Intro
Identify 7 iron poisoning symptoms, including fatigue, pale skin, and shortness of breath, and learn about iron overdose effects, toxicity signs, and treatment options to prevent severe health complications.
Iron is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in many bodily functions, including the production of red blood cells and the transportation of oxygen throughout the body. However, excessive iron consumption can lead to iron poisoning, a potentially life-threatening condition. Iron poisoning can occur through various means, such as ingesting iron supplements, exposure to iron-containing substances, or certain medical conditions. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of iron poisoning to seek prompt medical attention.
Iron poisoning can affect anyone, but it is most common in children under the age of 6, as they are more likely to ingest iron supplements or other iron-containing substances. According to the American Association of Poison Control Centers, iron poisoning is one of the leading causes of poisoning in children. In severe cases, iron poisoning can lead to organ failure, coma, and even death. Therefore, it is crucial to be aware of the symptoms of iron poisoning and take immediate action if suspected.
The symptoms of iron poisoning can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's overall health. In the early stages, symptoms may be mild and nonspecific, making it challenging to diagnose iron poisoning. However, as the condition progresses, symptoms can become more severe and life-threatening. Recognizing the symptoms of iron poisoning is critical to preventing long-term damage and ensuring prompt medical attention.
Understanding Iron Poisoning
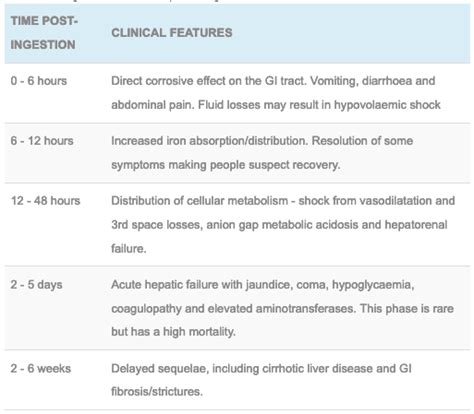
Iron poisoning occurs when the body absorbs too much iron, leading to a buildup of iron in the body's tissues and organs. This can cause damage to the liver, heart, and other vital organs. Iron poisoning can be acute or chronic, depending on the duration and severity of the exposure. Acute iron poisoning occurs when a large amount of iron is ingested in a short period, while chronic iron poisoning occurs when smaller amounts of iron are ingested over an extended period.
Causes of Iron Poisoning
Iron poisoning can be caused by various factors, including: * Ingesting iron supplements or vitamins * Exposure to iron-containing substances, such as iron oxide or iron sulfate * Certain medical conditions, such as hemochromatosis or thalassemia * Accidental ingestion of iron-containing products, such as iron-based pesticides or iron-containing fertilizersSymptoms of Iron Poisoning
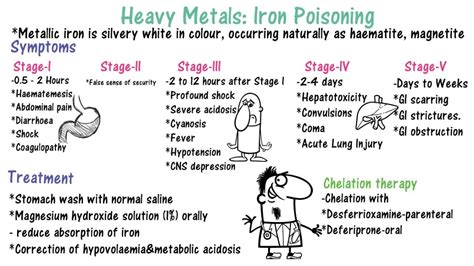
The symptoms of iron poisoning can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's overall health. Common symptoms of iron poisoning include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain and diarrhea
- Fatigue and weakness
- Headache and dizziness
- Rapid heartbeat and palpitations
- Seizures and coma (in severe cases)
Stages of Iron Poisoning
Iron poisoning can progress through several stages, each with distinct symptoms and consequences. The stages of iron poisoning include: 1. **Initial stage**: Symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain occur within 6 hours of iron ingestion. 2. **Shock stage**: Symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, palpitations, and hypotension occur within 12-24 hours of iron ingestion. 3. **Gastrointestinal stage**: Symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting occur within 24-48 hours of iron ingestion. 4. **Cardiovascular stage**: Symptoms such as cardiac arrhythmias, hypotension, and cardiac arrest occur within 48-72 hours of iron ingestion.Diagnosing Iron Poisoning

Diagnosing iron poisoning requires a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The diagnosis of iron poisoning is typically based on:
- Physical examination and medical history
- Laboratory tests, such as serum iron levels, liver function tests, and complete blood counts
- Imaging studies, such as X-rays or CT scans, to evaluate organ damage
Treatment Options for Iron Poisoning
Treatment for iron poisoning depends on the severity of the condition and the individual's overall health. Common treatment options for iron poisoning include: * Supportive care, such as fluid replacement and monitoring of vital signs * Chelation therapy, which involves administering medications that bind to iron and remove it from the body * Gastric lavage, which involves flushing the stomach to remove iron-containing substances * Activated charcoal, which helps absorb iron and prevent further absorptionPreventing Iron Poisoning

Preventing iron poisoning requires awareness and caution when handling iron-containing substances. To prevent iron poisoning:
- Keep iron supplements and vitamins out of reach of children
- Read labels carefully and follow instructions for iron-containing products
- Avoid taking iron supplements or vitamins in excess of recommended doses
- Dispose of iron-containing substances properly
Risk Factors for Iron Poisoning
Certain individuals are at higher risk of iron poisoning, including: * Children under the age of 6 * Pregnant women * Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as hemochromatosis or thalassemia * Individuals taking iron supplements or vitaminsComplications of Iron Poisoning
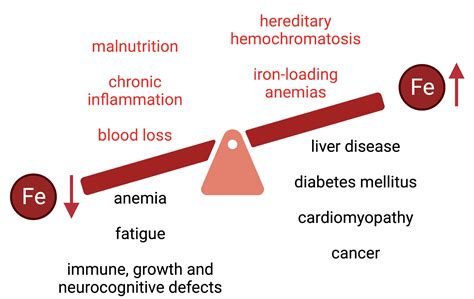
Iron poisoning can lead to various complications, including:
- Organ damage, such as liver or heart damage
- Coma or seizures
- Respiratory failure
- Cardiac arrest
- Death
Long-term Effects of Iron Poisoning
The long-term effects of iron poisoning depend on the severity of the condition and the individual's overall health. Possible long-term effects of iron poisoning include: * Organ damage or failure * Neurological damage or impairment * Increased risk of infections or illnesses * Decreased quality of lifeWhat are the common causes of iron poisoning?
+Iron poisoning can be caused by ingesting iron supplements or vitamins, exposure to iron-containing substances, or certain medical conditions, such as hemochromatosis or thalassemia.
What are the symptoms of iron poisoning?
+The symptoms of iron poisoning include nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea, fatigue and weakness, headache and dizziness, rapid heartbeat and palpitations, and seizures and coma in severe cases.
How is iron poisoning diagnosed?
+Diagnosing iron poisoning requires a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, including serum iron levels, liver function tests, and complete blood counts.
What are the treatment options for iron poisoning?
+Treatment options for iron poisoning include supportive care, chelation therapy, gastric lavage, and activated charcoal, depending on the severity of the condition and the individual's overall health.
How can iron poisoning be prevented?
+Preventing iron poisoning requires awareness and caution when handling iron-containing substances, keeping iron supplements and vitamins out of reach of children, reading labels carefully, and avoiding taking iron supplements or vitamins in excess of recommended doses.
In
Final Thoughts

