Intro
Discover the potency of 600mg Ibuprofen, a common pain relief dosage, and learn about its effects, benefits, and potential side effects, including inflammation reduction and analgesic properties.
Pain relief is a crucial aspect of managing various health conditions, and ibuprofen is one of the most commonly used over-the-counter medications for this purpose. Ibuprofen belongs to a class of drugs known as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which work by reducing inflammation, pain, and fever. The effectiveness of ibuprofen can depend on several factors, including the dosage, the individual's health status, and the type of pain being treated. One of the frequently asked questions regarding ibuprofen is whether a 600mg dose is considered strong.
Ibuprofen is available in various strengths, ranging from 200mg to 800mg per tablet or capsule. The recommended dosage for adults is typically between 200mg and 400mg every 4 to 6 hours as needed for pain relief, with a maximum daily dose not exceeding 1200mg. However, for more severe pain or conditions such as arthritis, higher doses might be prescribed by a healthcare provider.
A 600mg dose of ibuprofen is indeed on the higher end of the spectrum for over-the-counter use but is within the range that might be prescribed for certain conditions. This dosage can be effective for relieving moderate to severe pain, reducing inflammation, and lowering fever. It is essential to note that the perception of "strong" can vary significantly from person to person, depending on factors such as body weight, metabolism, and individual tolerance to the medication.
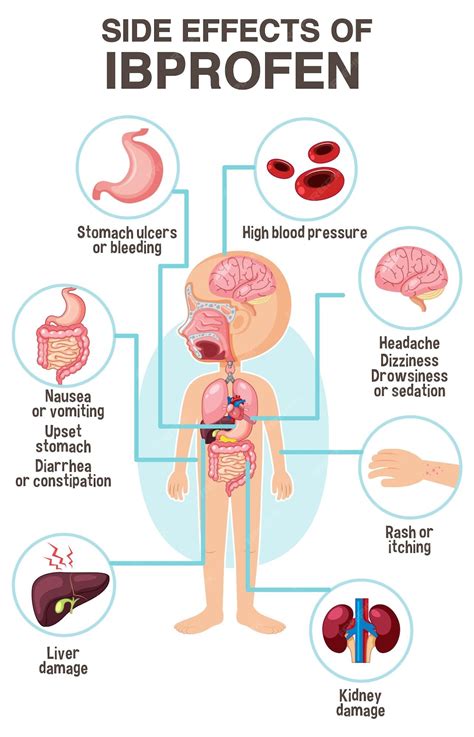
For some individuals, a 600mg dose of ibuprofen may provide adequate relief from their symptoms, while for others, it might not be sufficient, especially if they are dealing with severe or chronic pain. It's also important to consider the potential side effects associated with higher doses of ibuprofen, such as increased risk of gastrointestinal issues, including stomach ulcers and bleeding, as well as effects on kidney function and blood pressure.
How Ibuprofen Works
Ibuprofen works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are chemicals in the body that mediate inflammation, pain, and fever. By blocking the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), ibuprofen reduces the synthesis of prostaglandins, thereby exerting its anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic effects. This mechanism of action is common to all NSAIDs, but the specific potency and duration of action can vary among different drugs within this class.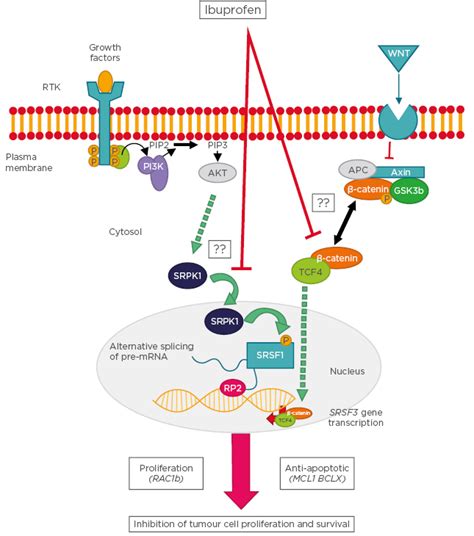
Benefits and Risks of 600mg Ibuprofen
The benefits of taking a 600mg dose of ibuprofen include effective relief from pain and inflammation, which can significantly improve quality of life for individuals suffering from conditions such as arthritis, menstrual cramps, or severe headaches. However, it's crucial to weigh these benefits against the potential risks, especially with long-term or high-dose use. Risks include gastrointestinal complications, renal impairment, and an increased risk of heart attack or stroke, particularly in patients with pre-existing cardiovascular disease.
Guidelines for Safe Use
To use ibuprofen safely and effectively, especially at higher doses like 600mg, it's essential to follow certain guidelines: - Always read and follow the label instructions or consult with a healthcare provider. - Do not exceed the recommended dose or frequency without medical supervision. - Be aware of potential interactions with other medications, including blood thinners, certain antidepressants, and other NSAIDs. - Monitor for signs of gastrointestinal issues, such as stomach pain, bleeding, or black tarry stools, and seek medical help if they occur. - Consider protective measures for the stomach, such as taking ibuprofen with food or using a proton pump inhibitor, under the guidance of a healthcare provider.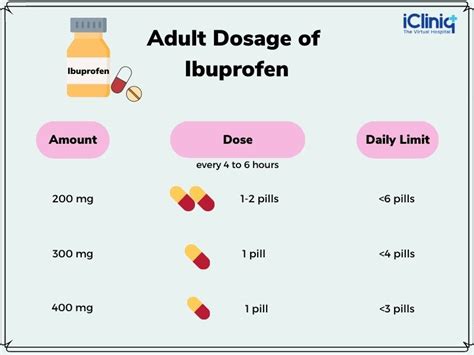
Alternatives to Ibuprofen
For individuals who cannot tolerate ibuprofen or need alternative pain management options, several other choices are available, including: - Acetaminophen (Tylenol), which is effective for pain and fever but lacks anti-inflammatory properties. - Other NSAIDs, such as naproxen (Aleve) or aspirin, which have similar mechanisms of action to ibuprofen but may have different side effect profiles. - Topical pain relievers, such as creams or patches containing capsaicin, menthol, or NSAIDs, which can provide localized relief without systemic side effects. - Prescription medications, including stronger NSAIDs, corticosteroids, or opioid analgesics, which should be used under the close supervision of a healthcare provider due to their potential for serious side effects and addiction.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, a 600mg dose of ibuprofen can be an effective treatment for moderate to severe pain and inflammation but should be used judiciously and under the right circumstances. As with any medication, it's vital to consider both the benefits and the risks and to follow guidelines for safe use. Future research may uncover new mechanisms of action for NSAIDs or develop safer, more effective alternatives for pain management, potentially reducing the reliance on ibuprofen and other NSAIDs for chronic pain conditions.
We invite our readers to share their experiences with ibuprofen or other pain management strategies. Your insights can help others navigate the complex world of pain relief and may inspire new discussions on safer, more effective treatments. Please feel free to comment below or share this article with someone who might find it helpful.
What is the maximum daily dose of ibuprofen?
+The maximum daily dose of ibuprofen for adults is 1200mg, but this can vary based on individual health needs and the specific condition being treated.
Can I take ibuprofen with other medications?
+It's generally not recommended to take ibuprofen with other NSAIDs or certain other medications without consulting a healthcare provider, due to the risk of increased side effects.
Are there any natural alternatives to ibuprofen for pain relief?
+Yes, several natural alternatives can provide pain relief, including turmeric, ginger, and willow bark, though their effectiveness can vary and they may interact with other medications.
