding infection with Helicobacter pylori: Avoiding infection with this bacteria can help reduce the risk of developing stomach cancer.
Current Research on Stomach Cancer
Researchers are continually working to improve our understanding of stomach cancer and develop new and more effective treatments. Some current areas of research include:
- Development of new medications: Researchers are working to develop new medications that can target specific molecules involved in the development and growth of stomach cancer.
- Improvement of surgical techniques: Researchers are working to improve surgical techniques, including the use of minimally invasive surgery and robotic surgery.
- Development of new imaging tests: Researchers are working to develop new imaging tests that can help diagnose stomach cancer earlier and more accurately.
Future Directions for Stomach Cancer Treatment
The future of stomach cancer treatment is promising, with several new and innovative treatments on the horizon. Some of these treatments include:- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy involves the use of medications that stimulate the immune system to attack cancer cells.
- Gene therapy: Gene therapy involves the use of medications that can help repair or replace damaged genes that contribute to the development of stomach cancer.
- Stem cell therapy: Stem cell therapy involves the use of stem cells to help repair or replace damaged tissue in the stomach.
What are the symptoms of stomach cancer?
+The symptoms of stomach cancer can vary depending on the stage and location of the tumor, but common symptoms include abdominal pain or discomfort, weight loss, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, bloating and gas, and difficulty swallowing.
How is stomach cancer diagnosed?
+The diagnosis of stomach cancer typically involves a combination of imaging tests, endoscopy, and biopsy. Imaging tests such as computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans can help identify the location and size of the tumor. Endoscopy involves the use of a flexible tube with a camera to visualize the inside of the stomach and take tissue samples. Biopsy involves the examination of tissue samples under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
What are the treatment options for stomach cancer?
+The treatment of stomach cancer depends on the stage and location of the tumor, as well as the overall health of the patient. Some common treatment options for stomach cancer include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy.
We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of stomach cancer, including its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention. If you have any questions or concerns about stomach cancer, we encourage you to speak with your doctor or a qualified healthcare professional. Additionally, we invite you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about stomach cancer, and to join the conversation on social media using the hashtag #stomachcancerawareness. Together, we can work to raise awareness and support research into this important disease.
