Intro
Learn normal infant respiratory rates and signs of distress with our guide, covering newborn breathing patterns, apnea, and respiratory issues, to ensure your babys health and wellbeing.
Infant respiratory rate is a crucial vital sign that indicates the health and well-being of a baby. Monitoring an infant's respiratory rate can help identify potential respiratory problems, such as respiratory distress or failure, which can be life-threatening if left untreated. In this article, we will delve into the importance of infant respiratory rate, its normal range, and how to measure it accurately.
The respiratory system of an infant is still developing, and their lungs are not fully mature until they are about 2-3 years old. As a result, infants are more susceptible to respiratory problems, such as bronchiolitis, pneumonia, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Therefore, it is essential to monitor an infant's respiratory rate closely, especially during the first few months of life. By doing so, parents and healthcare professionals can quickly identify any potential issues and provide timely interventions to prevent complications.
Measuring an infant's respiratory rate can be a challenging task, especially for new parents. However, with the right techniques and tools, it can be done accurately and efficiently. There are several methods to measure an infant's respiratory rate, including visual observation, stethoscope, and pulse oximetry. Visual observation involves counting the number of breaths an infant takes per minute, while a stethoscope can be used to listen to the sounds of an infant's breathing. Pulse oximetry, on the other hand, measures the oxygen saturation of an infant's blood and can provide an indirect estimate of their respiratory rate.
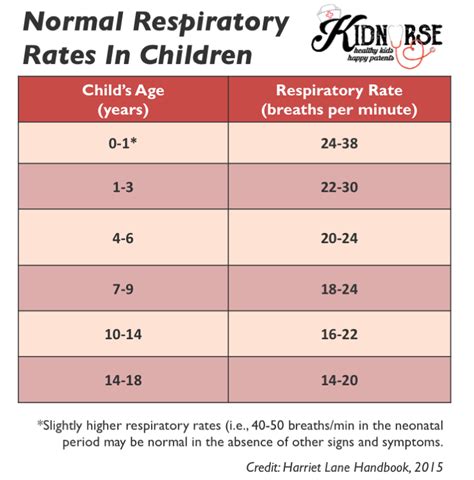
Normal Infant Respiratory Rate
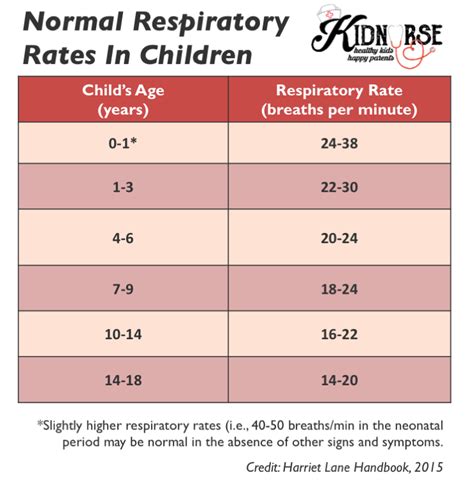
Factors Affecting Infant Respiratory Rate
Several factors can affect an infant's respiratory rate, including their age, weight, and overall health. For example, premature infants tend to have higher respiratory rates than full-term infants, while infants with respiratory problems, such as bronchiolitis or pneumonia, may have faster or slower respiratory rates than normal. Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, can also impact an infant's respiratory rate.Measuring Infant Respiratory Rate
Common Respiratory Problems in Infants
Infants are susceptible to various respiratory problems, including bronchiolitis, pneumonia, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). These conditions can cause symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing, which can be distressing for both the infant and their parents. If an infant is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications and ensure timely treatment.Respiratory Distress in Infants

If an infant is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical help right away. Respiratory distress can be life-threatening if left untreated, and prompt intervention can help prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Prevention and Treatment of Respiratory Problems
Preventing respiratory problems in infants requires a combination of good hygiene practices, immunizations, and environmental measures. Here are some tips to help prevent respiratory problems in infants: * Practice good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with people who are sick * Ensure the infant is up-to-date on all recommended immunizations, including the flu vaccine * Avoid exposure to tobacco smoke and other environmental pollutants * Use a humidifier to maintain a comfortable humidity level in the home * Keep the infant's environment clean and free of dust and allergensConclusion and Next Steps

We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences on infant respiratory rate in the comments section below. If you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of monitoring infant respiratory rate.
What is the normal respiratory rate for a newborn infant?
+The normal respiratory rate for a newborn infant is between 30-60 breaths per minute.
How can I measure my infant's respiratory rate accurately?
+To measure your infant's respiratory rate accurately, choose a quiet and comfortable location, ensure the infant is in a supine position or sitting upright, and count the number of breaths the infant takes per minute using a timer or a watch.
What are the signs of respiratory distress in infants?
+Signs of respiratory distress in infants include fast or slow breathing rate, flaring of the nostrils, retraction of the chest or abdomen, grunting or stridor sounds, and cyanosis (blue discoloration of the skin).
