Intro
Discover crucial 5 Lyme Disease Facts, including symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, to understand this tick-borne illness and its effects on human health, prevention, and management.
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection that is spread through the bite of an infected tick. It is a significant public health concern, particularly in areas where ticks are common. Despite its prevalence, many people are unaware of the risks and consequences of Lyme disease. In this article, we will delve into the world of Lyme disease, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. By understanding the facts about Lyme disease, individuals can take steps to protect themselves and their loved ones from this potentially debilitating illness.
Lyme disease is a complex and multifaceted condition that affects thousands of people each year. It is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, which is transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected blacklegged tick. The disease can cause a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, joints, and nervous system. As we explore the facts about Lyme disease, it becomes clear that awareness and education are key to preventing and managing this condition.
The importance of understanding Lyme disease cannot be overstated. With its potential to cause long-term health problems and disability, it is essential to take proactive steps to prevent infection and seek medical attention if symptoms arise. By learning about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for Lyme disease, individuals can empower themselves to take control of their health and well-being. In the following sections, we will examine the facts about Lyme disease in greater detail, providing a comprehensive overview of this complex and fascinating topic.
Lyme Disease Causes and Risk Factors
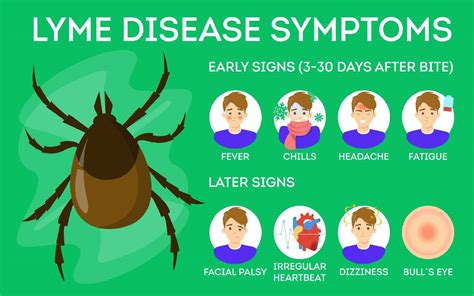
Transmission and Incubation Period
The transmission of Lyme disease typically occurs when an infected tick bites a human and remains attached for a period of 36-48 hours. During this time, the tick can feed on the person's blood and transmit the bacteria into the bloodstream. The incubation period of Lyme disease, which is the time between the tick bite and the onset of symptoms, can range from 3-30 days. Understanding the transmission and incubation period of Lyme disease is crucial for early detection and treatment.Lyme Disease Symptoms and Diagnosis
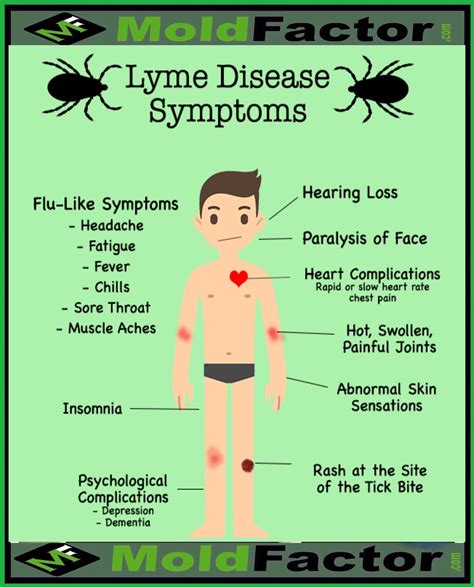
Diagnostic Tests and Challenges
Diagnosing Lyme disease can be challenging, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions. Laboratory tests, such as the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and the Western blot test, can help confirm the presence of Lyme disease. However, these tests are not always accurate, and a diagnosis may be based on a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history, and laboratory results. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms of Lyme disease are present, as early treatment can significantly improve outcomes.Lyme Disease Treatment and Management

Alternative Therapies and Prevention Strategies
In addition to conventional treatment, some people may explore alternative therapies, such as herbal remedies and nutritional supplements, to manage Lyme disease symptoms. However, the effectiveness of these approaches is not well established, and individuals should consult with their healthcare provider before using any alternative therapies. Preventing Lyme disease is also crucial, and strategies such as using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and conducting regular tick checks can help reduce the risk of infection.Lyme Disease Prevention and Awareness

Community-Based Initiatives and Research
Community-based initiatives, such as public awareness campaigns and educational programs, can play a vital role in promoting Lyme disease prevention and awareness. Research into the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of Lyme disease is also ongoing, with scientists exploring new diagnostic tests, therapeutic approaches, and prevention strategies. By supporting these efforts, individuals can contribute to a better understanding of Lyme disease and the development of effective prevention and treatment methods.Lyme Disease and Mental Health
Coping Mechanisms and Support Networks
Coping with Lyme disease requires a range of strategies, including stress management, self-care, and social support. Individuals can benefit from connecting with others who have experienced Lyme disease, either through support groups or online forums. By sharing their experiences and advice, people can help each other navigate the challenges of Lyme disease and promote overall well-being.Lyme Disease and Children

Pediatric Lyme Disease Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing and treating Lyme disease in children can be challenging, as the symptoms may be similar to those of other conditions. Healthcare providers should be aware of the signs and symptoms of Lyme disease in children and use a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and medical history to make an accurate diagnosis. Treatment of Lyme disease in children typically involves antibiotics, and parents should work closely with their healthcare provider to ensure their child receives appropriate care.What are the common symptoms of Lyme disease?
+The common symptoms of Lyme disease include fever, headache, fatigue, and a distinctive rash. As the disease progresses, symptoms can become more severe and may include joint pain, neurological problems, and heart abnormalities.
How is Lyme disease diagnosed?
+Lyme disease is diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as the ELISA and Western blot tests. A diagnosis may also be based on the presence of a distinctive rash and other symptoms.
Can Lyme disease be prevented?
+Yes, Lyme disease can be prevented by taking proactive measures, such as using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and conducting regular tick checks. Avoiding tick habitats and promptly removing attached ticks can also help reduce the risk of infection.
As we conclude our exploration of Lyme disease, it is clear that awareness, education, and prevention are essential for managing this complex and multifaceted condition. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies for Lyme disease, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their loved ones from this potentially debilitating illness. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about Lyme disease in the comments below, and to spread awareness about this important public health concern. Together, we can promote a better understanding of Lyme disease and work towards a future where this condition is preventable and treatable.
